How Enterprise Application Management Work & Sharp Insights
Nowadays, corporate entities are increasingly reliant on software applications, as they support most internal systems and processes, including employee communication, manufacturing, maintenance, and distribution. As a consequence, apps play a critical role in the overall delivery of client products and services, and therefore, by extension, a company’s ability to satisfy its customer base.
Given these contemporary developments, it’s perhaps unsurprising to note that the demand for high-quality, competent, and trustworthy enterprise application support services is increasing, as businesses seek to enroll the expertise of app developers in order to enhance their operational efficiency.
This article targets Enterprise Application Management and the role of MDM (mobile device management) that is in the business application management process.
- Part 1 : What is Enterprise Application Management?
- Part 2 : Lifecycle of Enterprise Application Development
- Part 3 : What Aspects does Enterprise Application Management Cover?
- Part 4 : Use MDM for Enterprise Application Management (Key Features)
- Part 5 : How to use MDM to test, manage, and monitor enterprise apps?
- Part 6 : Enterprise Application (EA) Insights in 2023
- Part 7 : FAQs
hide
What is Enterprise Application Management?
Enterprise application management refers to the process of managing, maintaining, and updating app software within a corporate context.
Operations within the organization can be complex. Enterprises sometimes use multiple applications to organize and exploit critical data in order to maintain effective relationships with clients and suppliers, and efficiently interact with employees.
Businesses adopt specific practices and methodologies dependent on their particular needs and requirements, and the nature of their respective operational environments. Some prefer ready-made third-party tools, and there are also self-developed ones.

Here're wide-used software to give a clear picture.
5 Common types of Enterprise Applications
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) – Deliver various business activities, including parts procurement, auditing and accounting, risk management and compliance, and project preparation and scheduling.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) - Stores essential customer information – such as contact details, product preferences, and transaction histories – on a central database, and further utilising the data to contact and re-engage with clients.
- Human Resource Management (HRM) - Enables businesses to retain vast amounts of employee information and data, including personal absence records, performance reviews, and salary details.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) - Most used in E-commerce, retail, warehousing, and logistics industries to fulfill consumer goods and service.
- Database Management - Uses to secure and manage database access.
More and more systems and applications are being used, managing them become a part of work. And this brings business application management into the organization.
One trend should be noted. Enterprise application management is now more focusing software developed by the enterprise itself covering app distribution to devices.

A Fact: Enterprises are increasingly building their own custom mobile applications.
As companies continually strive to improve their operational efficiency and customer service proposition, the desire to create bespoke applications, tailored to the needs and requirements of the business, has naturally increased.
Therefore, generic ‘off-the-shelf’ software, which are cheaper but don’t have the capacity to provide precise solutions to specific internal issues, have become gradually less popular in recent years.
Within the next twelve months, its understand that 81% organizations will have an active custom mobile application on the market – 40% of businesses having utilized the services of a third-party specialist to produce the app on their behalf, with the remainder developing their platform in-house.
Lifecycle of Enterprise Application Development
This charts the journey from the birth of the initial concept to the application’s ongoing role. The disassembly illustrates the manageable aspects of an enterprise app.
- Design
- Prior to producing the app, stakeholders must agree on its intended purpose and function. The application can then be designed accordingly.
- Development
- This is the construction phase. The application is built to the specification set out by the enterprise applications administration team.
- Testing
- This process enables IT teams to discover whether the app can consistently perform under operational conditions Before releasing to the company network.
- Deployment
- By this point, the app has been suitably provisioned and strength-tested, and has been deemed ready to enter the company network. The application goes live.
- Fix Bugs
- The team will need to monitor the app's performance. The troubleshoot any issues when using the enterprise app.
- Update
- Update app version for better performance and user experience.

What Aspects does Enterprise Application Management Cover?
During the entire process, enterprise app management service is able to cover testing, deployment, fixing bugs and update.
Tools you can use:
- Mobile deivce management solution
- Enterprise mobility management solution
- Application management service platform
- IT service management (ITSM) platform
- Application performance monitoring (APM) tool
Use MDM for Enterprise Application Management (Key Features)
If you're finding solutions for deploying your enterprise apps to devices, MDM might be the best answer.
The enterprise applications administration team can use mobile device management platforms to help with remote app installation and fully utilize MAM functions.
Some mobile device management solutions, such as AirDroid Business, are equipped with AMS (application management service) features, which makes the process much simpler.
Key MDM Features to Manage Enterprise Apps
1) App Library
A consolidated dashboard whereby IT teams can add or delete applications as appropriate. It's regarded as an app inventory and to facilitate subsequent app management setting.
2) Test Release
It allow IT team to sense-check whether the business’ app is compatible with various device models. Minimal operation is the winning point.
3) Formal Release
Two actions can be delivered via formal release: Staged Rollouts & Scheduled Release.
– Scheduled Release: Release apps and administer updates at a time that best accommodates employee/client requirements.
4) App Release Reports
Review app release progress, adoption rate, app version and other info in one place.
5) App update
Sends out mandatory updates to the entire device population.
6) App Install & Uninstall & Force Install
Able to remotely install applications on devices and as well as remove. For unattended devices, force installation is the best option to complete operations.
7) Clear App Data and Cache
For security or storage optimization purposes, IT teams may want to manage application data.
8) Application Monitoring
IT teams can access a comprehensive suite of reports, like All Applications Report and App Data Usage Report. Beside, an app list of a specific device is available for granular monitoring.
9) Application-related Alerts
This feature allows IT teams to set-up a notification system that to get alert messages for notable or suspicious app activity triggers. IT operatives are able to easily track the live performance of applications via this mechanism, reviewing measures such as foreground app status, and application running status.

