Does Safari Private Browsing Give You Real Privacy?
Apple prioritizes user privacy across all its devices, and Safari Private Browsing is one of its key features to help you browse without leaving a trace on your device. It prevents Safari from saving browsing history, cookies, and website data, giving you more control over your online activity.
However, Safari Private Browsing doesn’t make you completely anonymous. While it stops websites from storing data locally, your internet provider, employer, or network administrator may still be able to see your activity.
In this article, I’ll break down how Safari Private Browsing works, who can still track your activity, and how to view, manage, or delete private browsing history on your iPhone or Mac.
How Does Safari Private Browsing Work?
When you enable Safari Private Browsing, it creates a temporary session that keeps your activity separate from regular browsing. Safari won’t save history, cookies, or website data, and private tabs won’t sync to iCloud. Once you close the session, everything is erased.
However, this doesn’t make you fully anonymous. Your ISP, employer, or websites can still track your activity through your IP address and other methods. To better understand how Safari Private Browsing processes your activity, please check the illustration.
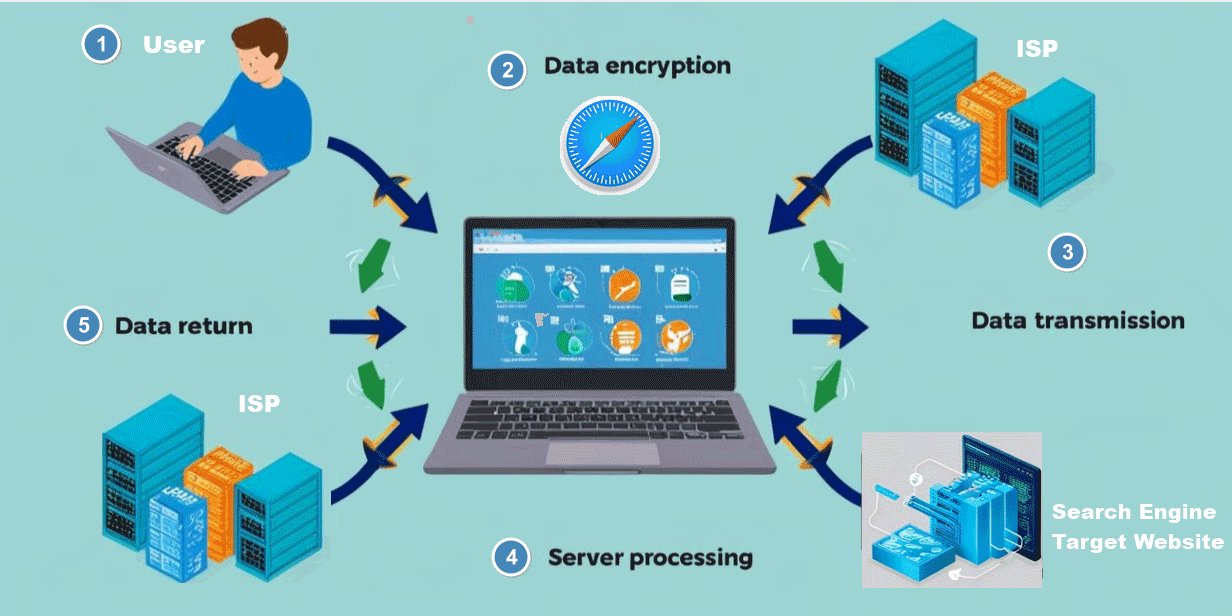
Here’s a simple breakdown of how Safari handles private browsing:
- You enter a website or search query in Private Browsing mode.
- Safari encrypts the request and sends it over the internet.
- The website server processes your request and sends back the page data.
- Safari displays the webpage without storing history or cookies.
- Once you close the private tab, all session data is erased.
- Safari prevents syncing private browsing activity to iCloud or other connected Apple devices.
Does Safari Private Browsing Save History, and Can Anyone See It?
If you’re using Safari Private Browsing, you might assume your history is completely hidden. While Safari doesn’t store your browsing history on your device, your online activity isn’t entirely private. Several entities, including internet providers, websites, network administrators, and even third-party tools, can still track what you do online. So, who can still see your private browsing history?
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
Your ISP tracks the websites you visit using your IP address, even in Safari Private Browsing mode. ISPs are legally required in many regions to store this data, including site visits and session durations. They can only release this information under legal circumstances or with your permission.
Websites and Online Services
Websites can still recognize your IP address and may use tracking methods like fingerprinting to identify you. If you log into an account, submit a form, or make a payment while browsing privately, that website still knows you visited—even if Safari doesn’t save your history.
