The Many Facets of Geofencing: Types of Geofencing Explored
In today's world powered by technology, geofencing stands out as a top-notch innovation in location-based services. This advanced tech sets up virtual boundaries around real places, smoothly blending where a user is right now with interesting nearby spots.
Moreover, geofencing proves to be an effective tool with applications spanning various sectors like retail, healthcare, construction, and logistics, to name a few.
As we go deeper into this article, we will discover all types of geofencing and their applications.
Geofencing by Shape
Geofencing comes in different shapes, and we can categorize them into two main types: centroid and polygonal.
1. Circular Geofencing
Circular geofencing allows users to create a radius around a point of interest at a predetermined distance. This term refers to a specific distance that's established in advance.
With circular geofencing, data can be gathered about individuals moving within this circular area. Despite its quick response, data collected through this method can be somewhat unreliable.
The use of longitude, latitude, and centerline coordinates in circular geofencing can also make targeting a precise location more challenging.
2. Polygonal Geofencing
Another approach is polygonal geofencing, which involves creating virtual boundaries on maps by connecting multiple points to form shapes, like polygons.
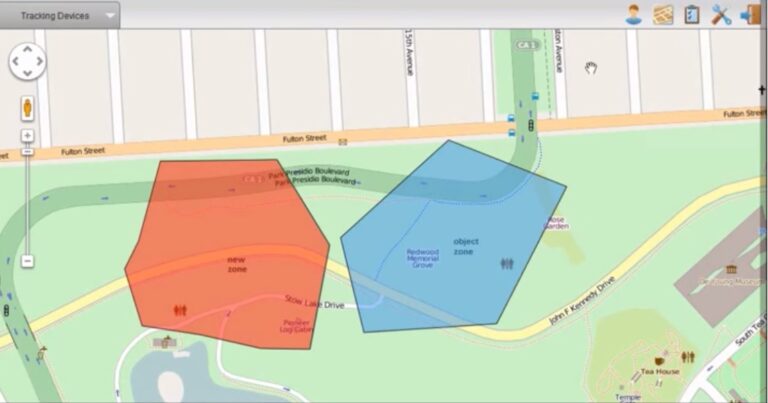
This technique is often employed in location-based services. Setting it up involves selecting points on a map to outline the desired fenced area.
Geofencing by Application
Geofencing serves various purposes, offering tailored experiences. Let's look at how geofencing is applied in different fields:
Retail and Marketing
In the retail industry, geofencing elevates the shopping experience. When shoppers enter or come near a store, they can receive personalized product suggestions or special discounts. This not only makes shoppers more engaged but also encourages them to become repeat customers.
Additionally, the data collected through geofencing provides insights into how customers behave and what they prefer. Retailers can use this data to understand customer movement patterns, popular store sections, and the effectiveness of different sales tactics.

Transportation
Geofencing technology is a valuable tool for transportation and logistics companies. It helps them keep tabs on the routes their vehicles take, which in turn allows these companies to make routes better, save on fuel, and make sure deliveries happen on time.
For instance, picture a group of delivery trucks moving through a busy city. Geofencing watches over each truck's route, letting the transportation company adjust these routes.
This helps the company use less fuel and get packages to customers when they should. This not only saves money but also makes the whole delivery process smoother.
![]()
Construction
Geofencing offers significant benefits to construction management. It acts as a vigilant guardian for heavy machinery and valuable assets on construction sites, providing real-time location updates to construction managers.
Additionally, if equipment or materials are moved beyond specific zones, instant notifications are triggered. These notifications prevent theft and enhance security.
For instance, imagine a large construction site with various machines and tools. Geofencing sets up an invisible boundary around the site. If any equipment is taken beyond this virtual line without permission, the geofencing system quickly alerts the construction manager. This quick response stops any unauthorized removals in their tracks.

Healthcare
In the field of healthcare, geofencing acts as a safety measure, particularly in elder care. It sets up virtual boundaries and sends alerts if a patient goes beyond certain areas. This helps caregivers provide timely assistance to patients in need and prevent any issues from getting worse.

