How to View Android Logs (2 Methods Listed)
IT teams have many tools available to manage Android devices. They need to troubleshoot issues, optimize performance, and maintain the highest possible security measures. Android logs provide valuable information.
Mastering Android logs will elevate your Android device management. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the purpose of Android logs, why they’re helpful, the information that can be discovered, and the two best methods to view and interpret them.
Quick Summary: How to view log files on android phone?
Android log files record system and app events, crucial for diagnosing app crashes, performance issues, and other problems. Here are common ways to view them:
- 1. Using Android Studio: Connect your device (with USB debugging enabled) and use the Logcat window for real-time log viewing.
- 2. Using ADB Commands: With ADB installed and your device connected (USB debugging on), run the adb logcat command in a terminal.
- 3. Using Third-Party Apps:like CatLog and MDM tools like AirDroid Business for fleets of device management.
- 4. Via Built-in Developer Options: Go to Settings > Developer options on your device and use "Take bug report" to generate a comprehensive log file.
1What are Android Logs?
Android logs serve as comprehensive records maintained by your Android device's operating system. They are continuously updated with critical information about events, issues, and debugged data.

Purpose
Like keeping a diary, Android logs provide essential insights into your smartphone's functioning and the behavior of installed apps. These logs play a pivotal role in fixing bugs, enhancing performance, and ensuring the seamless operation of your device.
How Long Android Logs Can Be Saved For?
Android logs are stored in a circular buffer with no fixed time period. Instead, they get overwritten as new ones are generated and if the buffer is full. Logs can also be cleared every time the device is rebooted.
If the logs need to be saved indefinitely, they’re best copied/pasted into text files.
2What Valuable Information Can Be Extracted from Android Logs?
- Stack Traces: Stack traces helps pinpoint the exact location and cause of application crashes or exceptions.
- App Flow: Logs allow developers to track the flow of their application and identify potential logical errors or unexpected behaviors.
- Network Activity: Logs can show network-related information, helping diagnose connectivity issues or data transmission problems.
- System Events: System logs provide insights into various device events, such as battery status, screen rotation, and hardware changes.
3Why Is It Essential to Examine Android Logs?
Let’s take a look at a real-life example to explain why this matters: A retail chain relies on Android tablets for point-of-sale systems. Employees report frequent freezing during transactions, leading to customer dissatisfaction. By accessing Android logs, the IT team discovers that a recent app update is causing compatibility issues. They promptly roll back the update, restoring functionality and minimizing downtime.
These are the reasons why analyzing Android logs is essential:
- Debugging and Troubleshooting: Developers can use information gathered from logs to troubleshoot problems like crashes, errors, and unusual behavior in their software.
- Performance Optimization: Developers can improve their programmes' efficiency by analyzing logs for signs of performance obstacles, leaks of memory, or excessive resource utilization.
- Security and Privacy: Logs can reveal potential security vulnerabilities and instances of logging sensitive user data, ensuring proper handling and redaction of such information.
4How to View Android Logs? ( 2 Methods Are Listed)
As developers and tech enthusiasts work with Android app development, they encounter many tools designed to simplify the process and enhance productivity.
Two methods stand out as indispensable assets:
- A program such as Android Debug Bridge (ADB)’s LogCat tool
- Third-party solutions include mobile device management (MDM) and enterprise mobility management (EMM) platforms.
Method 1 : Android Debug Bridge (ADB)
Designed for developers and advanced users, Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a potent command-line tool within the Android SDK. It allows seamless interaction with Android devices and emulators from a computer, offering real-time logging with LogCat, app installation, file system access, and device interaction through the command line. ADB proves indispensable during app development, debugging, and testing processes. It also empowers advanced users to undertake tasks like rooting devices and installing custom ROMs.
How to use Android Debug Bridge (ADB) to view android logs
- Step 1. Install ADB on Your Computer
- Ensure you have Android SDK Platform Tools installed on your computer. If not, download the platform tools from the Android developer website: (https://developer.android.com/studio/releases/platform-tools) and install them.
