What is Zero-touch Provisioning, Different Deployment Methods Explained
With the process of modern device configuration becoming more and more complex, enterprises, organizations and it professionals must realize the automation of equipment configuration and minimize manual intervention, thus improving efficiency and reducing the risk of human error. Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) is the solution to this challenge.
In this article, we’re discussing what ZTP is, ZTP deployment methods, benefits, use cases, and more.
- 1 : What is Zero-touch Provisioning?
- 2 : Zero-Touch Provisioning Deployment Methods
- 3 : How Does Zero-touch Provisioning Work?
- 4 : What ZTP Means for Enterprises?
- 5 : Use Cases of ZTP
- 6 : Challenges & Solutions
- 7 : ZTP vs OTP vs PnP
1 What is Zero-touch Provisioning?
Zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) is a solution that automates the setup and configuration of devices, such as routers, switches, and other network equipment, without the need for manual intervention.
Zero-touch
To better understand the meaning, it's necessary to understand what "touch" specifically refers to. In the context of ZTP, "touch" means manual intervention or interaction. This could be the operations like configuration, setup, installation, and any other physical actions on the device or system. When "zero" is added to it, that is to say, the process requires no human interaction and is replaced with automated processes brought by pre-programmed instructions.
Provisioning
Provisioning encompasses the configuration and management of various devices, such as:
- End-user devices: like smartphones, laptops, and tablets. In this case, provisioning typically involves deploying applications, user polices, security settings, and network access configurations. In some cases, configurations can be tailored to specific user roles.
- Network infrastructures: like routers, servers, and switches. These devices can have firmware updates, network policies, and routing configurations that, with ZTP, are applied automatically.
- IoT devices: such as sensors, and smart home devices. With ZTP, IT admins and teams can make sure they connect securely and function correctly within the network.
- Telecommunication devices: like base stations or CPE, that can benefit from ZTP by automating the setup of connectivity, firmware updates, and network configurations.
Features of Zero Touch Provisioning
The main features of zero touch provisioning include:
- Automation: With pre-set configuration files and the Internet, devices are able to deploy efficiently.
- Mass deployment: ZTP allows you to set up company devices on a mass scale. Using a CSV file that includes device model and serial number is available.
- Network required: Zero-touch provisioning requires an established connection between the DHCP or TFTP server and the device.

Popular ZTP Tools for Different Device Types
Several platforms offer zero-touch provisioning capabilities, including:
- AirDroid Business: A company that develops software to enhance efficiency and productivity for businesses of all sizes. The ZTP offered by AirDroid streamlines device enrollment and configuration, reducing setup time and saving costs.
- Cisco: A leading technology firm that creates, manufactures, and sells networking hardware and software. Cisco’s ZTP is suitable for various devices, including routers, switches, and security appliances.
- Artista Newtorks: Specialized in software-driven cloud networking solutions for IT environments and large-scale data storage, it allows users to apply ZTP mainly to routers and switches.
- Juniper Networks: Known for developing and selling networking products, Juniper's ZTP is compatible with routers, switches, and security solutions, facilitating seamless configuration and management.
- Cumulus Networks: It provides a Linux OS for network switches and managements software, making its ZTP suitable for Linux-based networking devices and data center switches.
The benefits of effective ZTP include improved operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced security. It also reduces time spent on manual configurations which translates to reduced costs for IT departments and organizations.
2 Zero-Touch Provisioning Deployment Methods
Zero-Touch Provisioning(ZTP) offers a variety of deployment methods, each designed to streamline the configuration process for different types of devices and network environments.
DHCP-Based Provisioning
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provisioning automates the assignment of IP addresses and network configurations to devices when they connect to a network.
When setting up a new device, instead of manually entering details like its network address, the device sends a DHCP request. The DHCP server sends back the necessary configuration details, such as the device’s IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and the location of its provisioning server..
With this process, the devices are automatically configured to communicate with each other, making it so much easier for IT admins to manage their networks.
TFTP/HTTP/HTTPS Boot
When a new device is connected to a network, it can automatically download an operating system and firmware using different types of protocols: TFT, HTTP, or HTTPS. These protocols are meant to transfer data from a host (server) to a client and can be used to automatically transfer configuration files to the new device.
Scripting/Automation Tools
Administrators can create scripts in languages like Python or Bash to configure network settings, install applications, and enforce policies across multiple devices simultaneously. This method allows the automation of device provisioning and it’s ideal for large-scale deployments.
Cloud-based Provisioning
Cloud-based provisioning uses cloud services to manage the configuration and deployment of devices remotely. Devices connect to the cloud platform upon booting, and from the cloud they can retrieve their configurations and software updates.