A Beginner's Guide to Geofencing
If you want deeper insights into how geofencing can help you manage your devices and boost your workforce productivity, you’ll want to grab our Geofencing guide. It’s loaded with detailed information to help you make the best decision for your organization's needs.
Geofencing by Technology
Geofencing isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. Each geofencing technology comes with its own strengths and limitations, as outlined below:
1) Global Positioning System (GPS)
• Strengths
Think of GPS as the satellite-based map for geofencing, excelling outdoors. It's great at tracking vehicles and people over large areas.
• Drawbacks
But GPS struggles indoors or in places with tall buildings, losing its connection and draining device batteries quickly. Plus, its accuracy gets affected by the surroundings and external factors.
2) Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
• Strengths
Imagine RFID as a digital ID card for geofencing. Just like an ID card carries personal info and helps recognize you, RFID stores data to identify objects uniquely.
When it comes to tracking particular items in smaller spaces like warehouses, RFID excels. It's highly effective at setting up geofences at close range and doesn't require a clear line of sight to function.
• Drawbacks
RFID's effectiveness depends on how near the reader is, which means it's not ideal for monitoring mobile objects like cars. Moreover, establishing RFID systems can incur high costs, making it less suitable for larger-scale tracking requirements.
3) Wi-Fi
• Strengths
Wi-Fi is another geofencing technology, performing well indoors and outdoors with respectable accuracy. With many devices having Wi-Fi capabilities, like smartphones, laptops, and smart TVs, its applications are widespread.
• Drawbacks
Wi-Fi requires active connections, which can lead to higher battery usage. While accurate, it's slightly less so than GPS in open spaces.
4) Bluetooth
• Strengths
Bluetooth geofencing focuses on detecting proximity rather than pinpoint location like GPS. It works well for scenarios where approximate location is enough, like notifying a user when they're near a store.
• Drawbacks
Bluetooth has a shorter range compared to other technologies. Issues like interference and signal strength variations can impact its accuracy.
| Technology | Strengths | Drawbacks | Suitable Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | Excellent for outdoor tracking; suitable for vehicles and people over large areas. | Struggles indoors, drains device batteries quickly, accuracy affected by surroundings. | Transportation and logistics (fleet management), construction (asset management), healthcare (patient monitoring) |
| RFID | Functions like a digital ID card; tracks specific items in small spaces; doesn't require line of sight. | Limited range, unsuitable for moving objects, expensive setup. | Warehousing (inventory management) |
| Wi-Fi | Effective both indoors and outdoors; wide device compatibility (smartphones, laptops, etc.). | Higher battery usage, slightly less accuracy outdoors compared to GPS. | Retail, hospitality, healthcare (indoor navigation) |
| Bluetooth | Great for proximity detection (store notifications); sufficient for approximate location awareness. | Limited range, susceptible to interference. | Retail (location-based marketing, event management) |
Geofencing by Triggers
Geofencing through triggers involves setting up specific actions or events that activate when a device enters or exits a designated geographic area. These actions are essentially prompted by the device's location in relation to the defined boundaries.
Geofencing operates based on several key triggers, namely: Entry, Exit, Proximity, and Time-Based. Let's delve into the specifics of each trigger.
Entry trigger
Think of a geofencing entry trigger as a virtual alert that gets activated when something or someone enters a certain area that's been marked out on a digital map.
It's like a digital alarm that goes off when, for example, a person walks into a store or a vehicle arrives at a specific location.
This trigger sets off a series of actions or messages to let the right people know that something has happened, like an employee arriving at a job site. It's a way to keep track of things and make things happen automatically based on where they are.
Exit trigger
In the world of geofencing, an exit trigger represents a practical feature that comes into play when a device or a person moves out of a designated geographic area.
For example, in the logistics industry, geofencing exit triggers can be crucial for tracking and managing the movement of vehicles, especially in cases where routes are predefined for efficient delivery.
As a delivery truck exits the designated route's geofenced area, the geofencing system detects this departure. An automated alert is sent to the fleet management team or driver supervisor, notifying them of the route deviation.
The fleet management team can assess the situation, communicate with the driver, and redirect them back to the correct route. This minimizes delivery delays and ensures adherence to planned schedules.
Proximity Trigger
Proximity triggers activate as someone approaches a specific point. Picture it as a virtual tap on the shoulder, signaling, "Hey, something interesting is nearby!"
Customized alerts can be tailored to highlight nearby attractions, provide directions to visitors, or offer exclusive deals.
Time-based Trigger
Time-based triggers in geofencing revolve around activating notifications according to specific time intervals or schedules. These triggers are independent of a user's or device's location, focusing purely on timing.
Imagine this scenario: An HR department integrates geofencing technology to automate time tracking for employees. As employees enter or exit the office premises, a geofence triggers the system to log their entry or exit time.
Wrapping up
We've covered the most common types of geofencing in our article. Nowadays, businesses heavily rely on mobile devices to improve their operations. Keeping a close eye on things like logistics and staff locations is crucial, especially when dealing with larger operations.
To meet these needs, companies are turning to innovative solutions. One such solution is AirDroid Business's Geofencing, which is built on top of Mobile Device Management (MDM).
Here are some benefits of using AirDroid Business's Geofencing with MDM:
- ● Track Device Movement
- ● Centralized Asset Tracking
- ● Device Security and Tracking
- ● Better Route Planning
By combining Geofencing with MDM, companies can make the most of these features to manage their devices effectively. This combination helps with following rules, improving how things work, and protecting important assets.





Leave a Reply.