Customizing Mobile App Configuration with MDM Solution
The Play Store is a double-edged sword for enterprises. On one hand, the Play Store gives employees instant access to millions of apps that can enhance productivity, collaboration, and execution. On the other hand, each app is a potential point of failure for brands. Employees are given free rein to download and interact with apps as they choose exposing businesses to potential risk.
Customizing mobile app configurations can align work devices with the specific needs and security requirements of the business, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and security.
1 Customizing Mobile App Configuration with MDM Solution
For enterprises, the best way to manage mobile app configuration is through a mobile device management (MDM) solution. One popular choice is AirDroid Business, an MDM specializing in Android-powered mobile devices.
Customize App Update Rules
IT team can customize the global configuration of app update rules, allowing them to specify whether apps on device groups should remain updated, never update, automatically update on Wi-Fi, or be freely chosen by device users. Organizations have the flexibility to tailor the update rules to their specific requirements.
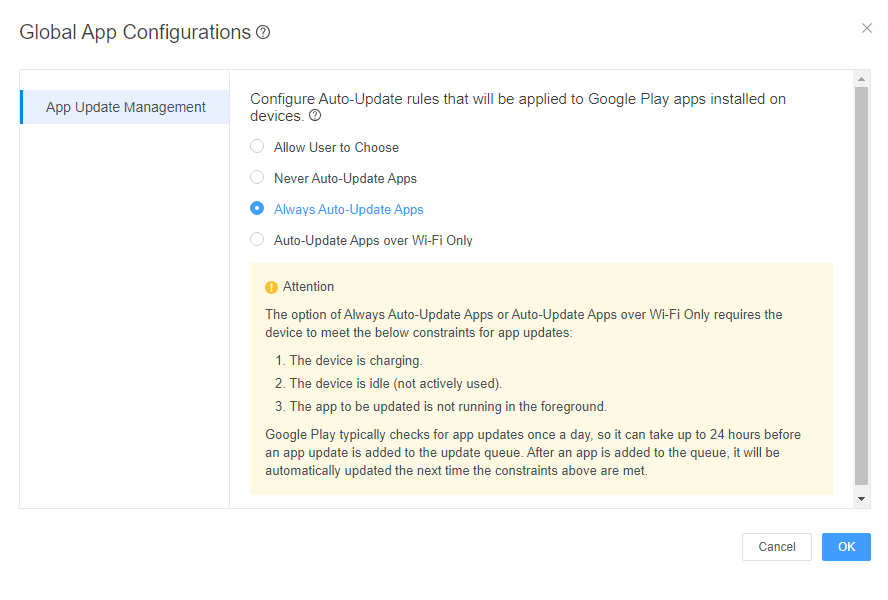
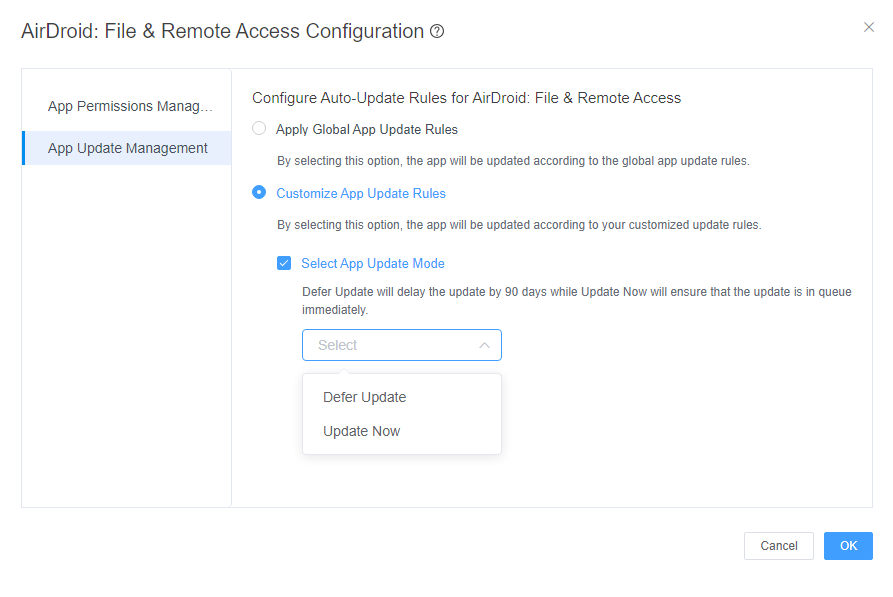
Additionally, it is possible to customize update rules for individual apps, tailoring them based on each app's specific condition. The available options include the following:
Customize App Permissions
To protect company privacy and data, it's important to carefully consider which app permissions to grant, as they determine the data and features an app can access on work devices.
