Full Guide to Automated Security Workflow for Corporate Assets
Attacks on digital and IT infrastructures are now more sophisticated than ever, able to evolve and adapt, dependent on defense structures and risk mitigation mechanisms in place. Therefore, it is critically important that businesses are equipped to deal with this ever-changing and increasingly potent threat and have appropriate security systems that work to protect their assets.
All devices on a corporate network, whether that be computers, laptops, smartphones, or storage units, are susceptible to penetration. Indeed, a device's internal operating system - the management control center that governs how it functions - can be breached at any moment. Consequently, businesses must have the ability to respond to security threats around the clock and have a process in place for efficiently eliminating threats.
1What is Security Automation?
Quite simply, security automation is a mechanisms to automatically handle preset alerts for emergencies. It usually integrates platforms that serve to consistently identify threats to cybersecurity, diagnose the nature of these attacks, and take appropriate action to reduce the likelihood of this activity compromising the integrity of a device within a corporate network.

But what does this look like in practical terms? Below, we have identified three key actions that are initiated by security automation, and outlined how these have a positive impact on the protection of workplace assets and corporate confidential information.
Key Actions
- Alerts & Workflows - Alerts notify company IT administrators of suspicious activity, or where there is a tangible risk to the performance of a device or network.
In most cases, the system will automatically and independently address the issue via running configured workflow, and log an incident report containing details of what has occurred. However, in cases where a severe threat has been detected, the issue may be escalated to specialist IT operatives, as some level of human intervention may be required in order to help tackle the problem. - Device provisioning - When businesses enroll new devices onto corporate networks, they need to ensure these assets are provisioned with appropriate security settings from day one. This allows devices to be primed and ready to handle threats, facilitate local authentication processes, and access relevant data.
- Security profiles - Through the use of automated security technology, businesses can develop bespoke security profiles. These are set-up to possess specific defense features and 'policies' which are most relevant to the local environment, and therefore are equipped to address common security risks. Security profiles are able to trigger specific workflow actions dependent on the nature of an incoming threat; this ensures responses can be consistent, measured, and fit for purpose.
25 Use Cases for Automated Security Workflow
In the previous section, we explored the general functionality of IT security automation - now we switch focus to the specific support mechanism of automated security workflow. We highlight five of the most frequent security actions undertake on a typical corporate scope:
1. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
A simple program designed to support the everyday management of corporate networks, Robotic Process Automation delivers a vast range of basic security tasks, but does not have the capability to pacify sophisticated cyberattacks.
A robust RPA system allows businesses to reduce the workload of IT operators, and therefore liberates these individuals to focus on more significant network activity.

2. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
This tool enables businesses to gather data on persistent security threats, and understand trends and patterns in risk activity. Furthermore, SOAR ensures that security profiles are active and suitable for their local environment and is the vehicle in which patch updates can be delivered to networked devices. Its response arm can adequately deal with complex cyberattacks without requiring support from a human operator.
3. Reporting Compliance-related Data
It is vital that all businesses adhere to cybersecurity management regulations, and that their defense policies and procedures keep pace with industry standards. Prior to their integration, automated security workflows are mobilized to monitor local network activity with respect to legal requirements, take evasive action if devices fall into non-compliance, and provide feedback relevant data on regulatory performance.
4. Phishing Detection
Phishing is the act of intentionally misleading an e-mail recipient for the purpose of extorting financial information. With an effective automated security workflow, businesses can construct workflows that act to reduce the threat of phishing, blocking e-mails sent by specific mailboxes and alerting employees when suspicious e-mails appear.
5. Endpoint Scans
1.A remote device that absorbs and relates information about the conditions of any given network; endpoints enable IT operators to understand the nature and potency of cyberattacks. By initiating regular scans of endpoint devices, security incident response workflow help businesses swiftly detect issues, and empower them to take appropriate defensive action when required.

3What Tools Can be Used for Security Workflow Automation?
We have discussed how automated systems possess the capability to support corporate entities in the execution of their daily security strategy, but what are the specific tools businesses use in order to preserve their digital estate?

