A Complete Guide to MDM App Management
Every enterprise has a complex device ecosystem, spanning hundreds of devices and thousands of Apps. While MDM App management is essential, it can also be daunting for businesses that have recently adopted this solution.
MDM App management will involve deploying Apps, configuring them, providing appropriate security measures, pushing updates, and sometimes uninstalling. Each stage of this life cycle has its complexities as well as opportunities.
This guide by AirDroid provides IT professionals with guidance on every stage so that they can professionalize their Android MDM App management and their businesses can succeed.
1 Comprehensive Guide to MDM Application Management
Deployment
Deploying Apps is a critical function of App management. Fortunately, MDM solution commonly provides enterprises with two means of doing so.
Way 1. Scheduled release
There are many use cases where a scheduled release would be ideal. For instance, an organization switching from Microsoft Teams to Slack would want to avoid making the transition on an ad-hoc basis, leaving team members with different Apps depending on their queue in the shift and unable to communicate with one another.
Instead, this company would want to opt for a scheduled release, launching Slack to all company phones simultaneously. IT teams can also standardize this time across different time zones, making it ideal for companies with national or international operations.
Another major use case for scheduled release is protecting focus during work hours. Instead of releasing an App on an ad hoc basis throughout the day, IT teams can set a scheduled release for after work hours, such as 8 pm or 5 am. This practice ensures employees get the needed Applications without disrupting their scheduled work hours by installing Apps.
Way 2. Staged rollout
There are also use cases where a scheduled release would not be ideal. For example, a company trialing a new customer relationship management (CRM) solution would not want sales professionals in all jurisdictions to switch to it simultaneously. The App may have bugs or other performance issues the enterprise would like to identify and fix before committing to a large-scale rollout. In this case, the company may wish for a staged rollout, when the App would be released staggered, beginning with a small trial launch in a single jurisdiction before a wider deployment.
IT teams can customize the rules for a staged rollout based on different parameters, such as location, device type, or device group, offering endless customization possibilities.
Executing custom managed App configuration
Most third-party Apps downloaded from the App Store generally offer few configuration options.
This lack of configuration options is problematic because it forces organizations into a one-size-fits-all approach to their software: They must adopt Apps in their current state, even if they may not be the best suited to the enterprise’s unique needs.
In contrast, Apps in Managed Goole Play Store like Chrome, Gmail, Firefox, Edge...are much more flexible. They have higher-level configuration options, businesses should use these configuration options to customize their Apps on corporate devices, from content moderation to branding. This level of granular customization is a hallmark of strong App management features.
Examples of MDM Managed App Configuration
Google Chrome
Unrestricted internet use can pose several dangers. Most commonly, employees will succumb to the temptation of aimlessly surfing the net instead of using their company-issued phone for relevant work matters. At worst, employees may interact with nefarious websites that can spread malware to that person’s device and the rest of the organization’s network.
- Companies can regulate internet use through one of two Google Chrome configurations. The first option, a blocklist, is the more lenient approach. IT professionals would add certain websites, such as YouTube or Facebook, to the blocklist, which prevents employee access. The downside to a blocklist is that IT teams must continually update it: If the business overlooks even a single distracting or dangerous website, the negative effect is the same.
- The stricter approach is an allowlist. This method blocks all websites except for those placed on the allowlist. An allowlist might be ideal for companies with high-security needs, such as those in financial services, or for professions where mobile distractions should be limited, such as sales officers or account managers.
Gmail
A person’s email signature is the online equivalent of their business card. It has their name, job title, company affiliation, and links to relevant assets, such as the organization’s website or social media channels. Unfortunately, many organizations do not standardize their email signatures, which results in colleagues having wildly different content. This lack of consistency does not look professional and will affect the brand’s reputation with external partners.
Brands using a solution in MDM App management do not have to deal with this problem. They can configure a universal format for their email signatures, ensuring visual consistency in their brand identity. Because IT teams can manage this feature centrally, they can insert relevant and timely call-to-actions in each email signature. For example, a business may want to promote the ability to download its latest white paper or encourage sign-ups for an upcoming webinar.
Secure Apps with MDM App management
While company-issued devices can facilitate collaboration, they also pose a threat. Some employees may abuse these devices, resulting in lost productivity, exposure to malware, and even data theft. There are several ways that IT teams can secure Apps from misuse.
App data usage report
On AirDroid Business, users can schedule App data usage reports to be regularly produced. Perhaps more conveniently, these reports can be accessed on-demand.
- Under the “Workbench” tab on their AirDroid Business dashboard, the IT professional must select the “Reports” tab.
- From there, users can view the data usage over a rolling period, such as the previous day, seven days, or thirty days. An anomaly in data usage, such as a massive spike on a weekend, may indicate misuse of a company-issued device.