Network Administrators
If you’re using school, work, or public Wi-Fi, network administrators can track your activity. Just like ISPs, they have access to logs that show the websites you visit, even in private browsing mode. Many workplaces and schools use this data to enforce browsing restrictions.
Government Agencies
Depending on your country, authorities may legally access your browsing activity through ISPs or website records. If a court order is issued, your Safari Private Browsing history can be traced via external logs, even though Safari itself doesn’t store it.
Third-Party Parental Control & Monitoring Tools
While Apple doesn’t store Safari Private Browsing history on your device, it allows third-party tools like AirDroid Parental Control to monitor web activity. These tools use Apple’s Web Content Filter feature in Screen Time settings to log website visits. However, due to Apple’s privacy policies, they can only record visited URLs, not personal data.
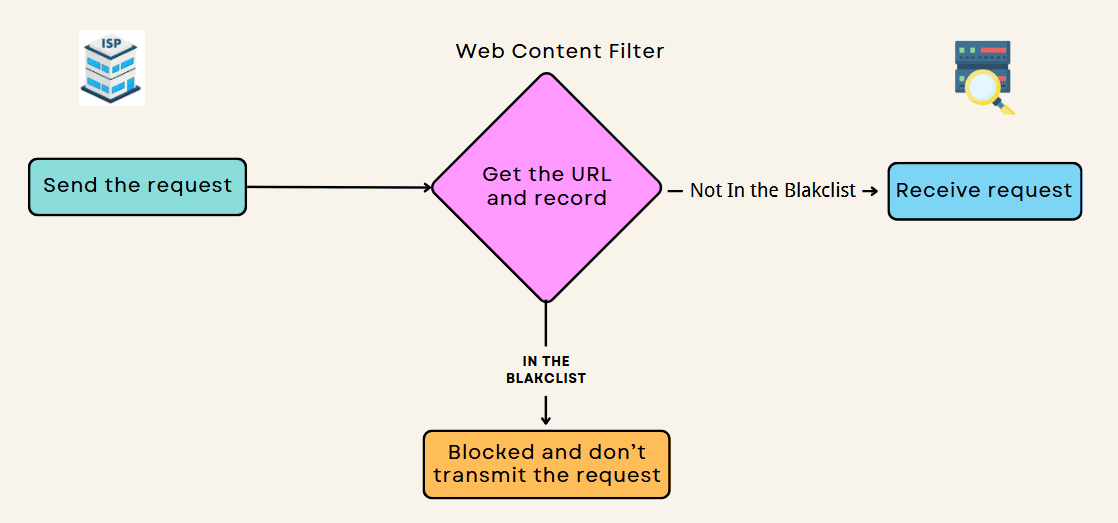
Even though Safari Private Browsing doesn’t save history on your device, your activity isn’t completely private. Schools, employers, ISPs, and websites can still track what you do through network logs and IP addresses. If you want real privacy, I’d recommend using a VPN, a private search engine, and ad blockers to stay off the radar.
How to Check Safari Private Browsing History on iPhone or Mac?
If you’re wondering whether you can access Safari Private Browsing history, the short answer is that Safari doesn’t save private browsing history on your device. However, in some cases, browsing activity can still be retrieved using third-party monitoring tools on iPhone or DNS cache records on Mac.
How to Check Safari Private Browsing History on iPhone?
Apple doesn’t provide a built-in way to see Safari Private Browsing history. However, as discussed above, third-party tools like AirDroid Parental Control can help track private browsing activity. These tools can log visited websites even when Safari is in private mode, making them useful for parental monitoring. Here are the steps to view private browsing history on iPhone:
- Download and install AirDroid Parental Control on your device and create an account.
- Install AirDroid Kids on the iPhone you want to monitor and follow the setup instructions.
- Pair the target device with your account.
- Go to the Website Restriction section to see browsing activity, even from Safari Private Browsing mode.