The three sub-headings listed below represent critical focus areas for internal IT teams. In relation to these three disciplines, we have provided examples of security tools readily used in corporate networks.
1For Data Loss Prevention
If a company's confidential data is leaked, the consequences could potentially be catastrophic. This threat does not exclusively derive from the efforts of unsavory external actors; employees (whether intentionally or not) can also be responsible for the loss of sensitive information.
Tools Used
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Software
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Software
- Encryption Software
- Password Manager
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Software
2For Device Protection
As all business devices are intimately connected to corporate networks, and, therefore potential conduits to the type of sensitive information discussed in the previous section, it's essential they do not fall victim to menacing cyberactivity.
Besides, circumstances such as device loss and stolen are also major security threats and need security incident response workflow.
Tools Used
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) Solution
- Mobile Application Management (MAM) Solution
- EMM / UEM Solution
- Network Access Control (NAC) Tools
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Tools
Using automated security technology, businesses can perform device locks to prevent undesirable users from gaining access, execute full factory re-sets to wipe confidential data, and uninstall harmful applications and viruses all from a remote location. In order to deliver each of these preventative tasks, IT operators must utilize device management platforms - AirDroid Business is widely regarded as one of the most comprehensive programmes on the market.
3For Cloud Computing Services
Cloud services afford businesses the opportunity to operate more efficiently and cost-effectively, by providing storage, server, and data reporting solutions from a single digital location, and reducing the requirement of human intervention in managing corporate networks.
Tools Used
- Cloud Custodian
- CloudTrail
- Security Hub
- AWS Key Management Service
4How to Create an Automated Security Workflow?
As alluded to on several occasions in the notes above, a workflow is a pre-determined action that is triggered when a specific event (or, in this context, a threat to security) occurs. The process for setting-up a workflow response is clearly dependent on the mobile device management platform being used; however, most automated security workflows will require users to follow a similar methodology.