- More crucially, IT professionals can get a more granular view of data usage by reviewing the ten Apps that consume the most data. This list will give businesses a clear idea of whether an employee misuses a phone. For example, an employee might have Netflix as their top data-consuming App.
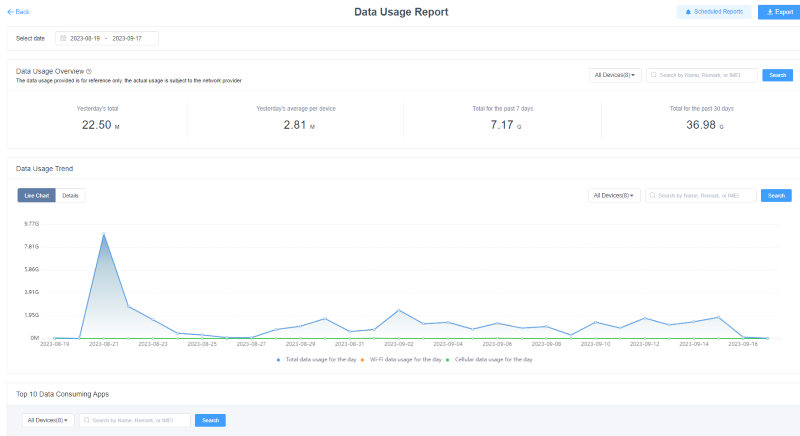
Given that the employee is using the phone for streaming, the company can reprimand the employee and add Netflix to its blocklist.
Application related alerts
While the App data usage reports are helpful, IT professionals will only sometimes have the time to examine each one. This fact is especially true at larger enterprises, where the number of employees with mobile phones may be in the thousands. It is impractical to try manually examining the data usage patterns of each employee.
In this case, the company should set up Application-related alerts. These are fully customizable to the needs of an organization. One company may want to set up an alert for data usage. The IT team will be notified if the user surpasses a particular threshold. Such alerts enable IT teams to scale their remote monitoring and, more crucially, intervene before a problem gets out of hand.
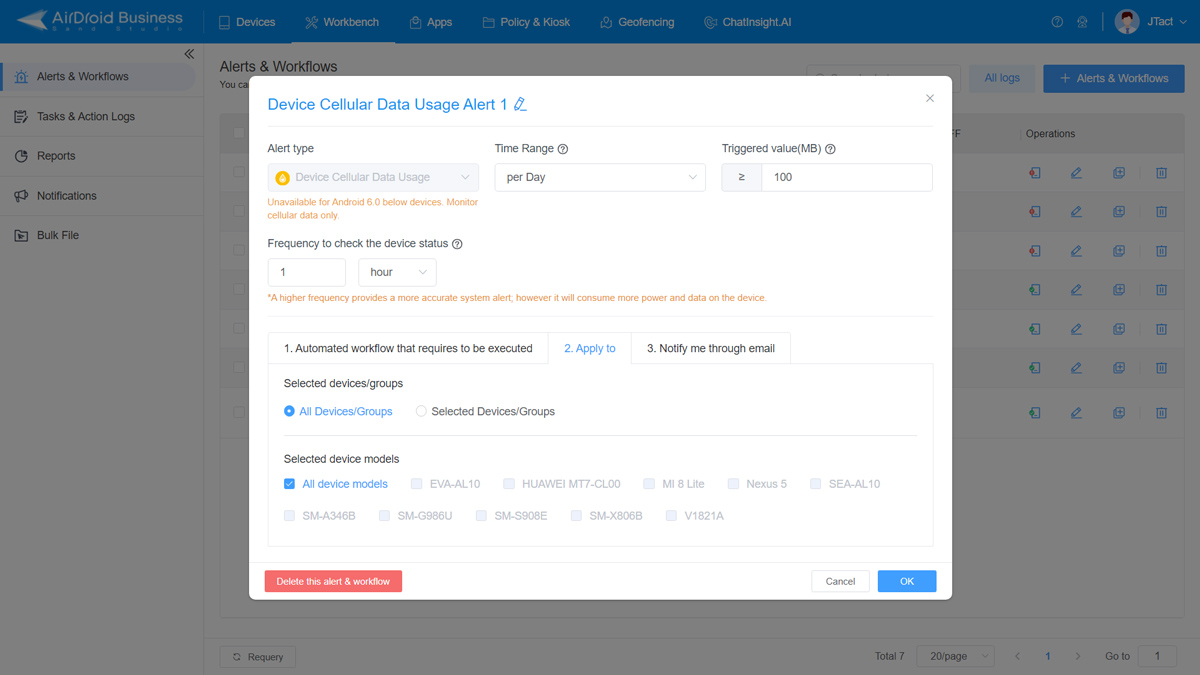
App Updates
Updating Apps is an often overlooked part of MDM App management, but it is one that brands should pay attention to. Significant differences may exist between one version of an App and the next, including everything from stability to cybersecurity. If portions of the workforce use older versions of an App, there may be dire consequences.