AirDroid Business allows you to configure app permission settings for individual apps, and apply the configurations to multiple devices remotely.
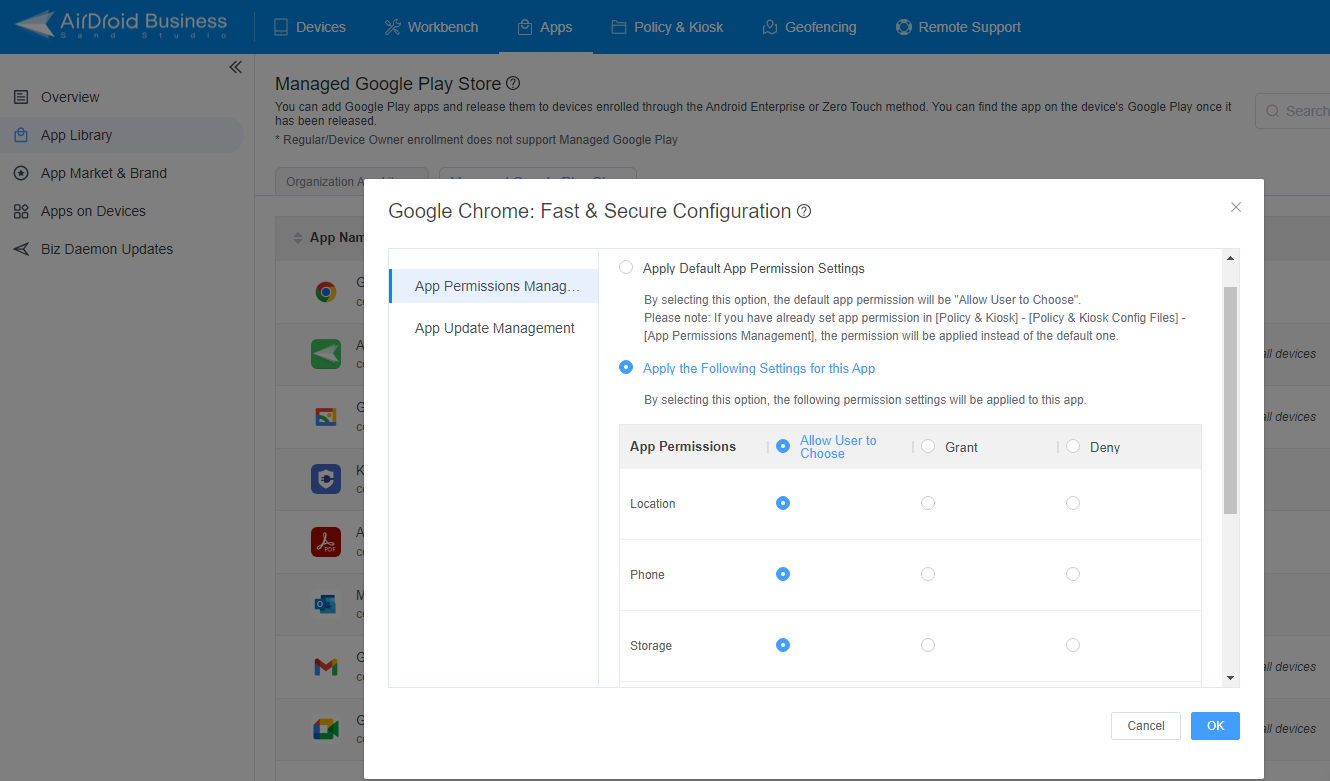
Managed Configuration(For Specific Apps)
"Managed Configuration" in Managed Google Play Store enables administrators to establish specific app configurations, including enabling or disabling features, pre-configuring settings, and applying policies, all without user intervention.