- Step 2. Enable Developer Options
- a) On your Android device, go to "Settings".
- b) Scroll down and select "About phone" or "About device".
- c) Locate the "Build number" entry and tap it multiple times (usually seven) until you see a message indicating that Developer Options have been enabled.
- Step 3. Enable USB Debugging
- a) In the "Settings" menu, go to "System" or "System & updates" (depending on your device).
- b) Select "Developer options." Toggle on "USB debugging".
- Step 4. Connect Your Android Device to the Computer
- a) Use a USB cable to connect your Android device to the computer.
- b) On your Android device, when prompted, allow USB debugging access from the computer.
- Step 5. Open a Command Prompt or Terminal
- On your computer, open a Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS/Linux).
- Step 6.Navigate to the ADB Directory
- Change the directory in the Command Prompt or Terminal to where the ADB executable is located. If you installed Android SDK Platform Tools in the default location, you can type the following command: C:\path\to\platform-tools\.
- Replace "C:\path\to\platform-tools" with the actual path to the platform-tools directory.
- Step 7. Verify Device Connection
- a) To ensure your device is connected and recognized by ADB, type the following command on CMD prompt and press Enter: adb devices.
A list of connected devices will be displayed. If your device is listed, you are good to proceed. - b) If the device is not visible, it's probable that you lack the necessary device drivers. To find and download the required adb drivers for device X on your PC, use a web browser and search (e.g., via Google, Yahoo). Install the drivers with administrative privileges.
- c) Verify if adb devices lists the device in question. If the device appears as unauthorized, disconnect it, then reconnect it and accept the prompt to trust the PC.
- Step 8. View Android Logs using LogCat
- a) To view Android logs, use the LogCat command. Type the following command and press Enter:adb logcat.
This will start displaying the real-time logs from your Android device in form of a text file. - b) Navigate to c:/adb in your file explorer, where the "txt" file holds the collected logs.
- Step 9. Filter Logs (Optional)
- To filter logs by priority level (e.g., verbose, debug, info, warn, error, and assert), you can use the following command: adb logcat
: .
Replacewith the desired log level (e.g., "verbose" or "error") and with the tag of the component or app you want to filter.
- Step 10. Stop LogCat (Optional)
- To stop displaying the logs in the Command Prompt or Terminal, press "Ctrl + C" on Windows or "Cmd + C" on macOS/Linux.

Method 2 : Third-party Solutions
Third-party solutions, like mobile device management (MDM) and enterprise mobility management (EMM), refer to software or services external vendors provide that help organizations, businesses, and IT administrators remotely manage, monitor, and secure mobile devices within their network.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a third-party software solution designed to manage, secure, and monitor mobile devices, including Android smartphones and tablets, within an organization. When it comes to enforcing security standards, distributing apps, tracking device health, and ensuring compliance with business requirements, MDM provides IT managers with centralized management over the navy of devices.
By leveraging third-party solutions, organizations can streamline workflows, enforce compliance, and protect sensitive data.
How to Employ Third-Party Software (MDM for example)
- Step 1. Select an MDM Solution
- Find a reliable MDM software vendor, such as AirDroid Business, that can cater to your business' specific requirements. Think about things like functionality, scalability, security, and Android device compatibility.
- Step 2. Sign Up and Set Up the MDM Account
- Create an account on the preferred MDM platform. Set up your company's profile in accordance with the provider's guidelines.
- Step 3. Enroll Android Devices
- Enrolling Android devices in AirDroid Business is effortless. There are several options, including QR code, deployment code, Android Enterprise, zero-touch, and connecting via a USB cable.
- Step 4. View Android Logs
- After enrollment, viewing the Android logs is seamless. Simply remote into the required device and access the logs from internal storage.
