MDM vs EMM vs UEM: Definition, Difference & Which to Choose?
In today’s evolving digital landscape, businesses are opening up to the use of a diversified range of endpoints from BOYD (Bring Your Own Device) devices to COPE (Corporate Owned Personally Enabled) devices and COBO (Corporate Owned Business Only) devices.
However, this diversity also brings with it new challenges, the most imminent ones of which are related to security, closely followed by management. In just the first 6 months of the year 2024, there were above 1500 cases of data breaches. Besides security, the complexity of devices calls for a more adaptive management system across the entire endpoints inventory.
The solutions like MDM, EMM, and UEM come in handy for managing a range of different devices and ensuring security. However, every one of these has its own set of limitations and strengths. This guide provides an in-depth account of what each one of these is meant for, and how they differ so that you can make a choice according to your particular preferences.
Part 1 : What is MDM, EMM, and UEM? What are the Use Cases?
Device management and security is an intricate multi-layer phenomenon. It includes various fronts from managing and securing the device only to data security and data flow, managing apps, and network settings, and more. Different management tools provide help with different fronts with some being broader than others. Let's explore each one of these in detail.
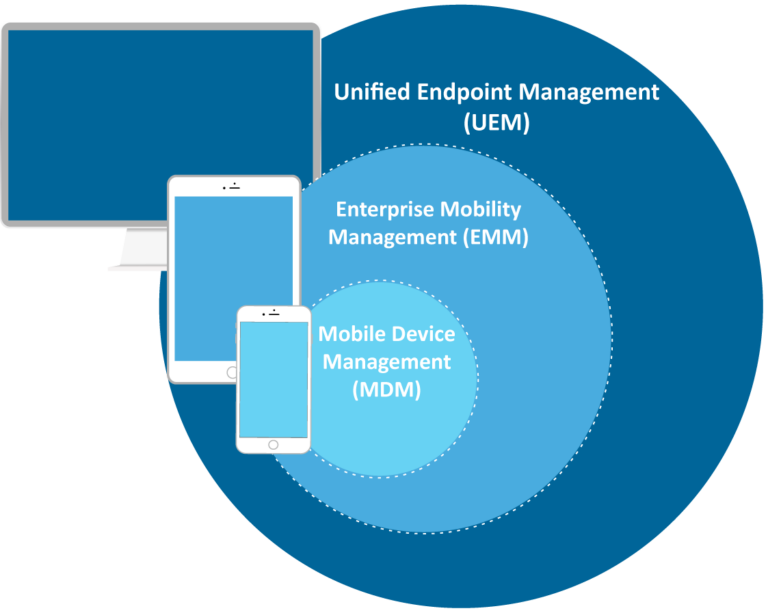
1What is MDM (Mobile Device Management) and its Use Cases?
Definition:
Mobile Device Management is a solution to control device system settings and monitor device status. Essentially, MDM software allows the admin to remote access an enrolled mobile device, such as a smartphone and then set up rules on the functionalities. MDM focuses on controlling and limiting the built-in features and also observing the status of the device.
Use Cases for MDM:
Due to the requirement of getting device info and operation permissions, MDM is best used for dedicated devices, for example:
- Handsets and tablets for truck drivers, teachers and students, or nursing personnel, etc.
- Mobile POS terminals used in restaurants, retail stores, or entertainment industries.
- Rugged phones for frontline workers from construction field or warehouse, etc.
2What is EMM (Enterprise Mobility Management) and its Use Cases?
EMM is a corporate device management solution that allows the admin to manage and secure not just the devices but also the apps, network connections, and data on those devices. It encompasses the company-owned as well as BYOD devices.
How EMM is Related to MDM?