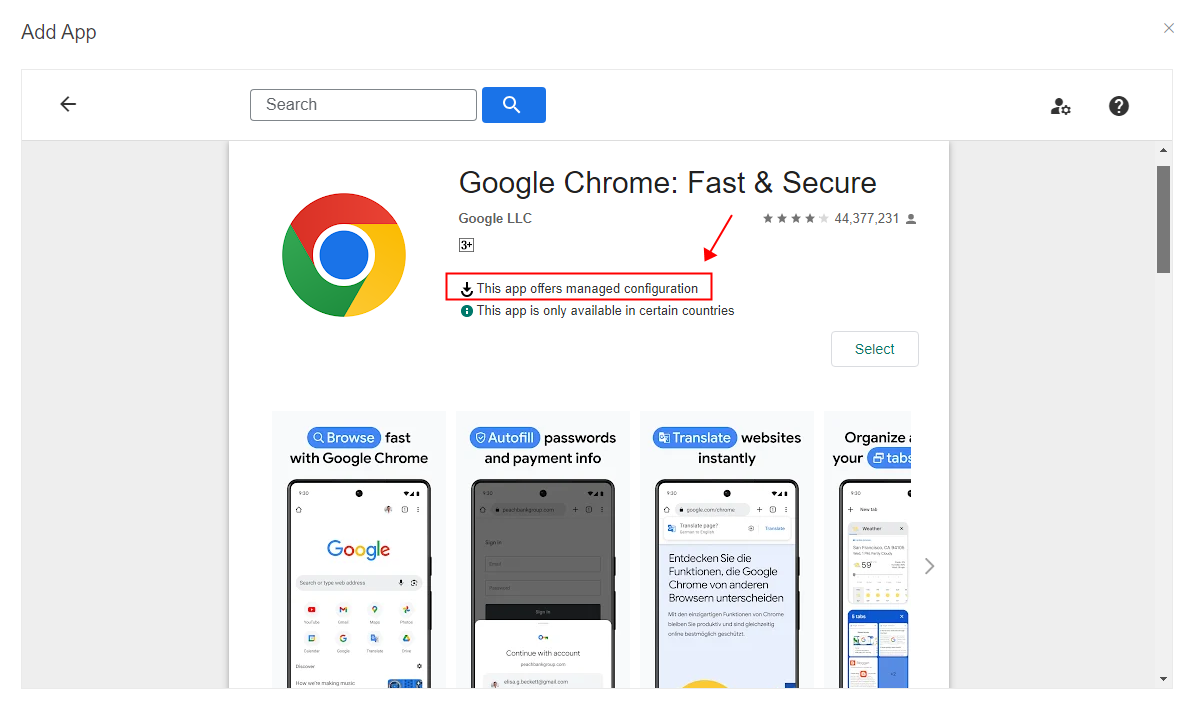
This feature helps organizations maintain consistent application configurations across all managed devices, thus enhancing security and compliance. The apps that support "Managed Configuration" are Google Chrome, Gmail, Microsoft Outlook, and many others. For example, companies can blacklist or whitelist websites on Google Chrome to simplify content moderation and set a universal signature on Gmail for a branding and marketing boost.
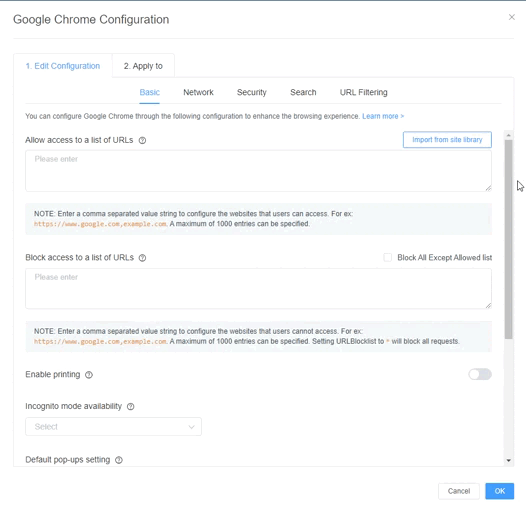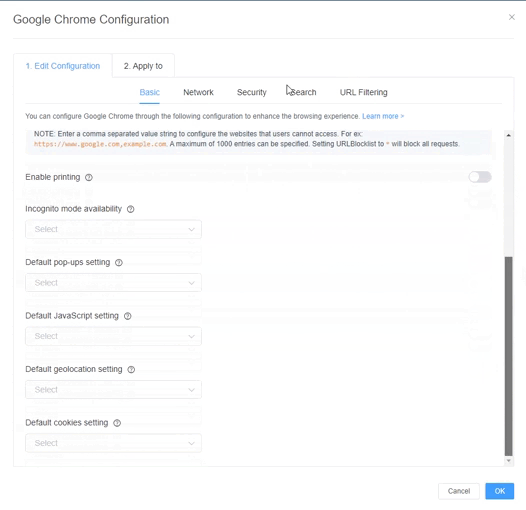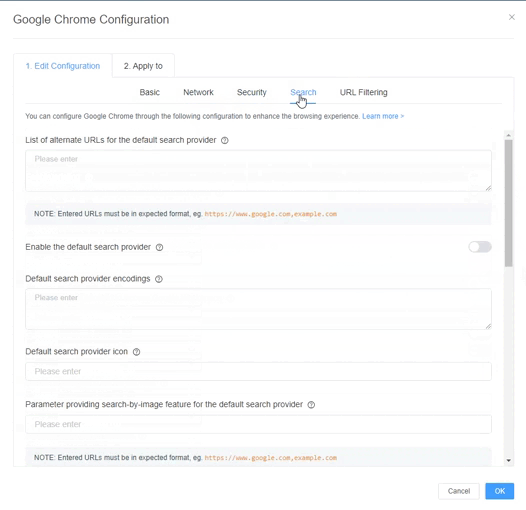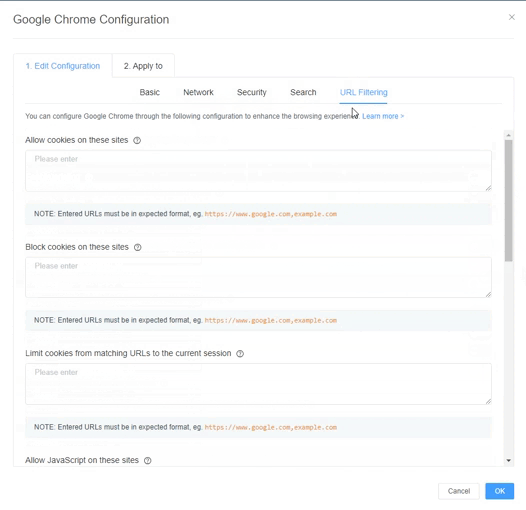
Here are the configuration items of Chrome:
Benefits to Using MDM for App Management
- Scalability: While configuring apps might be manageable for a handful of phones, this task will be increasingly unwieldy and impractical as their number rises. An MDM can help businesses remotely configure apps for a large device ecosystem, ranging from the hundreds to the tens of thousands.
- Granularity: Without an MDM, businesses might need to set global configurations for expedience. In contrast, companies can configure unique settings for different teams or employees with an MDM. Freed of a one-size-fits-all approach, employees get the app settings that make the most sense.
- Security: An MDM makes it easier for businesses to moderate access to apps and websites that pose a cybersecurity or operational risk. This ability gives employees a safer, distraction-free environment so they can focus entirely on their work.
2Importances of Different App Configuration Items
App Update Rules
Most phones will have auto-updates enabled by default. While this option is viable, companies should actively decide how to approach their app updates because they must navigate trade-offs. There are two main options.
The IT team can initiate an immediate update of a particular app or select an option for devices to update once a new version of an app is detected, regardless of the connection type. For example, some employees may use mobile data, which will incur heavier charges for processing a data-intensive update. The advantage is speed: Employees get the latest version faster, which may be necessary for business-critical apps like those related to cybersecurity.
The company can restrict updates to when the device is connected to a WiFi network. This option is cheaper and more stable, reducing the likelihood of update failures due to poor connectivity.
Defer updates
