How to Add a Certificate on Android? Step by Step
Businesses today face two critical security challenges: the unauthorized access of sensitive data and security breaches. One security measure that is often overlooked is the use of digital certificates on Android devices. Certificates serve as authentication tools for users and provide network security and encrypted communication abilities, which are essential for IT professionals managing corporate devices.
Many enterprises rely on certificates to secure their Wi-Fi networks, VPNs, email services, and private APIs. However, improper configuration of certificates or untrusted certificate sources can create security vulnerabilities that put data at risk of exposure. Correct implementation and administration of certificates results in smooth authentication processes and protective data management.
This guide will explain the different types of Android certificates, why enterprises use them, and how to install them manually or via Mobile Device Management (MDM). The following article contains detailed installation procedures for certificates that meet security needs, compliance requirements, or business continuity purposes.
1Certificate Types for Android
Android devices require different types of certificates to authenticate connections while maintaining communication security. The certificates exist in three functional categories:
1.System-Level Certificates: Android devices come with these pre-installed certificates from the manufacturer to verify trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). Enterprises may also ensure compliance with internal security policies through the enforcement of system-level certificates.
2.User-Level Certificates: These are manually installed by users and IT administrators. User-level certificates are commonly used for Wi-Fi authentication, VPN access, and email security. They also provide secure access to company resources that become accessible through user-level certificates but may need additional trust configurations.
3.Application-Level Certificates: Certain apps use their own certificates for code signing, API authentication, and privileged access. These certificates help maintain secure communication between applications and remote servers.
2Why Enterprises Need Certificates on Android
Enterprises depend on digital certificates to ensure data protection, policy compliance, and network communication. The absence of proper authentication allows unauthorized individuals to access business-sensitive resources, which produces data breaches alongside regulatory violations. Android certificates serve essential functions in these primary business situations:
1. Wi-Fi, VPN, and Email Security
Enterprises use certificates to authenticate users when they connect to corporate Wi-Fi networks, VPNs, and email systems. Organizations choose certificates as their preferred authentication tool since they offer enhanced security compared to passwords, as it reduces the chance of unauthorized access.
2. Private Certificate Authority (CA) for Internal Security
Private Certificate Authorities (CAs) are used by organizations to issue and manage digital certificates for internal use. Through private CAs, organizations can enforce strong encryption along with data integrity and regulatory compliance, ensuring that only trusted users and devices can access business applications.
3. API Communication and Secure Transactions
Many businesses implement certificates to protect the API communication between mobile apps and their backend servers. This ensures mutual authentication between Android devices and enterprise networks, minimizing the risk of man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and ensuring that only authorized apps can exchange data.
4. Privileged Access for Banking and Payment Security
Financial institutions depend on privileged access certificates to secure online banking and payment applications. Certificates can help to verify the legitimacy of Android devices before granting access to sensitive financial information, which ensures that transactions remain encrypted and safe from cyber threats.
By implementing these certificate-based security measures, enterprises can protect network security and sensitive data as well as prevent unauthorized access on Android devices.
3How to Install a Certificate on Android
The installation process for Android certificates depends on the certificate type together with its planned usage. Android users can install certificates either manually or through Mobile Device Management (MDM) protocols to complete the installation process.
Note: Android 7.0+ Certificate Trust Restrictions
- In Android versions 7.0 and above, security measures have been strengthened when it comes to certificate usage. User-installed certificates are no longer automatically trusted for network connections like HTTPS to enhance protection against malicious attacks. This means that in order for certificates to gain system-wide trust, they need to be installed at the system level, which necessitates root access or enforcement via Mobile Device Management (MDM).
Comparison Table: Manual vs. MDM Installation
Features | Manual Installation | MDM Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Usability | Requires user interaction, best for single devices | Hands-off deployment, suitable for multiple devices |
| Time Efficiency | Can take several minutes per device | Automated, applies to all enrolled devices instantly |
| Security | Certificates installed at the user level may not be trusted system-wide | Ensures system-level trust and compliance |
| Management | Each device must be manually configured | Centralized certificate management |
| Best For | Individual users, small teams | Large enterprises, IT-managed environments |
Method 1: Manual Installation
For users who need to install certificates manually, follow these steps:
Step 1 Download the Certificate
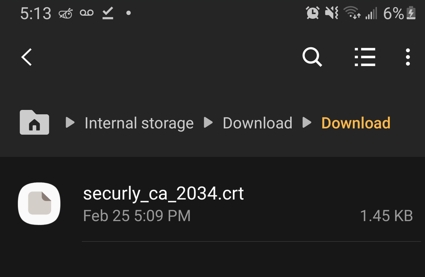
● Obtain the certificate file (.crt, .cer, or .p12) from a trusted source.
