Containerization In MDM & BYOD: How It Works In Security
As an Android phone user, perhaps you have already noticed a special entry called 'Second Space (e.g. in Xiaomi)' or 'Guest Mode' that enables you to enter another home screen on the same device.
This feature can flexibly switch two partitioned screen layouts as if you are using different rooms with apps, settings, and data separated.
The methodology to implement it is called 'Containerization.'
Containerization is widely used in OS and application developement and has strategic significance for enterprise data protection. In this article, we will explain the term and explore its effect on mobile device management.
1 Explain: Containerization In MDM
Containerization is a technique to create an isolated zone to run apps, in which, containing application code, system library, configuration files, and generated data.
The isolated zone is called a 'container.' It works on the cornerstone of the device operating system. And multiple units are able to coexist on one device and run individually.
Applications of containers are various. In addition to the mentioned 'Second Space', containerization in MDM has more prominent practices, for example, Android work profile in Android device management and Managed Apple ID in Apple device management.
With these tangible illustrations, we can have a better understanding of MDM containerization.
MDM Containerization is the method to create isolated spaces in the same device while keeping both applications and data in different environments.
And the isolation criteria for MDM container is based on work-used apps or personal-used. This separation makes it feasible to protect both employee privacy and corporate data simultaneously.

MDM containerization provides a solution to embrace employee private device management with corporate data protection. And the impact is that Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy is adopted by more and more companies.
2 MDM Container in Android
Android work profile is an example of MDM container applications in Android devices.
After creating a profile for work, the Android phone will activate two buttons in its panel - Personal and Work so that the device user can easily switch the Android containers. In the work profile area, apps can be installed separately and a briefcase icon will show in the right corner. And, cached and data generated during the app use will retain in this work area.
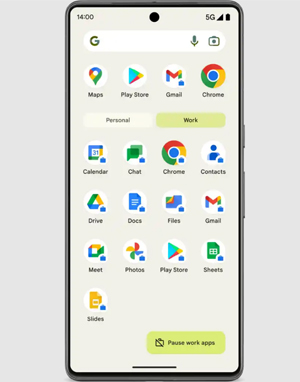
Source: android.com
Enterprises can maximize the work profile feature with Profile-owner-supported MDM solutions. After enrolling the device, the MDM solution can manage the Android MDM container in these ways:
| Security for Device and Data | Enfore password policy; remotely lock work profile; remotely wipe work profile data; automatically block access to work profile for non-compliance devices; enable or disable Smart Lock and screenshot |
| App Management | Manage app catalog; silent installation; install and update apps from Managed Google Play; configure app settings like auto-update rules and others; publish enterprise private apps |
| Device management | Runtime permission policy; Configure Wi-Fi settings, location sharing settings, VPN, and others |
| Account & Access management | Create a work profile with Workspace or Cloud Identity account; manage identity certificates; configure accessibility features |
Organizations have full control of the work profile. However, the management will not affect the personal profile on the device. It solves the main concern of BYOD devices - protecting personal privacy and preventing corporate data breaches.
3 MDM Container in iOS
iOS or iPadOS devices are major BYOD devices today. Apple containers can be used on them as well but require Managed Apple IDs created by Apple Business Manager (the official MDM solution).
Managed Apple IDs are similar with personal Apple ID. However, they are for business purposes only. How do they work? When an employee gets a Managed Apple ID from the IT team, he can use this account to log in on his device. Then he can enjoy using the organization's Apple apps and other Apple services such as iCloud iWork and Notes.
The Managed Apple IDs will help divide corporate managed apps and personal apps on the device. And the IT team will only manage and access work-related resources.