It may not always be ideal to update an app. For example, employees may rarely use some apps, and others may take up significant memory. One app developer may announce that they no longer support an app because they have sold the business. Even if this app developer has a more recent version of this app, companies may not want to update it because it will soon be obsolete.
Fortunately, companies do not have to make a universal policy between automatic and deferred updates. Instead, they can choose between each option on an app-by-app basis. For instance, a company may select immediate updates when on WiFi for their productivity suite but opt to defer for all other non-essential apps.
App Permissions
Set global application configurations
The strength of setting permissions through an MDM is its applicability. Once the IT professional enters the MDM back-end, they can proceed to the Managed Google Play Store to find a list of all the apps deployed to company devices. Adjusting permissions here will roll out the change to all devices under management. This feature gives enterprises the benefit of scale. They can efficiently set their chosen permissions for up to tens of thousands of devices.
Achieve granularity with config application
Permissions do not have to be all or nothing. With an MDM, enterprises are empowered: They can choose when it would be appropriate to extend app permissions and, just as significantly, when not to. For example, allowing a communication app access to employee smartphones would make sense. Allowing a timekeeping app access to employee photos would not make sense.
The ability to make sensible decisions around app permissions will enable organizations to take care of their data better.
Empower employees with the correct application configurations
Sometimes, it may not make sense for organizations to set global configurations for specific apps. For example, some companies may allow employees to use social media apps to build stronger client relationships. The organization may feel uncomfortable determining the permissions for these social media apps because they also intersect with an employee's personal life.
In this situation, the organization can allow employees to choose whether to extend permissions to the app. Organizations can set this ability on a per-feature basis, such as only allowing employees to decide whether to extend access to location but not for other permissions.
Managed Configuration
Regulate internet use through managed app configuration Android
Employees do not need to access all of the internet to perform their job duties. Such unfiltered access leads to surfing, streaming, and other non-work uses. Companies can set custom application configurations for Google Chrome to regulate internet use.