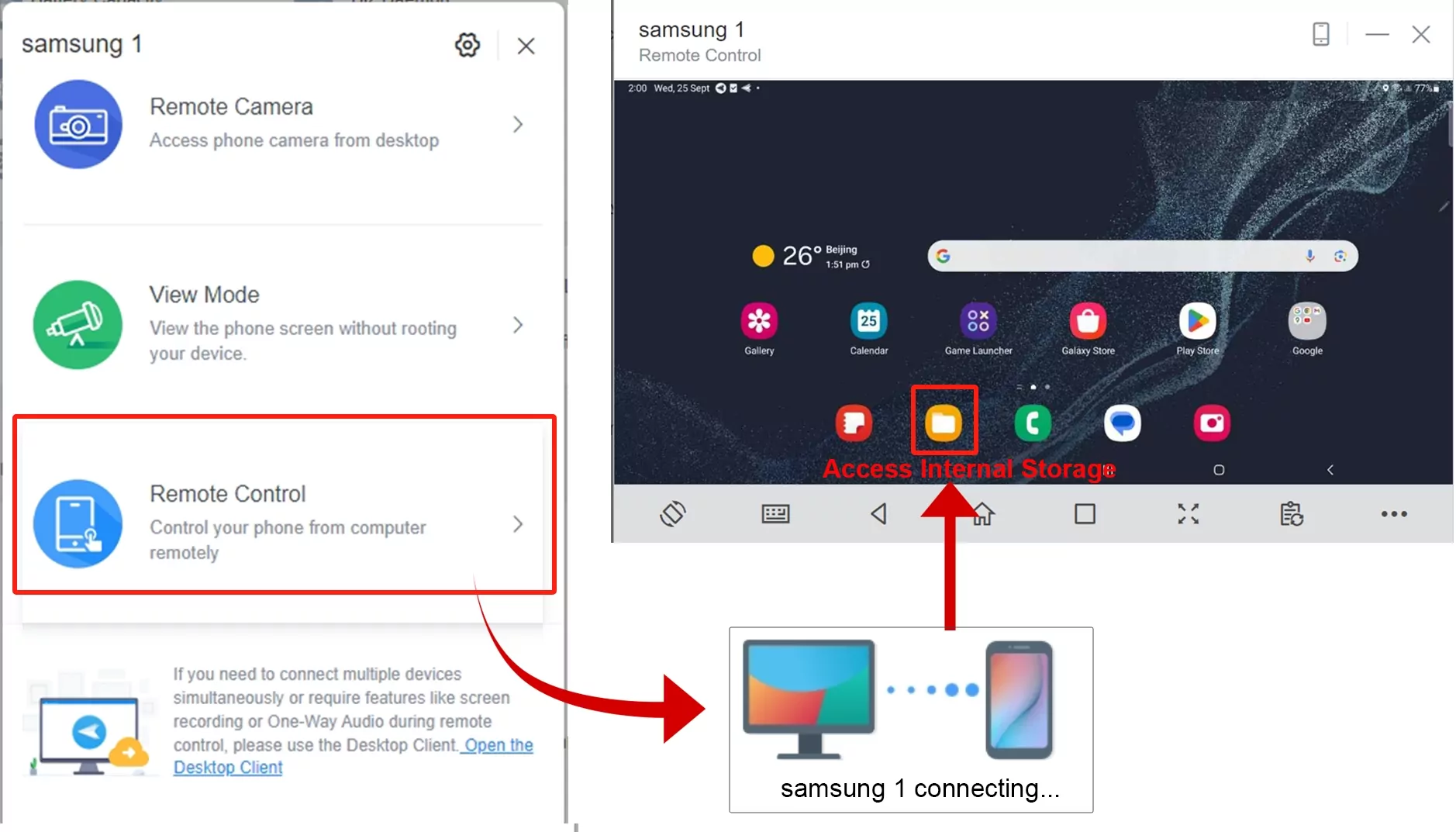
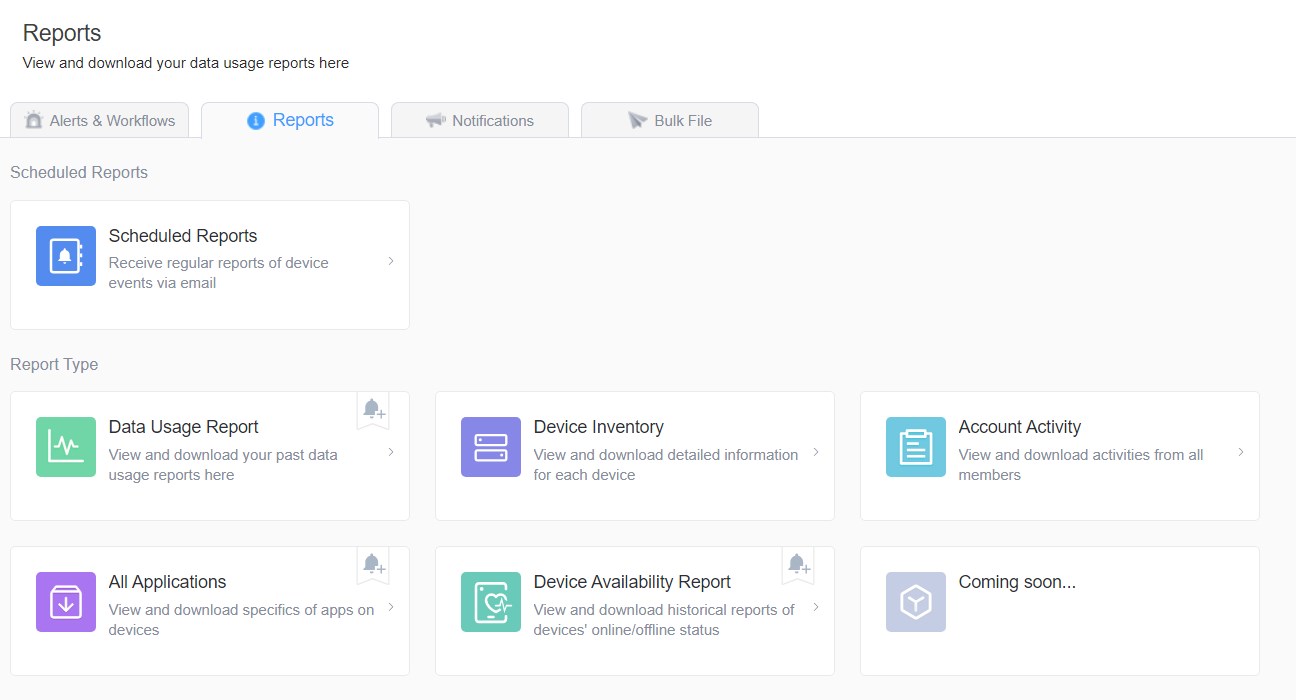
- Step 5. Take Advantage of AirDroid for Business’s Other Features
- AirDroid for Business does more than allow you to view Android logs. It also helps you check how your Android phones perform, including data, battery and RAM usage, and device info like Wi-Fi address, location, and network. IT teams can conduct remote device monitoring to troubleshoot issues, send out notifications, and update or remove apps.
Conclusion
The ability to view Android logs can assist IT teams in fixing a range of device issues. The two most popular ways are with an ADB or an MDM solution. ADB works fine for those familiar with utilizing the control panel. AirDroid for Business is an MDM solution that simplifies how Android logs can be viewed and offers powerful device management tools.
FAQs About Viewing Android Logs
2. Application Logs: Records application usage through application logs to track both errors and app debugging reports.
3. Radio Logs: Provides network-related log monitoring for cellular, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth events.
4. Kernel Logs: Offers hardware status together with device drivers and low-level system information.
1. Logcat (ADB Command): Logs are kept for a short time and can be obtained by using: adb logcat
2. System Log Files Location(for Rooted Devices): "/var/log" or "/data/log"
3. App-Specific Logs: Some applications log information and store it in the application data directory (e.g. /data/data/
1. To log the messages, use the following command: adb logcat *:E
2. Pay attention to the crash-related keywords: Fatal > Crash > AndroidRuntime > Exception > Error
3. Use the adb bugreport command to create a comprehensive report: adb bugreport bugreport.zip
4. Open the bug report and look for FATAL EXCEPTION to identify the source of the problem.







Leave a Reply.