The negative impact of outdated Apps
Newer versions of Apps typically patch known security vulnerabilities. Employees with older App versions may thus expose the business to cybersecurity breaches, primarily when these attack vectors are publicly known. These attacks will result in lost revenue, decreased productivity, and operational chaos for the business.
Older Apps may also be less stable and may crash frequently. This lack of stability may also affect business operations, often when employees least expect it. For example, an employee giving an essential presentation through a remote meeting App might get cut off, creating a wrong impression with the prospective client. In short, outdated Apps create an outsized problem for businesses.
Keep Your Application Up-to-date with MDM
Fortunately, updating Apps through an MDM like AirDroid Business is simple.
- IT personnel can choose to manually update apps for the enterprise device groups through the MDM dashboard, or set up automatic update rules for the apps.
- For create auto-update rules: IT professionals must proceed to the Managed Google Play Store tab under their App Library. From there, they can set global configurations to govern how all Apps are updated. The first option, “Always Auto-Update Apps,” will update Apps even if employees use mobile data in the field. The second option, “Auto-Update Apps over WiFi only,” will reserve updates for when employees are connected to a WiFi connection. Businesses must decide which trade-off they value more between these options: the speed of an immediate update or the stability of one over WiFi.
- Apart from these global settings, IT professionals can update Apps individually. They must locate the App for which they want to customize rules. From there, the IT professional can customize the update rule. The flexibility for both global App settings and individual App rules means that businesses can update Apps using the App management strategy that is ideal for them.
Uninstall Apps
Why businesses may want to uninstall Apps
There are many reasons an enterprise may want to uninstall an App. The business could be switching from one App to a competing solution. The IT team may have discovered a severe security flaw in an App. The App may be distracting employees from their job duties.
Companies should not have to possess an employee’s phone to delete an App. This manual process is impractical when so many employees are on remote or hybrid work configurations, and deleting an App may often be urgent.
Remotely uninstalling Apps
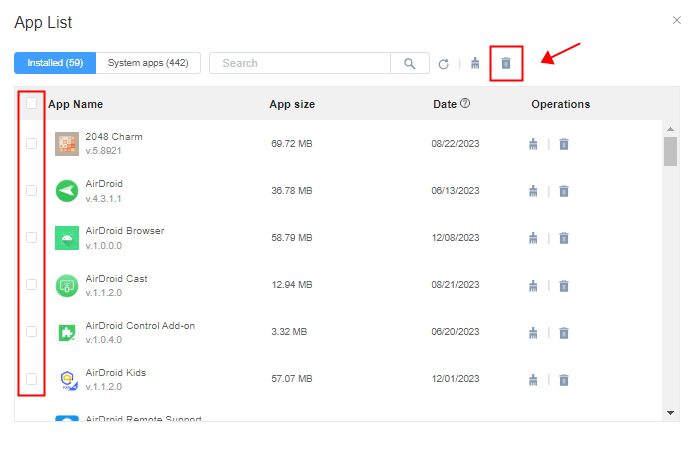
Through Android MDM App management, businesses can remotely uninstall Apps, even if the App is unattended. To do so, the IT professional needs to navigate to their Device List, choose the necessary device, and search for the App in the App List. Upon locating the App, the IT professional must select the trash icon and confirm the installation. The App will then be deleted.
To uninstall multiple Apps simultaneously, the IT professional must select the checkboxes to the left of relevant Apps and then repeat the same process. The ease with which businesses can remotely uninstall Apps improves operational efficiency: No employee ever has to be stuck with an unstable, dangerous, or distracting App.
2Conclusive Note
Any business that wishes to scale up its device ecosystem must use an MDM solution for App management. One example is AirDroid Business, which offers helpful features for every stage of a device’s lifecycle. With AirDroid Business, IT teams can perform regular actions like install, update, uninstall and configure Apps remotely.
IT teams can protect their devices and company networks through App data usage reports. To simplify this process, IT teams can also enable Application-related alerts, automatically triggering a notification when a condition is met, such as data use exceeding a certain threshold.
Businesses can also set global conditions for updating Apps, prioritizing either the speed of automatic updates or the stability of updating only when on WiFi. Importantly, they can remove Apps, even when phones are unattended, through the AirDroid Business interface.
Enterprises that master MDM App management will empower their IT teams and their employees in the field to focus on what matters most: business growth.









Leave a Reply.