● Save it in the Downloads folder on your Android device.
Step 2 Open Certificate Installation Settings
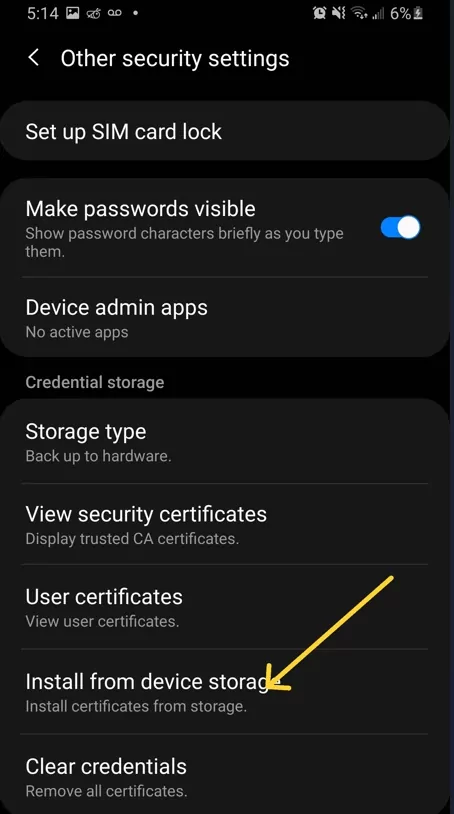
● Navigate to Settings > Security > Encryption & Credentials.
● Tap Install from storage or Install a certificate.
Step 3 Select the Certificate File
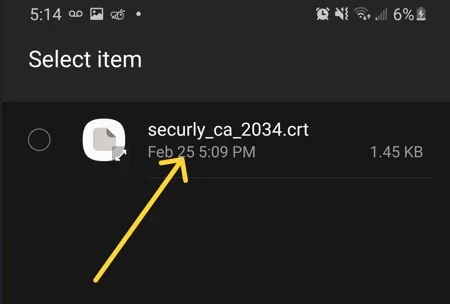
● Locate and select the downloaded certificate.
● Choose the appropriate use case (Wi-Fi, VPN, or App Authentication).
Step 4 Confirm and Complete Installation
● Follow on-screen prompts to confirm the installation.
● If required, enter a PIN or password to authorize the change.
When to Use Manual Installation
- When configuring a single device.
- For personal Wi-Fi, VPN, or email authentication.