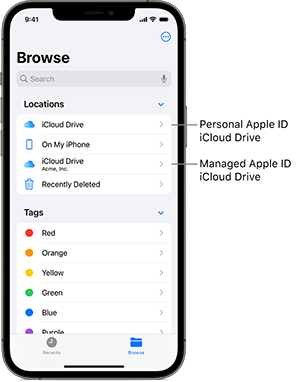
Source: apple.com
User Enrollment is another container feature for Apple BYOD devices and used for device deployment. Once the enrollment is done, a separated zone will be automatically created. It contains the following items:
- App data
- Calendar
- Mail attachments
- Mail message
- Reminders
- Organization's iCloud Drive
4 How Does MDM Containerization Enhances Security for BYOD
1 Data Separation
As containerization comes to bring-your-own devices, extra accesses to applications and storage spaces will appear on the mobile interface. These accesses allow to keeping of all corporate data in a designed container that does not involve personal-used apps. It means that, if an employee is using unsafe private apps, there is a blockade for these risky origins.
2 Policy Enforcement and Access Control
MDM software plays an important role in containerization in BYOD. It allows enterprises to apply security policies on the container, for example, password complexity requirements, password updates, storage data encryption, feature restrictions over camera or Bluetooth, system updates, etc.
3 App Management
MDM is able to manage and configure work apps within containers. Operations include: blocking unapproved apps, auto-updating app versions, and configuring app settings.
4 Remote Wipe
In dealing with unexpected situations like device loss, IT admins can remotely wipe corporate data in MDM containers only. And the erase operation will not work on personal data.
5 Pros And Cons Of Containerization MDM
Containerization mobile device management (MDM) is a popular solution for organizations seeking to secure corporate data while enabling employees to use their own devices for work. This approach offers advantages but also has drawbacks. Here, let's explore the pros and cons of containerization MDM.
Pros
For Organizations
- Selective and Legal Data Encryption: Containerization MDM allows organizations to selectively encrypt corporate data, ensuring compliance with legal requirements and protecting valuable information.
- Granular User Access Control: With containerization MDM, organizations have precise control over user access to work data, reducing the risk of data breaches by limiting access to authorized individuals.
- Easy Work App Management: Containerization MDM simplifies work app management, enabling remote installation, updates, and removal to provide employees with the necessary tools.
- Remote Wipe Capability: In case of a lost or stolen device, containerization MDM allows organizations to remotely wipe work data, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Effortless Employee Profile Management: Containerization MDM streamlines the process of managing employee profiles, simplifying onboarding and offboarding for IT administrators.
- Cost Savings: By implementing containerization MDM, organizations save on device purchases for employees, as they can use their own devices, reducing expenses.
For Employees
- Enhanced Privacy: Containerization MDM ensures that an organization's monitoring is limited to the work zone, respecting employees' privacy by keeping personal data and activities outside of work apps private.
- Increased Productivity with Familiar Devices: Employees can use their own devices with containerization MDM, boosting productivity by working on familiar devices.
- Improved Work-Life Balance: Containerization MDM helps employees achieve a better work-life balance by seamlessly transitioning between work and personal tasks on their own devices.
Cons
For Organizations
Containerization MDM restricts control over the entire device, potentially leading to data loss, malware infections, or phishing attacks outside of the work container.
For Employees
Containerization MDM might affect the overall user experience due to the separation of work and personal apps. Also, the storage restrictions enforced by containerization MDM could pose challenges for employees requiring substantial storage for work-related files and apps. In addition, IT operation errors may cause personal data loss.
6Challenges Of Implementing Containerization In MDM
Containerization in MDM has its own set of challenges. Here are some of the most common ones:
Container Compliance
Regulatory standards such as GDPR, CIS, and PCI DSS require organizations to comply with specific security and privacy requirements. Containerization must be implemented in a way that meets these standards.
Data Recovery
Another challenge is the ability to recover data from containers during a disaster. Containerized environments often consist of multiple interconnected components, making data recovery a complex process. Organizations need to have a well-defined plan in place to ensure their data can be recovered quickly in case of any unexpected incidents.
Poor Data Management
Improper implementation of containerization can lead to poor data management practices. This can result in data loss, security breaches, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Compatibility Of Device
Not all device types are compatible with containerization solutions. This can limit the ability of organizations to implement containerization across their entire device fleet.
Conclusion
Containerization enhances corporate data security in MDM and BYOD environments by isolating business apps from personal ones.
Businesses and organizations should adopt robust MDM solutions with comprehensive containerization features.






Leave a Reply.