Application Management Service Guide
If you want deeper insights into enterprise application management, view our PDF file. It’s loaded with detailed information to help you make the best decision for your organization's needs.
How to use MDM to test, manage, and monitor enterprise apps?
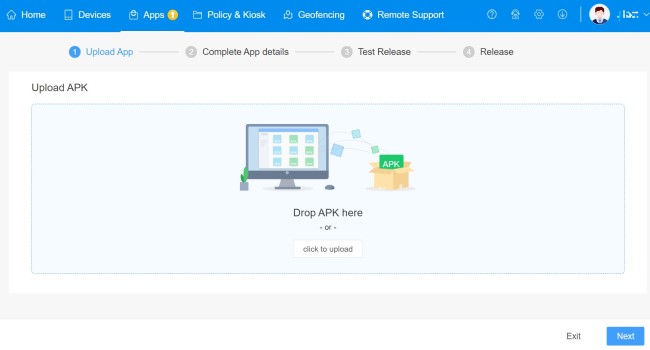
Before initiating any of the features listed below, you must first enroll devices into the central MDM console. This step is deploying enterprise applications and then further proceed management. When this process has been completed, you can upload your APK (this file format is used by Android operating systems to facilitate the remote installation of applications) and access all support mechanisms.
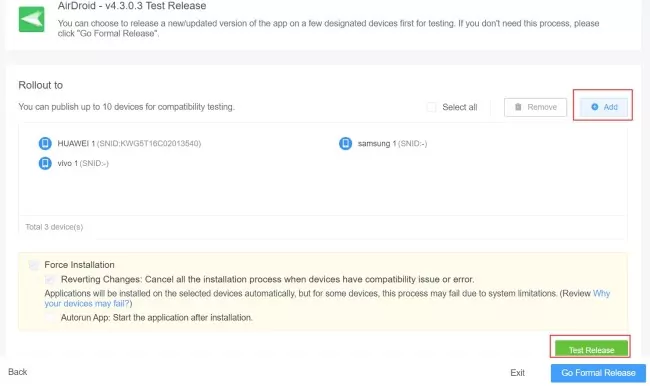
1. Test release enterprise applications
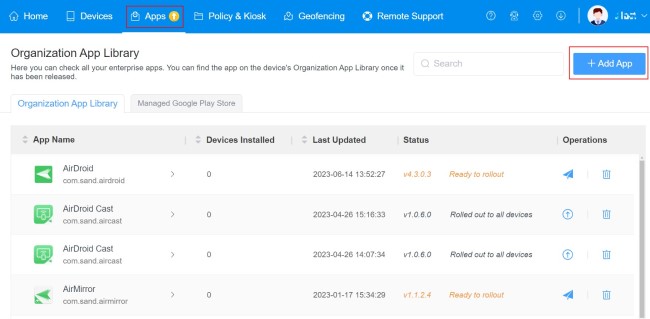
Go to admin console > App > App Library > Organization App Library > + Add App.
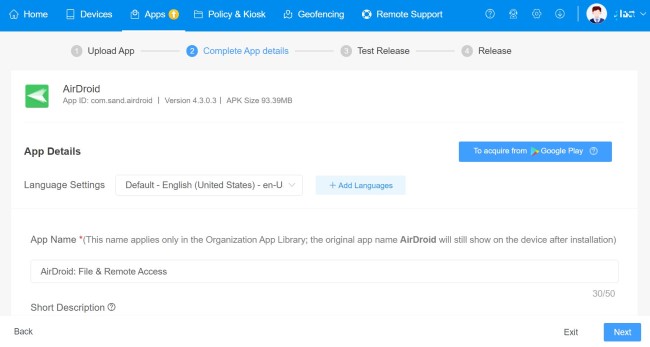
Then upload the enterprise app APK, click Next to complete app information like Language Settings, App Name, Description, Icon, etc.
After completion, you will go to the Test Release panel. Here you can choose enrolled devices with different OS versions or models via + Add.
A note-worthy tip: Force Installation is default set, and you can also tick Autorun App so the application will start working after installation.
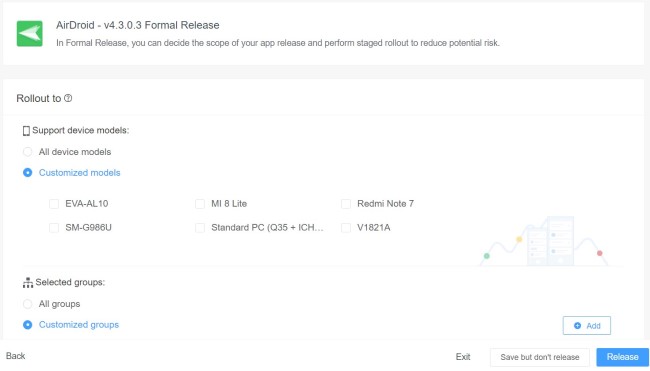
2. Formal release enterprise applications
Different from test release, there are more setting options in formal release, such as rollout to specific device model or groups, staged rollouts, schedule release time, and force installation with more settings.
To start, click Go Formal Release in the same release panel. Next, you can proceed with the following aspects:
- Rollout to: select all device models or customized models; all device groups or customized groups.
- Staged Rollouts: release by percentage, countries/areas, device info, or device groups in order to reduce issues.
- Release settings and time: 1) Release Now; 2) Schedule Release.
- (Optional) Force Installation: 1) Fixed Time Installation based on device timezone; 2) Reverting Changes; 3) Autorun App; 4) Download via Wi-Fi Only.
3. Track release progress
You're able to track the installation progress of your enterprise application by entering the detail info page. Here are what you can see: Daily Active Devices, Versions Installed by Devices, Release History and Status, APK Details, and so on.