EMM has all the features provided by an MDM solution, plus it allows managing the content of the devices as well. In other words, MDM is a subsidiary of EMM. In short, as compared to MDM which is restricted to device management and security, EMM allows app management, network management, and file management as well. This is because EMM encompasses four major areas of management:
Management Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Mobile Device Management (MDM) | It allows the admin to secure a fleet of devices by implementing security policy across all the endpoints remotely from a centralized control. It is centered at device security and monitoring and allows remote wiping of data to avoid security breaches. |
| Mobile Application Management (MAM) | It allows setting policies that help manage and monitor specific apps rather than the device. Organizations can configure apps remotely through MAM. For example, installing and uninstalling apps across the entire device inventory and sharing data through specific apps, or using tailored, private apps for specific purposes. |
| Mobile Content Management (MCM) | Actions like bulk file sharing and bulk file deletion etc. can be performed and MCM allows the admin to decide which apps can be used for sharing specific data. It helps restrict or allow certain apps to use sensitive data. |
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Security features like Single Sign On (SSO) feature and Multifactor Authentication can be used to allow access to authorized employees only. IAM is all about deciding who can access certain data and for how long. It also helps allocate duties and roles within an organization. |
To sum it up, EMM does what MDM does, plus it also allows app management and content management along with access management. So, it has a broader domain as compared to MDM.
To sum it up, EMM does what MDM does, plus it also allows app management and content management along with access management. So, it has a broader domain as compared to MDM.
Use Cases of EMM:
EMM manages and controls more items than MDM - the flexible access and usage of apps and cooperated resources. Thus, it is best used in:
- Enterprises that adopt BYOD (Bring Your Own Devices) policy.
- Enterprises with overseas offices and remote working employees, including but not limited to IT companies, MSPs, E-commerce companies, BFSI industry, etc.
- Sales and marketing team, HR department, IT department, etc.
3What is UEM (Unified Endpoint Management) and its Use Cases?
Definition:
It is a set of tools and software that allows to manage and secure not just basic mobile devices but also wearables, PCs, IoT, and other types of devices from a single, unified console. It allows cross-platform control and gives granular control over apps and data management. It secures both devices and data across varied endpoints and is compatible with multiple systems.
Use Cases:
- Companies with BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), COPE (Corporate Owned Personally Enabled), or COBO (Corporate Owned Business Only) device policy.
- Industries that apply self-service kiosks and other unattended devices, such as banking, transportation, restaurants, retail stores, hotel, etc.
- SaaS companies from industries such as retail, healthcare, education, communication, financial services, etc.
Part 2 : MDM vs EMM vs UEM: What are the Differences?
Although all these three terms are used interchangeably, they differ widely in their scope and features. While they do have overlapping areas, they have limitations and strengths. Where one of them might be more useful for a particular type of setup, the other one might be just a useless investment with features that the organization might never use.
Let us have a round-up of how they differ to know which one offers better usability for your business.
1Supported Devices
Category | MDM | EMM | UEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Based on Ownership | COBO (Corporate Owned Business Only) devices | BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), COPE (Corporate Owned Personally Enabled) Devices, COBO (Corporate Owned Business Only) devices | BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), COPE (Corporate Owned Personally Enabled) Devices, COBO (Corporate Owned Business Only) devices, CYOD (Choose Your Own Device) |
| Based on Endpoint | Phone, Tablet, Phablet, Laptop, Other mobile devices | Phone, Tablet, Laptop | Phone, Tablet, Laptop, TV, PC, Printer, Smartwatch, Kiosk, Rugged device, Other wearable & IoT devices |
To summarize, when it comes to types of supported devices, MDM supports mainly company-owned devices only. On the other hand, EMM takes a step forward to include both corporate-owned and personal devices. This means a wider range of devices can be enrolled under EMM. The same is the case with UEM. It also encompasses both corporate-owned and personal devices of all sorts.
When it comes to supporting the types of endpoints, however, UEM has a broader scope than both the MDM and EMM. Where MDM and EMM support most of the conventional mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and Phablets, UEM-supported endpoints include virtually every network-connected device.
2Scope of Management
Category | MDM | EMM | UEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Management Scope | Deals solely with device management. Examples: Device enrolment, device compliance, remote locking, geofencing, policy forcing, remote data deleting, remote device locking. | Device Management + application management and content management. Examples: Application whitelisting, workflow management, file management, access control management, etc. | Device management, app and content management plus cross-platform app management and multi-system device management. Example: Implementation of universal security policies across various device types of endpoints, managing self-service kiosks. |
As it is evident from the above table, MDM is at the basic level when it comes to the scope of management. It is related to managing the devices only and ensuring the security of data through remote wiping and device locking in case the device is lost or stolen. EMM on the other hand combines device management with apps and content management. For example, network management, workflow management, app whitelisting, and more. In short, besides ensuring security it also ensures productivity on the employee’s end.
