- Remote lock the phone screen and wipe data on the devices.
- Set app allowlist & blocklist for work devices to prevent misuse.
- Restrict users download apps from unknown source and browser sites in apps to prevent data leakage.
- Track devices' real-time locations and set geofence.
- Remote access and control for troubleshooting.
What is App Protection Policies? & How to Implement Them?
According to one report published by Statista, data breaches in the third quarter of 2024 triggered around 422.61 million data record leaks, impacting millions of individuals and companies across the globe. While there are many possible causes of these data breaches and leaks, a significant percentage, especially in enterprises, are caused by employee devices. This is why as an organization you must manage how employees access, manipulate, and share the company’s data with various devices and apps.
One of the most effective ways to counter data leaks occasioned by employee devices is via an app protection policy. Well, this article takes you through everything you need to know about app protection policy for Android and other devices to help you protect your sensitive data from costly data breaches and leaks.
1What is App Protection Policy?
App Protection Policy is simply a set of rules of actions enforced on mobile apps by organizations to manage and control how data is accessed and shared. For example, your company might allow employees to use their personal smartphones to access corporate email and documents through mobile apps yet you also need to ensure that sensitive company data is protected. In this case, you’ll need proper app protection policies targeting those apps that your employees use specifically for work.
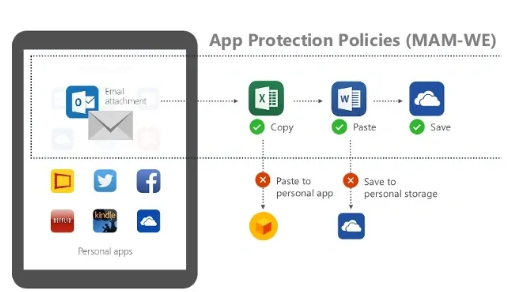
Well, these policies do offer an array of benefits to organizations or enterprises. Here are some of them.
- These policies ensure that your data, such as emails, documents, and customer information, are securely stored and accessed within apps.
- As an organization, you can allow employees to use their personal devices for work, without having to necessarily control their entire devices. In fact, your employees can still use their personal apps and services.
- These policies can help your company meet common compliance requirements, particularly if you operate in an industry that has strict regulations (like GDPR, HIPAA).
2How Can App Protection Policy Protect Corporate Data?
App Protection Policy protects corporate data in different ways. It is worth noting that these policies range from basic to more secure controlled policies and are often implemented based on the specific needs of the organization, the type of device, and the functions the respective protected apps handle.
Generally speaking, App protection policy is classified into three distinct categories namely.
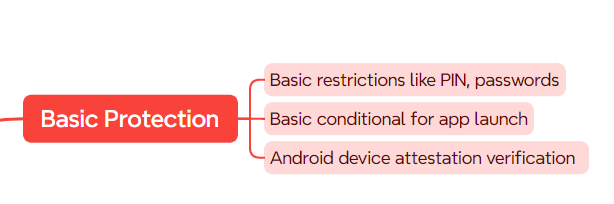
Basic Enterprise Data Protection (Level 1)
As the name suggests, this is the lowest App Protection Policy level. This level offers basic data protection and access restrictions with minimal disruption of the end-user experience.
It allows basic app data transfer, app encryption, and access to basic app functionality, and ensures that apps are protected with basic access requirements like PIN, face ID, biometrics, and passwords. Furthermore, it allows basic conditional application launch and restrictions like the restriction of apps based on the basic integrity of devices.
For Android devices, for example, this level also verifies Android device attestation. Generally, this is an entry-level of protection that is similar to data protection controls in Exchange Online mailbox policies. It also helps introduce IT and user groups into APP protection policies.
User Case:
If an employee uses a personal device to access company email, a Level 1 policy can ensure that the email app is protected by a PIN. In the event the device is lost, the company data cannot be accessed by unauthorized persons unless they have the PIN. Additionally, level 1 also provides an option to wipe work-related data hence boosting data security.
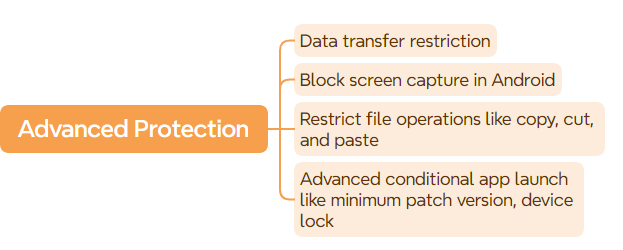
Advanced Enterprise Data Protection (Level 2)
Advanced/enhanced data protection is suitable for devices used to access sensitive or confidential information. It recommends the standard levels of protection that aim to prevent data leakage with minimum OS requirements. It is suitable for mobile users accessing organizational data such as work or school data.
In addition to Level 1 settings, Level 2 enables users to configure several protection options and access apps. These include the transfer of organizational-related data, block screen capture in Android, and transfer of telecommunication data. It also restricts file operations such as cut, copy, and paste between apps.
Furthermore, it lets you enforce conditional application launches such as access based on device integrity, minimum patch version, device lock, and minimum device OS requirements among others. It is worth noting that some of the configurations at this level can affect the end-user experience.
User Case:
A healthcare provider like a hospital can use this tier of policy. In this case the provider might want to allow doctors and nurses to access patient records through mobile apps while ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
Remember the organization handles Protected Health Information (PHI), so the security requirements are stricter.