USB-based Provisioning
With this method, the USB drive, containing the necessary configuration files, is where the new device can retrieve the necessary configuration files. The IT admin only needs to prepare the USB drive once (uploading all the necessary configuration files in it). After that, the process is entirely automated.
Email-based Method
The email-based provisioning method allows devices to receive configuration information via email. The device checks a predefined email account for setup instructions or configuration files.
3 How Does Zero-touch Provisioning Work?
Here's a diagram to show how the automated process works.
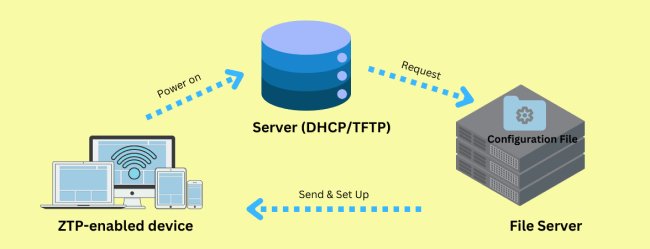
To comprehend the zero touch provisioning process, you will also need to understand several technical terms.
Library for Technical Terms
- Network Device: devices that allow to send, receive, or transmit data using networks, and with.
- Server: cloud-based or on-premise data center for managing access during networking.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP): network protocol used by devices to request and obtain an IP address and other parameters from a server.
- Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP): file transfer protocol commonly used for automated transfer of configuration or boot files between devices in a local network.
- Configuration File: file with specific settings and parameters for device configuration
- Boot File: file loaded by a device during its startup (or boot) process, which contains instructions that tell the device what to do and how to operate.
- Central Location: in the context of ZTP, this refers to a server or cloud storage service where configuration files are stored and can be accessed by devices.
Requirements
While the requirements for implementing ZTP can vary depending on the different deployment methods and devices involved, there are some elements that must be always present:
- The devices must support ZTP functionalities.
- The devices must be equipped with a network connectivity (otherwise they couldn’t communicate with the provisioning server).
Additional requirements, depending on the deployment method, could include:
- DHCP servers.
- File transfer protocols like TFTP, HTTP, HTTPS.
- Automation tools for scripting custom configurations.
Zero-Touch Provisioning Process
The processes for different deployment methods differ. Here, we will demonstrate the process of the most common method: DHCP-based ZTP.
Process of DHCP-based ZTP (Detailed)
1. A network device that is enabled for Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) arrives at the site and starts up with basic settings.
2. IT teams can make templates for setting up devices. These templates can include network settings, security details, necessary applications, and user choices. This is helpful when setting up many devices at once.
3. The device enters ZTP mode and automatically locates a DHCP server.
4. It automatically reaches out to the server and connects using the IP address, gateway, and DNS server IP address.
5. The device requests a DHCP address.
6. The DHCP server authenticates the device and gives the address for telling it where to find the file server.
7. The device searches for configuration files, running scripts, and software updates in the file server.
8. As the file server provides the configuration profile, the device will install preset configurations.
9. If the device can't find file server information, or if the configuration file has errors, it starts the ZTP process again.
10. The device applies the new settings and ends the ZTP process.
What Comes After the Process of Zero Touch Provisioning?
Once the zero-touch provisioning process is complete, the device is ready to use without any additional configuration or setting up. The company can ship the device to its employee so that he can use it in the workplace. And IT administrators from the organization will carry out follow-ups, such as:
- App updates
- Perform remote troubleshooting
- Device monitoring
- Device management
4 What ZTP Means for Enterprises?
It simplifies IT processes by automating device configuration and reducing manual setup. Other than enhancing productivity, this allows IT team members to have more time and energy to focus on other important tasks, optimizing the entire work process.
By enabling devices to configure themselves automatically, it reduces deployment times.
As all devices receive the same configurations, updates, and security policies, it ensures device compliance and consistency, also minimizing discrepancies in network management.
As automation eliminates manual interventions it also eliminates human mistakes. This ensures more reliable and secure deployments while reducing downtimes and misfunctions.
5 Use Cases of ZTP
Zero-Touch Provisioning has become a critical solution for efficient device management across multiple sectors:
MDM
ZTP plays a key role in managing organizations’ fleet of devices. Through ZTP, the configuration of smartphones, tablets, and laptops is automated, and this becomes particularly important in those businesses that deploys hundreds of mobile devices.
-Example: Apple’s Device Enrollment Program that uses ZTP to automatically configure devices and ensure compliance with the company’s security and quality standards.
IoT device management
In home automation, industrial IoT, smart cities and other environments, ZTP automates the provisioning process for IoT devices, such as sensors and smart home gadgets, allowing them to automatically connect to the network and receive configuration settings without human intervention.
-Example: The manufacturing sector, where ZTP is deployed to ensure that device, sensors, and machinery are properly configured and connected.