There are two general ways to do so. The first is a blocklist. Companies can forbid access to popular non-work websites like Netflix and dangerous websites that may host malware. This approach is most suitable for enterprises that have fewer websites to prohibit.
Some companies may need to block more websites, such as those belonging to data-sensitive industries like healthcare or finance. It would be impractical in these cases to manually list all the websites to forbid. These companies can use the config application for a whitelist. Companies can even import a site library to populate the list of allowed websites.
With this mobile app configuration, companies can moderate internet access in an ideal way.
Standardize brand identity
Imagine discussing a potential business deal with a vendor, and each of their employees has a different email signature. One lists the company name, another has the website URL, and the final has the brand's logo.
This lack of standardization is unprofessional, and it may affect business. After all, who would trust an organization's services that cannot even unify their email signature? IT teams can handle this problem through a mobile app configuration on Gmail. Brands can standardize the email signature company-wide with this feature.
Some organizations will want to include legal fine print about the email. Others may want to focus more on brand identity with the company name, slogan, and logo. The most forward-thinking companies will use this space as an additional customer touchpoint, adding a relevant call-to-action, such as a download link. Because each employee may send dozens of emails daily, which multiplies with the organization's size, an email signature with a CTA can effectively promote a relevant product or service.
The mobile app configuration on Gmail helps businesses maximize the digital footprint of their emails for brand equity and marketing.
3The Dangers of Overlooking Mobile App Configuration
IT teams that fail to execute a strategy for mobile app configuration can damage the business in three key ways.
1Lost productivity from lack of config application
Apps belonging to Google, such as Chrome and Gmail, offer advanced configurations enabling businesses to govern what sites employees can and cannot visit. Left unchecked, employees may use company-issued mobile devices for personal reasons, such as browsing the net, scrolling on social media, or streaming content.
This usage affects individual productivity. Instead of performing the functions of their role, these employees are shirking, effectively getting paid to entertain themselves while on company time.
2Privacy breaches due to no config application
While more and more developers are creating software emphasizing privacy, these players are still in the minority. The vast majority of app developers are only aggressive in requesting permissions. They often ask for permissions that are unnecessary to deliver the current functionality of the app, such as a timekeeping app requiring access to a person's camera. The general thinking is that the data generated from this access may be helpful in the future.
Apps that do not have proper mobile app configuration will have issues in access control. The app developer will gain access to data that they do not realistically need. Entrusting data needlessly to third parties is a privacy risk, as the world famously saw in the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica data scandal.
3Scheduling conflict from lack of application configurations
One of the most critical settings for mobile app configuration is related to updates. By default, most phones will enable auto-updates. With this feature enabled, people often turn to their phone to find it updating.
Poorly timed updates can interfere with employee work. These updates run on the phone when the employee may need the full power of the phone for other matters, such as attending a virtual meeting or calling a client. Companies that want to maximize their investment in mobile devices should set the application configurations for app updates.
4Unrestricted Access
Procuring mobile devices and issuing them to employees is already a difficult task. Because these initial steps are already resource-intensive, companies often use out-of-the-box mobile app configurations.
Defaulting to these settings presents numerous risks to organizations. Employees with unrestricted internet access may spend significant time on non-work activities. Third-party apps may be given unnecessary access that may lead to privacy or data breaches. Updates can come at inopportune times, affecting employee scheduling.
Businesses can best handle mobile app configuration through an MDM like AirDroid Business. With an MDM, enterprises can set global configurations for app permissions, change them for different employees or departments, and even allow users to set them independently.
An MDM can also help with app updates. Businesses can initiate updates immediately and allow future updates on mobile or only when connected to WiFi. They can also defer updates, keeping them only for the most essential work apps. Businesses maximize their device ecosystem by customizing their mobile app configurations, empowering employees to work effectively, flexibly, and securely.
4The Future of Enterprise Device Management
Enterprise device management was once characterized by talent. Organizations had to work hard to recruit, hire, and retain the best IT professionals. While talent is crucial, this perspective overlooks the other half of the equation: technology.
For IT professionals to execute a robust program of enterprise device management, they need to be equipped with the best possible innovations. IT professionals should have a robust MDM like AirDroid Business in mobile app configuration.
With an MDM, IT professionals can maximize app configurations for the benefit of individual employees and the organization as a whole. Employees with company-issued mobile devices can enjoy safe and distraction-free apps and connectivity while working. Businesses can rest assured with the knowledge that their device ecosystem contributes to the workforce's overall productivity.









Leave a Reply.