- When an MDM solution is not available.
Method 2: Installing Certificates via MDM
For businesses handling multiple devices in their operations, MDMs help streamline the process of deploying and enforcing certificates. Here are the instructions for installing certificates using AirDroid Business:
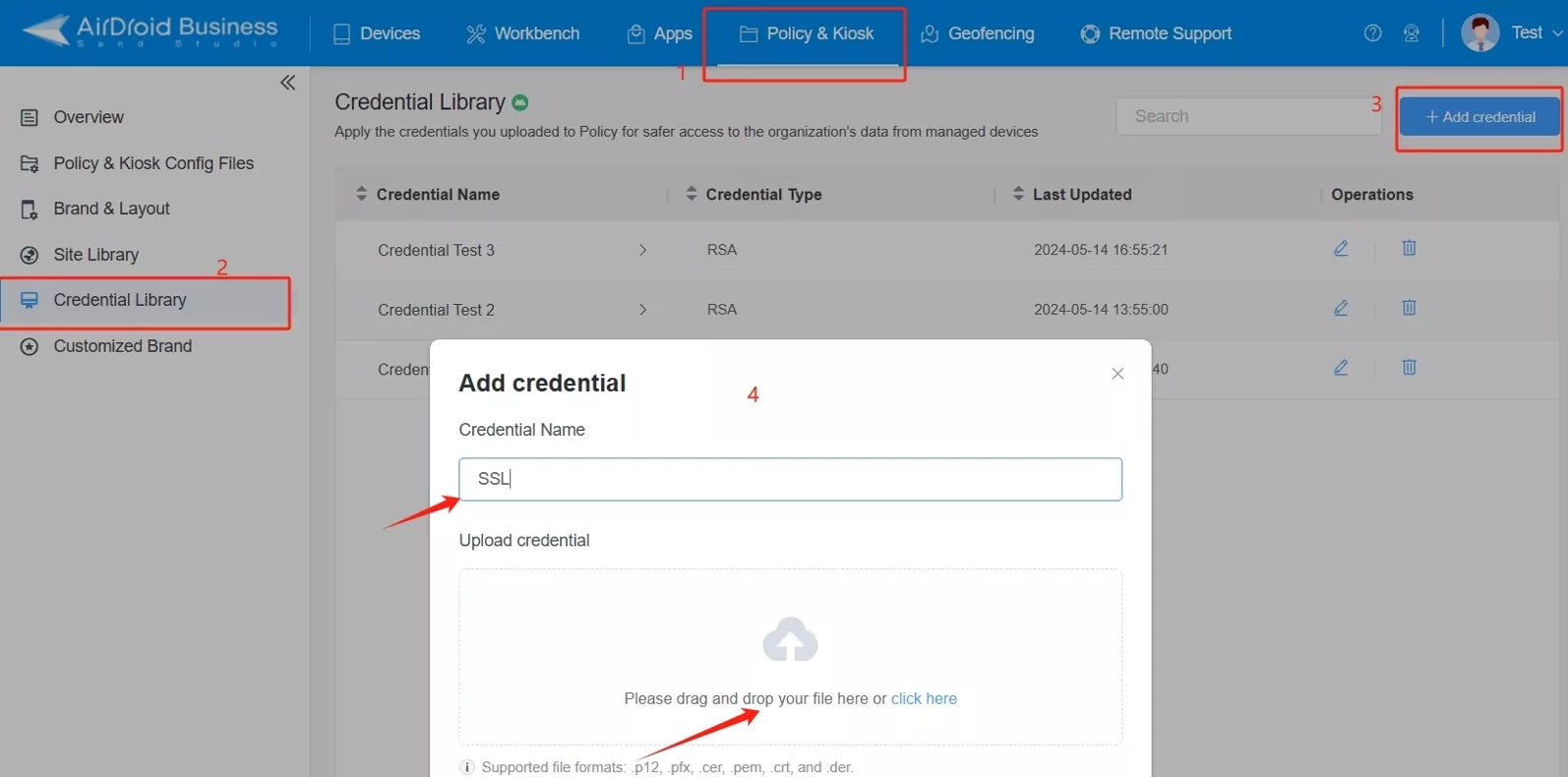
Step 1 Set Up an MDM Platform
● Log in to AirDroid Business and navigate to Policy & Kiosk Config Files.
● Select Credential Library and click Add Credential.
● Upload the certificate file (.p12, .pfx, .cer, .pem, .crt, or .der format).
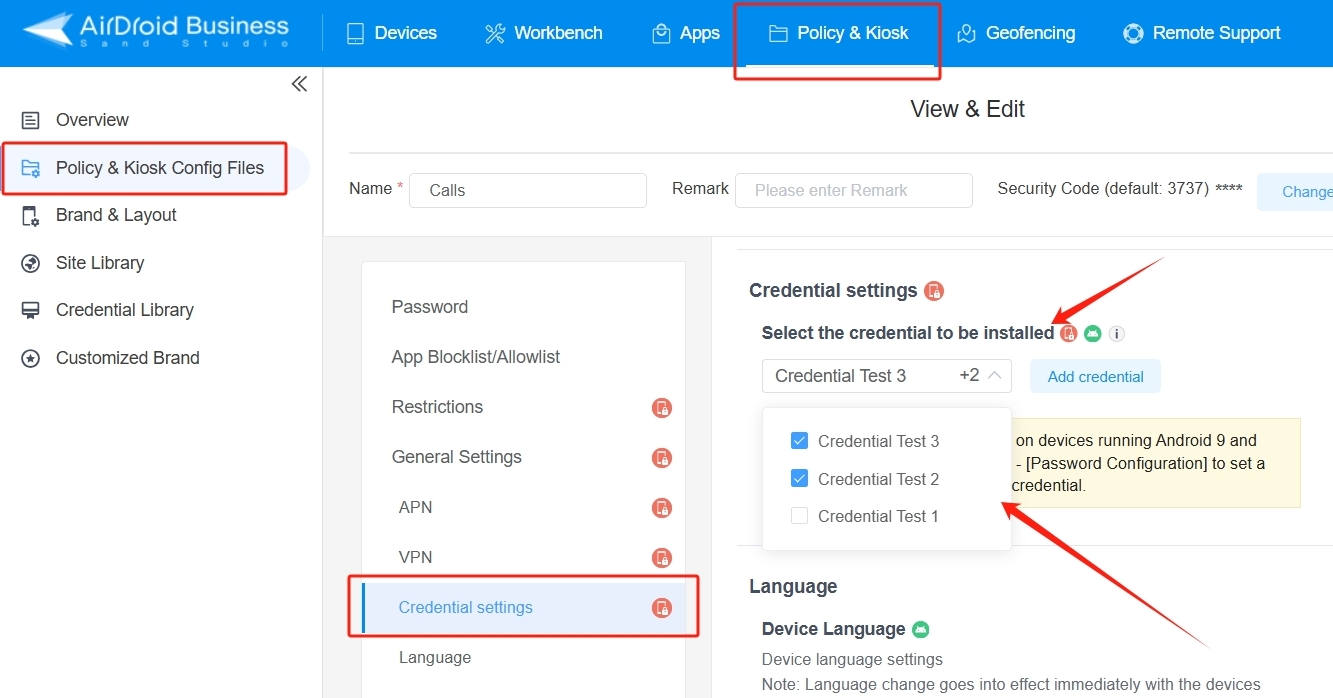
Step 2 Assign Certificate to Device Groups
● Navigate to Credential Settings within the policy editor.