In order to illustrate how to create an automated security workflow and indeed establish a relevant notification procedure, we have highlighted the steps businesses would need to undertake when conducting this task using AirDroid Business's device management solution:
- Step 1. Log into the AirDroid Business Admin Console.
- Go to the official website and create an account with your email address. Then log into the platform.
- Step 2.Enroll devices that you want to set alerts on.
- There are 3 enrollment methods - Regular Enrollment, Device Owner Enrollment, and Android Enterprise Enrollment - that are based on device types. Learn more here.
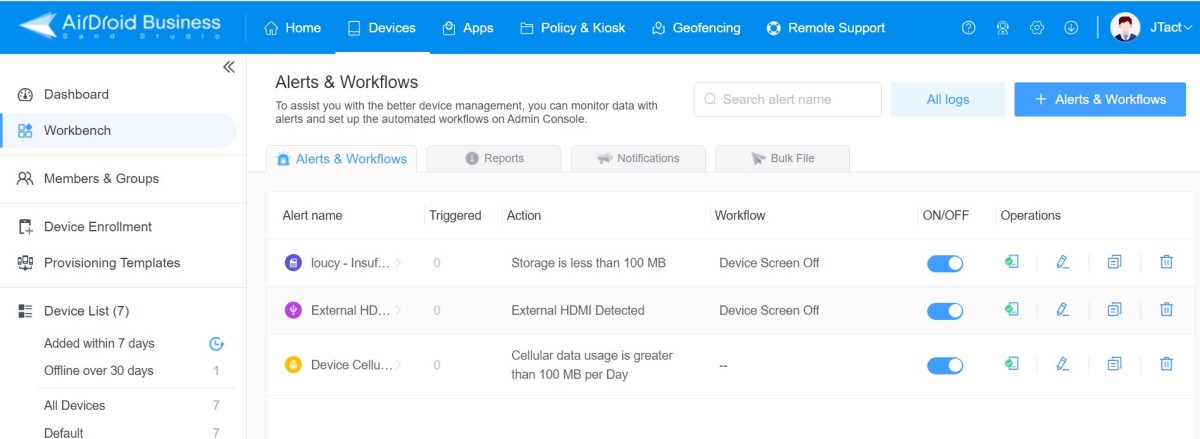
- Step 3.Set up alerts and receive notifications via email.
- Go to "Device" > "Workbench" > "Alerts & Workflows" and click the button "+ Alerts & Workflows" to create one.
- In the pop-up window, you can select the alert type and enter the conditions requiring the workflow activity to trigger. Alert types include:
| For Device Status | For Apps | For Location |
|---|---|---|
| Device Motion Status Device Online/Offline Status SIM Card Placed/Removed Device Cellular Data Usage | App Cellular Data Usage App Running Status App Running Status | Geofencing |
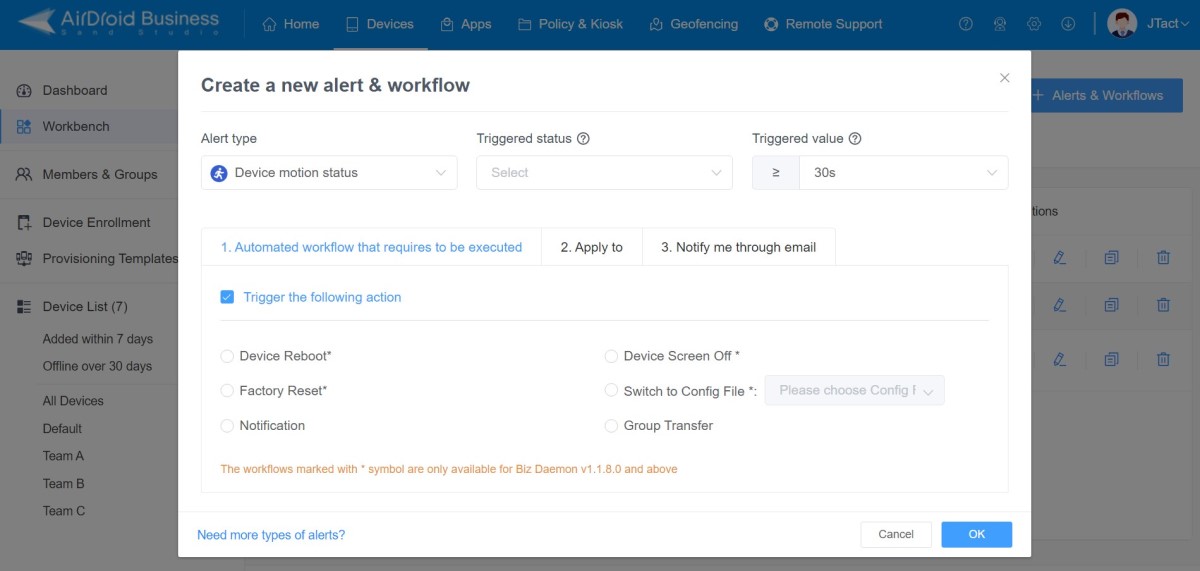
- Step 4.Configure the automated workflow that needs to run remotely.
- Tick "Tigger the following action" and select desired action from the menu provided, for example: Factory Reset, Device Reboot, Device Screen Off, Notification, or use Policy/Kiosk Mode and etc.
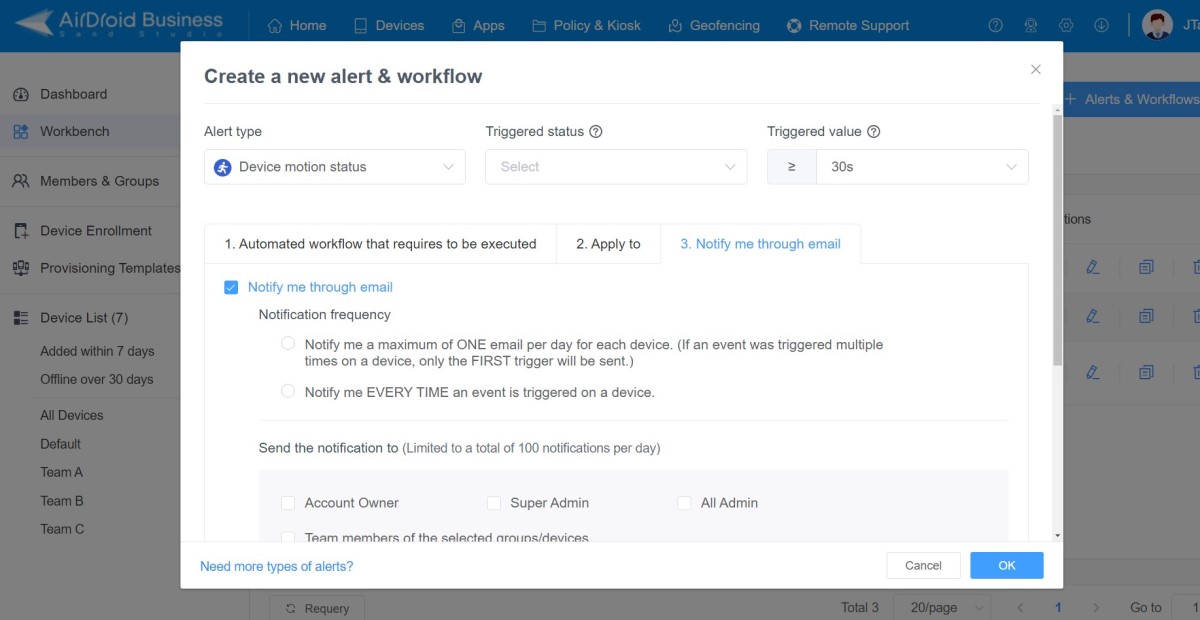
- Step 5.Apply the setting to device groups and complete notifications.
- Choose the devices you want to provision and finish the setting for email notification.
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
5Why Companies Need Security Workflow Automation?
The security workflow automation is essential in combatting the threat of cyberattacks, providing businesses with a host of security-related benefits:
- Device provisioning ensures assets exist safely, with relevant protection, within corporate networks.
- Security policies, created with the needs and requirements of the specific user they serve, protect devices and networks from familiar threats, and continuously adapt to help businesses defend against new and increasingly sophisticated attacks.
- Kiosk modes help govern employee accessibility to corporate data, reducing the risk of data leakages.
- Automated endpoint scans ensure IT teams can quickly identify network breaches, and react to threats as appropriate.
- Commands can be pushed instantly and remotely onto corporate devices, pre-empting activities such as device locks, factory re-sets, and app uninstallation.






Leave a Reply.