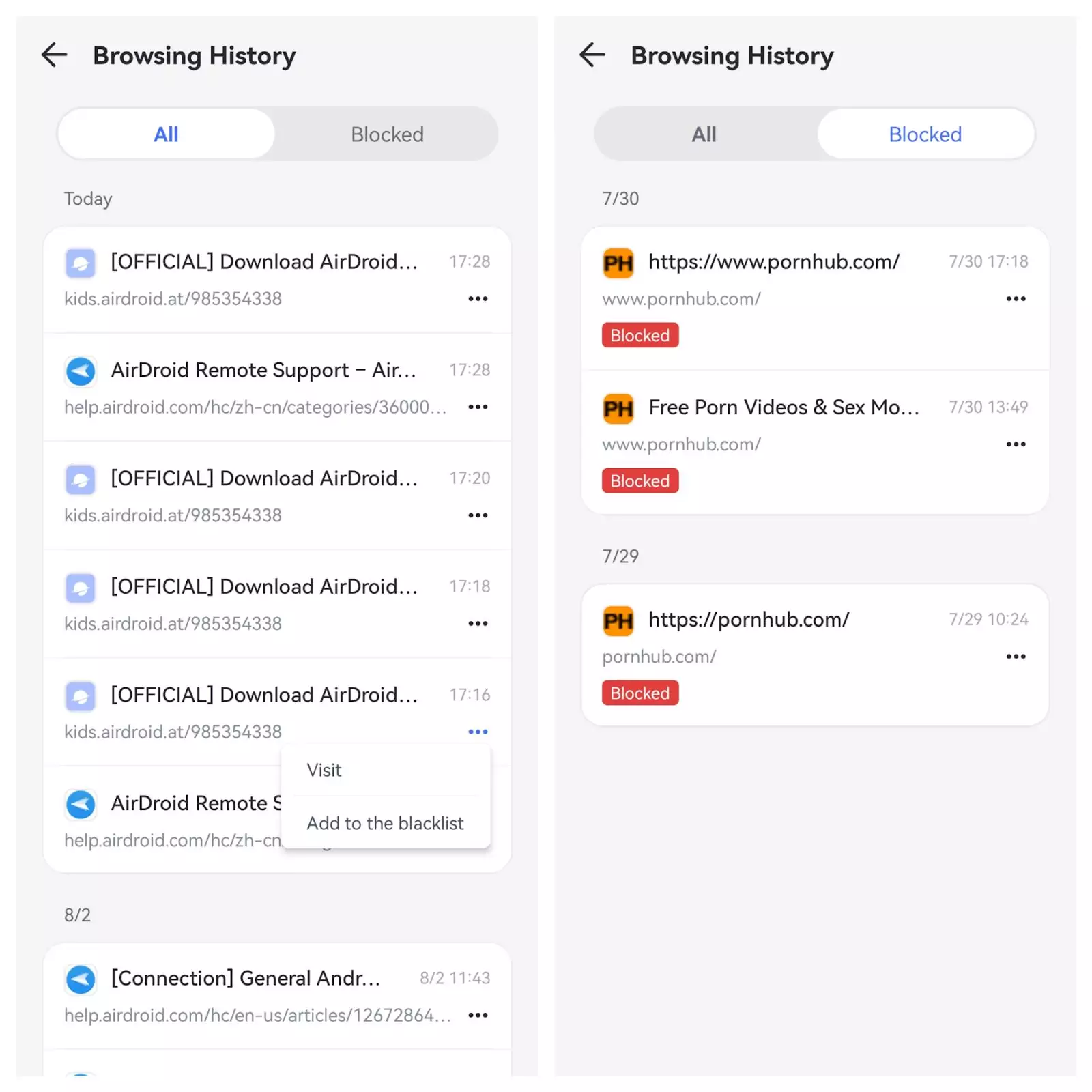
This method is simple due to the app’s user-friendly interface. It also allows you to block websites, manage app usage, and set screen time limits.
How to View Safari Private Browsing History on Mac?
Unlike iPhones, Mac users can attempt to view recent private browsing activity by checking DNS cache records. Safari doesn’t store history in private mode, but temporary DNS logs may still capture browsing activity—as long as they haven’t been cleared.
- Go to Applications > Utilities > Terminal.
- Enter the command: sudo killall -INFO mDNSResponder and press Enter
- Enter your Mac’s administrator password when prompted.
- 4.After running the command, open Console from Applications > Utilities.
- Search for mdnsresponder in the search bar.
- Click the Start button to see the recent browsing history.