The provider will thus set policies like enforcing stronger authentication methods, like multi-factor authentication (MFA), to access patient data. They could also restrict data sharing between apps. The data could also be encrypted both in transit and at rest to meet compliance standards.
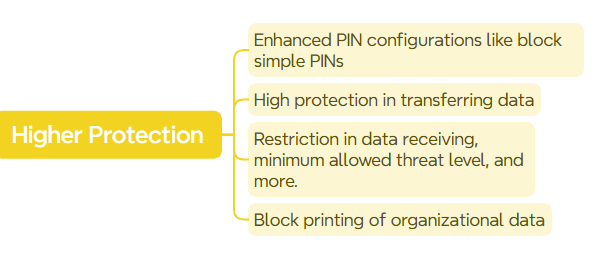
Higher Enterprise Data Protection (Level 3)
As the name suggests, this is the highest app data protection layer for enterprise data protection. This level is recommended for devices that access highly sensitive data where unauthorized disclosure triggers huge losses to the organization.
Such organizations are often targeting sophisticated attacks and it is not unusual for these organizations to have a dedicated or a larger security team.
Level 3 incorporates advanced data protection, sophisticated threat defense systems, and enhanced PIN configurations. These include blocking simple PINs, PIN reset after a number of days, device lock-in app protection policy android, minimum allowed threat level, maximum OS version, receiving data only from policy-managed apps, blocking printing of organizational data, and high protection when transferring telecommunication data.
User Case:
At such a level, the agency will need to enforce the highest security measures like Multi Factor authentication, preventing any copying or sharing of data with personal apps, and ensuring that data is fully isolated within the secure environment. The agency can also implement remote wipe capabilities to ensure that if a device is lost or stolen, all classified data can be erased immediately.
The introduction to the three levels of app protection policy sourced from Microsoft.
3How to Deploy App Protection Policy?
Knowing about app protection policy is one thing and deploying it is another thing. Well, many tools can be used to deploy app protection policies on either enrolled or unenrolled devices.
For example, you can use a Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Mobile Application Management (MAM) solution like Microsoft Intune app which is one of the most popular cloud-based endpoint management solutions that helps organizations manage and secure their devices and applications.
The tool has a App Protection Policies (APP) feature that allows admins/IT teams to manage, assess, and protect the installed apps and data using app protection policies that safeguard organizational data. You can essentially handle everything from access control, data sharing restrictions to monitoring how your corporate data is being accessed and used.
Protection Policy Features of Intune:
Microsoft Intune offers several app protection policy features including:
- Remote lock or data wipe to prevent sensitive data theft/leak or unauthorized access.
- Restricting file actions including copying, pasting, and corporate data into personal apps.
- It allows conditional access to corporate resources through security configurations and policies.
- It supports integration with Microsoft 365, making it easier for organizations to use plenty of productivity and collaboration tools without compromising security and compliance.
- It supports Windows Autopilot.
Popular Microsoft Intune Integrations:
Microsoft Intune supports various app integrations for better workflow and security across enterprise devices. Some of these integrations include:

- Email App-It supports integration with the Outlook mobile app.
- Microsoft Office- It allows users to securely use Word, Excel, and PowerPoint.
- OneDrive-Intune integrates with this storage platform and helps mark data as either corporate or personal.
- Skype for Business- This allows integration with Skype for secure collaboration and communication with teams across different devices.
How to Deploy App Protection Policy with Microsoft Intune?
Deploying Microsoft Intune on your mobile devices involves using Intune app protection policies. Here, you implement app-level policies to restrict access to your company resources while keeping data control within your IT department. The major steps include:
- Step 1: Signing in to Microsoft Intune admin center.
- Step 2: Creating or editing existing app policies depending on your needs. These policies include configuration settings, access restrictions, data protection, and conditional launches among others.
- Step 3: Once you are done, you can preview and deploy your app policies.
Here is detailed guide for you to know how to deploy the app protection policy in Intune:
4Protect Data Security with an MDM Solution
Although the app protection policy provides a lot of features for you to protect your enterprise's data security, it mainly imposes some restrictions on the apps. If you are looking for more restrictions to effectively and conveniently protect data security for devices the MDM solution is your best option. Besides app management, a suitable MDM solution like AirDroid Business can help you set other policies and tailor them to your enterprise needs.
You can set policies to restrict file transfer, network connection, app installation, OS updates, and device access among others for better data security. The good thing with MDM solutions like AirDroid Business is that you can target specific apps on specific devices.
MDM vs App Protection Policy
Enrolment- MDM requires device enrollment so as to apply the respective policies while the App Protection Policy doesn’t necessarily require device enrolment. It can be applied to both managed and unmanaged devices.
Management target- MDM offers comprehensive management. It can manage the entire device including the settings, data, and applications on the device. App Protection Policy on the other hand is often limited to specific corporate apps.
Devices- MDM is suitable for company-owned devices because it allows admins to monitor, control, and deploy policies to a fleet of devices from a central point. App Protection Policy is suitable for BYOD because you don’t need to enroll the device and it is meant for certain apps within a device.
5Summary
App Protection Policy is a useful security feature that protects corporate data from unauthorized data access and leaks. However, if you want more control and management of your enterprise devices, MDM is your best bet. With a suitable enterprise-grade MDM solution like AirDroid Business, be sure to transform how you manage and protect your enterprise devices from costly data breaches and leaks.








Leave a Reply.