Network
ZTP is also deployed to efficiently configure and manage networks. In this scenario, ZTP provides a solution to automate the setup and deployment process across the network infrastructures such as routers, switches, and firewalls.
-Example: Cisco, a leading provider of networking hardware, uses ZTP to automate the provisioning of switches and routers, ensuring that they are correctly configured to meet the organization’s standards. This minimizes downtime during network expansion or upgrades and guarantees consistent network policies and security settings across all devices.
6 Challenges & Solutions
Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) offers many benefits, but it also comes with challenges that businesses need to address for successful deployments. The following are two key issues that IT admins must face when deploying ZTP with the recommended solutions to overcome these challenges.
Configuration Errors
One of the most common mistakes that ZTP programmers can encounter is setting up incorrect or incomplete configuration files and uploading them to the provisioning server.
This simple mistake can have huge consequences, because, when devices download faulty configuration files, they do not function properly, and this can consequently lead to security vulnerabilities or operational misfunctions.
These errors can result from syntax mistakes but also from outdated files or improper customization for different devices or user roles.
They can be addressed by implementing automated testing for the configuration scripts to make sure that, once uploaded into the provisioning server, they are error-free and suitable for the necessary devices.
Network Issues
As devices rely on network connectivity to communicate with the servers, network issues can also pose challenges to ZTP.
Problems like unstable connection can delay the provisioning process and cause downtime or affect the overall network performance.
To address this challenge, IT professionals should always rely on robust network infrastructures. In this regard, it’s important to pre-test the network to identify and resolve potential issues before initiating the ZTP deployment.
Furthermore, redundant servers and backups can be implemented to provide emergency options in case of network failure.
7 ZTP vs OTP vs PnP
When discussing ZTP, it’s extremely easy to end up talking about OTP and PnP as well. Sometimes, the three concepts are even mistaken between one another, because – even though they are three well distinct things – they have similarities. It is therefore extremely important to discuss ZTP, OTP, PnP, highlighting what they are and what are the main differences between them.
Below is a table summarising the differences between ZTP, OTP, and PnP.
ZTP | OTP | PnP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup | No human intervention; automatically configures when connected to the network. | Need a single manual action to start automatic configuration. | Automatically detects and configures by the operating system. |
| Devices | Network devices like switches, routers, and servers. | Similar with ZTP. | Multiple device types including USB drives, printers, etc. |
| Configuration | Download configuration files from a pre-determined server. | Download configuration files after an action. | Using OS built-in drivers to download |
| Protocols | DHCP and TFTP. | Specific protocols based on the system. | Various protocols depend on the device and OS. |
| Automation Level | Full automation after device connection. | Requires one manual action, then fully automatic. | Automatic detection and configuration by the operating system. |
| Use Case | Large-scale deployments in data centers and enterprise networks. | Scenarios where a single manual initiation is acceptable | For consumer hardware and peripherals, or any scenario where devices need to be used immediately upon connection. |

8 Closing Line
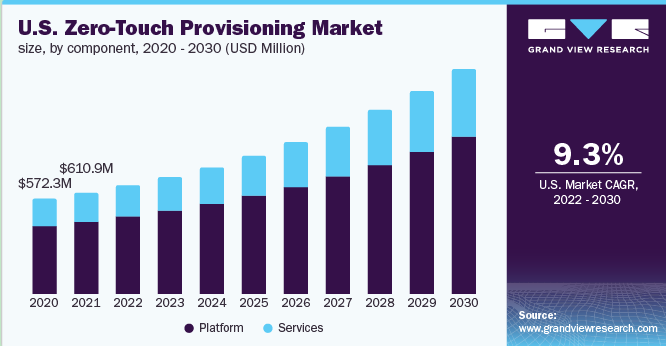
As businesses continue to adopt ZTP, the global ZTP market is expected to see substantial growth, with projections estimating a 9.3% annual increase from 2022 to 2030. This trend highlights the growing recognition of ZTP's value in automating deployment processes, ensuring consistent device configurations, and reducing costs.
Zero-touch Provisioning in MDM
Zero-touch provisioning is particularly useful for companies that deploy a large number of mobile devices to their employees, including smartphones, tablet computers, and laptops. It can be used with MDM solutions and here is how they work together:
A company purchases mobile devices that support zero-touch provisioning from a reseller (Android enterprise is recommended). These devices are then registered with the company's zero-touch provisioning enrolment account.
IT administrators then create a configuration file on a zero-touch provisioning console, using the ZTP configuration parameters from MDM solution.
The network devices are shipped to the company’s employees with the MDM- related tools already installed. IT administrators can then manage the devices remotely using zero-touch provisioning and the MDM solution.
FAQs





Leave a Reply.