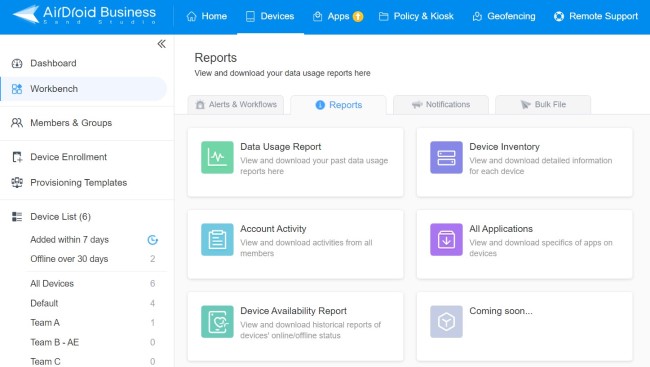
4. Monitor Enterprise Apps
Various reports are offered. You can go to Devices > Workbench > Reports > All Applications. Here you can see all installed apps on devices and their versions, last update time, device number, name, etc. You can also monitor their data usage in Data Usage Report.
In addition to it, set up alerts for specific conditions is available. In Alerts & Workflows, you can monitor foreground app status, app running status, app cellular data usage, etc. Once the alert is triggered, an automated workflow will be taken, such as screen lock and remote factory reset.
Clearly, in addition to these features, which exclusively support the application upload process, AirDroid Business provides you with a vast range of alternate mobile device management tools.
More about AirDroid Business
- Kiosk Mode: single & multi-app mode, kiosk browser, and website whitelist.
- Managed Google Play Apps Management: only for GMS devices.
- Remote Access & Control: manage device data, files, and others.
- Policy: manage and configure device system settings.
- Geofencing: track device location.
Enterprise Application (EA) Insights in 2023
According to market research firm Internal Data Corporation, who specialize in identifying common trends throughout the technology sector, those selling enterprise application services generated a staggering $279.6bn in revenue last year.
Moreover, this figure is expected to reach $385.2bn by 2026, whilst the overall enterprise application market is projected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8% over the next five years. Analysts believe the key catalyst behind this substantial rise in revenue will be within the public cloud software segment, which is earmarked to account for two-thirds of the market’s sales activity.

As is typically the case in most markets tethered to the wider technology industry, the nature and scope of customer activity within the enterprise application sector is constantly evolving. Our analysis of the current market points us to several key trends:
- There are two deployment modes generally used in enterprise application management; cloud-based deployments (activity is facilitated through cloud services) and on-premise deployment (companies use internal computing resource and source local copies of software to support their IT infrastructure).
Cloud-segment deployment accounted for 57% of market share in 2021, however overall usage is declining. On-premise deployment is expected to experience an annual growth rate of 5.2% over the next seven years. - As on-premise deployment affords more robust security solutions, whereby sensitive corporate data, employee information, and visibility of financial performance metrics are better protected, we learn that businesses are investing significantly more focus toward defence strategies than in previous times.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) activity generated over a quarter of the marketplace’s total revenue in 2021.
- A significantly increasing number of heavy metal and machinery businesses are developing enterprise applications; activity amongst this group is currently growing by 11% per annum, in a trend which is projected to continue until at least 2030.
AirDroid Business - Best MDM & MAM Solution
AirDroid Business helps to manage and control the Android mobile workforce. This enables real-time monitoring of Android devices and configurations of device settings, applications, files, and others.
It also provides a secure and centralized platform to manage all devices. All these make it an excellent choice to help enhance device management and security in an organization.







Leave a Reply.