UEM on the other hand encapsulates the management scope of both MDM and EMM and moves a step ahead of them by enabling all these management functions across all platforms and all devices. In short, UEM has the widest scope when it comes to management.
Part 3 : MDM vs EMM vs UEM: Which One to Choose?
While all of them have their positives and negatives, what suits you best is dependent on the size and complexity of your digital assets, your management goals, and of course your budget. Let us have a candid overview of what each one of these is best at, so that you can decide what’s your pick.
1When should You Choose MDM?
MDM is preferred by those looking for a basic level of control and monitoring mechanism. It would be a reasonable choice for you if your IT environment has the following characteristics:
- Simple IT Environment: Do you rely on a simpler, less complex IT system with not a very diversified type of endpoint system? If so, your company might benefit from an MDM solution that provides remote management, timely patching, device security, and streamlined distribution of resources. Hence it is ideal for a simpler digital landscape that lacks variety.
- Large Fleet of Mobile Devices: An MDM solution is ideal to be used in an IT environment where a large fleet of devices needs to be monitored and managed from a centralized console. It provides admins with streamlined control over the entire fleet, enabling them to mass implement and update security settings.
- Cost Effectiveness: Don’t have deep pockets and yet need a reasonable mobile device management solution for your company? MDM is certainly your pick. It is generally cheaper than EMM and UEM solutions and provides a decent amount of remote management and feature-rich solutions for enhancing productivity.
Tools Recommended: AirDroid Business
2When Should You Choose EMM?
For a diversified IT environment where basic device management might not be enough, EMM with its feature-rich security and management solutions is an ideal option.
- Diverse Devices and Operating Systems: An organization that houses varying types of mobile devices and more than one operating system can highly benefit from an EMM solution. It is ideal for diversified environments, especially suitable when the company supports BYOD devices at the workplace.
- Application and Content Management: When the goal of your mobile device management is a bit wider and you want to have control over not just the device security but also on the app management and content management, EMM can come in handy. It is focused not just on security but also on productivity through seamless content management.
- Collaborative Management in BYOD Environments: EMM enhances collaborative management in BYOD environments by providing tools for seamless integration and management of personal and corporate devices, thus improving overall efficiency. For example, it allows companies to introduce their own customized apps for streamlined collaboration across the entire fleet of endpoints—whether company-owned or employee-owned.
3When Should You Choose UEM?
UEM is an all-in-one management solution that is best suited for larger, more diversified businesses. Here is what you should look for if you are considering investing in a UEM solution:
- Comprehensive Device Management: No matter how many types of endpoints and what number of operating systems your organization is relying on, a UEM provides an all-inclusive management solution.
- Scalability: UEM is ideal for you if you are ever-ready to embrace the ever-evolving world of IT. With a UEM solution, you simply don’t need to worry about the newly introduced innovations in operating systems or endpoints as it covers all sorts of virtual and physical endpoints ensuring the highest possible security and control.
- Stringent Security Requirements: For a varied IT inventory and workforce that is stationed at various locations, UEM provides stringent security. It allows forcing strict security policies across all types of devices and for the entire workforce.
Part 4 : Limitations of MDM, EMM, and UEM
1Limitations of MDM
- While it is a budget-friendly solution, MDM is not a suitable solution if you are looking to cover a range of different devices. The endpoints like desktops, wearables, and many others cannot be secured and managed through an MDM solution.
- Moreover, where MDM is suitable for device security, it doesn’t provide a very granular control when it comes to enhancing productivity. For example, you cannot manage apps and content through a typical MDM solution.

2Limitations of EMM
- Where providing control over BYOD is one of the strengths of EMM, the same becomes its weakness sometimes. This is because the employees who are extra-conscious about their privacy may not like the fact that their device is being monitored and accessed by the admin in various ways.
3Limitations of UEM
- UEM is although an all-inclusive and dynamic solution for larger enterprises, it isn’t among the most budget-friendly options. Its feature-rich nature asks for deep pockets to be affordable.
- A management system as complex and diverse as UEM requires specialized skills. The absence of the same can cost a lot to the company in terms of security and operational efficiency. Hence, it requires trained individuals.






Leave a Reply.