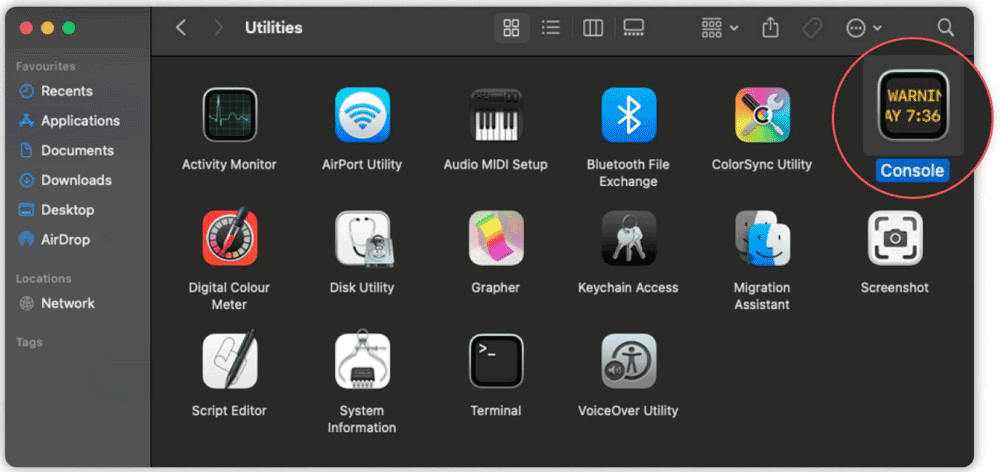
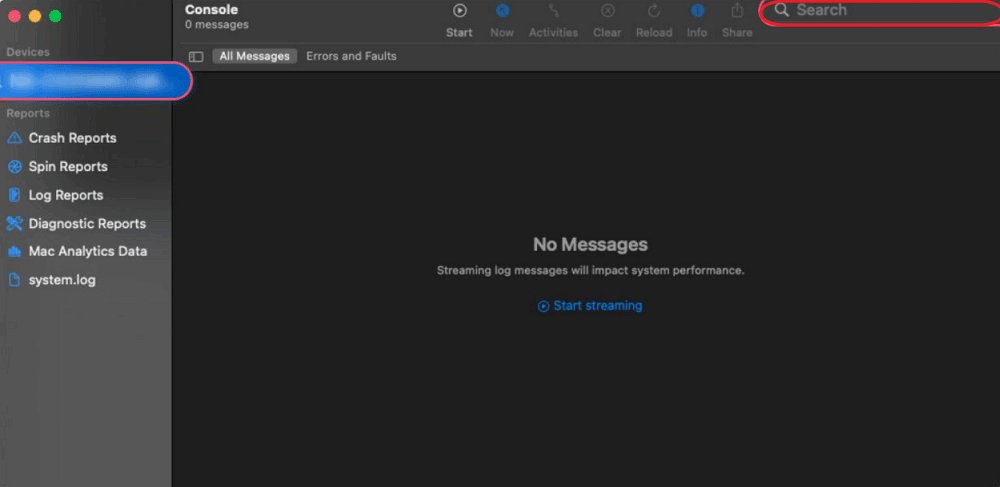
While this method can reveal some browsing activity, it doesn’t provide a direct list of visited websites—only their associated IP addresses. It also requires technical knowledge and may not work if the DNS cache has been cleared.
Is It Possible to Permanently Delete Safari Private Browsing History?
Yes, you can delete private history permanently—but only from your device. Safari doesn’t save private browsing history, but external parties like ISPs, network administrators, and third-party monitoring tools can still track your activity. Clearing history on your device won’t erase records stored externally. Here’s how you can minimize traces of private browsing on iPhone and Mac.
How to Delete Safari Private Browsing History on iPhone?
Enable Airplane Mode. Since Safari Private Browsing doesn’t store history, the best way to prevent tracking is to stop network activity from being logged. One way to do this is by enabling Airplane Mode before browsing privately.
When Airplane Mode is on, your device disconnects from the internet, preventing DNS requests and IP tracking. This way your browsing activity isn’t stored externally by your ISP or network provider.
How to Delete Safari Private Browsing History on Mac?
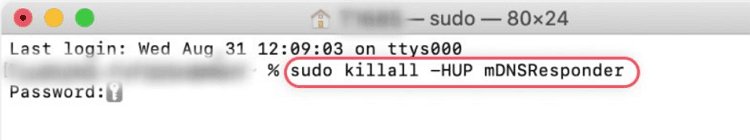
Clear DNS Cache. On a Mac, DNS records may still store temporary browsing activity, even if Safari doesn’t keep history. Clearing the DNS cache removes these stored entries. Please follow the below steps:
- Open the Terminal application from Applications > Utilities.
- Enter the command: sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
- Enter your Mac administrator password when prompted.
Is Safari Private Browsing Enough?
Safari Private Browsing helps keep history off your device, but it doesn’t make you invisible online. ISPs, network admins, and websites can still track your activity.
For real privacy, I recommend using a VPN, a private search engine, and clearing your DNS cache on Mac. If you need to monitor private browsing, AirDroid Parental Control is a great option.
Stay in control of your privacy—combine Safari with stronger security tools for better protection.
Wondering which private mode offers better protection — Safari or Chrome? We put both to the test in our next article so you can choose wisely. Don’t miss it!













Leave a Reply.