● Select the certificate to install on enrolled devices.
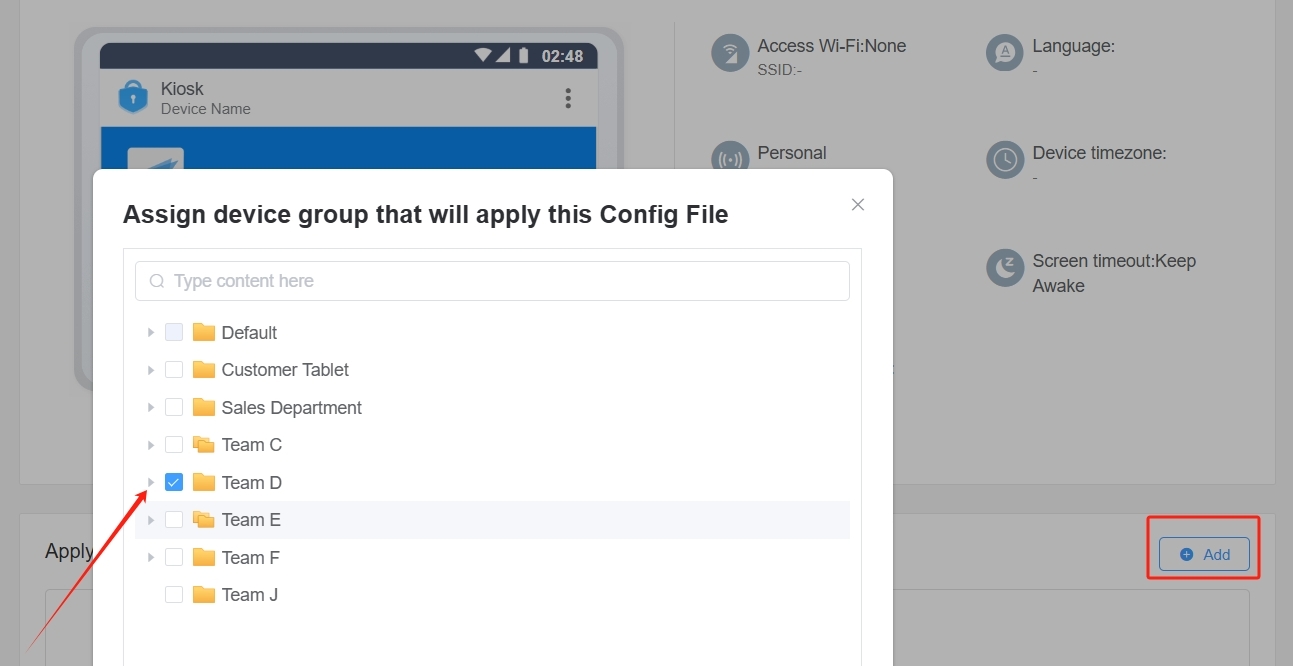
● Apply it to specific device groups, ensuring correct distribution.
Step 3 Deploy the Certificate
● Click Save and push the policy to the devices.
● The certificate will install automatically without manual user intervention.
Benefits of MDM Installation
- System-level trust can be established without manual configuration.
- Enables centralized certificate management, which extends to multiple devices.
- Generates extra security policies to comply with regulations.
Conclusion
Digital certificates are essential for keeping Android devices safe and secure by enabling encrypted communication and blocking access. Properly installing certificates is key whether you're setting them up manually on devices or deploying them through MDM for business management to boost data protection and network security.
IT professionals should carefully assess a suitable approach according to the requirements of their organization. By adopting the right method, enterprises can uphold security measures while ensuring smooth connectivity for their users.
If your company depends on certificates for security, consider Mobile Device Management as a solution to streamline the setup and control of devices simultaneously.





Leave a Reply.