6 Ways Someone Can Sign into Your Gmail without Your Password
You're going about your day, checking emails like usual, when suddenly you notice something strange. Maybe you receive a notification about a login from a device you don't recognize, or even worse, emails in your "Sent" folder that you never wrote.
It's that gut-wrenching feeling of realizing someone could be snooping around your Gmail account without your knowledge—and without even needing your password. Scary, right? In this post, we're diving into six ways that can happen and, more importantly, how you can protect yourself.
How Someone Else May Log into Your Gmail without Password
1Via a Device with Your Google Account Logged In
Direct Access: If you've previously logged into your Gmail account on a device and haven't signed out, someone with physical access to that device can easily open Gmail without needing to enter your password again.
Retrieving Saved Passwords: Devices that store login credentials can be exploited to retrieve your Gmail password:
- On Mac: Apple devices store passwords in Keychain, which can be accessed if someone has access to your device. The Keychain stores all saved passwords and may reveal your Gmail credentials.
- On PC: Similarly, on a Windows PC, Gmail credentials can be saved and accessed through the Credential Manager, allowing someone to view your stored password if they can log into your computer.
2Using Monitoring or Keylogger Apps
These are malicious programs that can be secretly installed on your computer or mobile device. Keyloggers record every keystroke you make, including your Gmail password, when you log in.
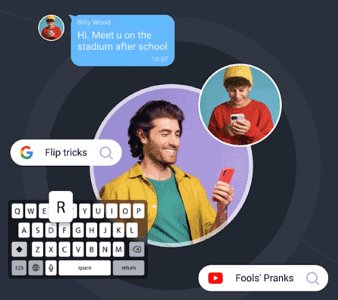
Some monitoring or spyware apps can track your activity and give an attacker full visibility into your online behavior, including email access. These apps can record passwords, capture screenshots, and even allow remote control of the device.
3Verifying with Alternate Methods
Alternate verification: If an attacker has access to your alternate email address, phone number, or other secondary recovery options tied to your Gmail account, they can use these to reset your password and gain access.
Security questions: If your security questions are weak, easily guessed, or found online (through social media or public records), they can be used to verify your identity and reset your password.
Authentication Apps: Attackers can potentially access Gmail if they can take control of the apps you use for two-factor authentication (such as Google Authenticator or Authy) or intercept SMS verification codes if your phone number is compromised.
4Surmising Your Passwords
Guessing Common Passwords: Many people use weak passwords or easily guessed ones, such as "password123" or their birth date. Attackers may try common combinations based on your publicly available information (e.g., social media posts).
Reused Passwords: If you've used the same password across multiple platforms and one of those services is compromised, hackers may try the same credentials on your Gmail account.
5Social Engineering Attacks
Impersonation: Attackers may impersonate someone you trust (like a colleague or family member) through email or social media to trick you into sharing your passwords or clicking on malicious links.
Pretexting: In this technique, an attacker pretends to be a trusted individual or institution, like Google support, to ask for your login credentials or security details.
Baiting: An attacker may lure you with free downloads or offers, tricking you into clicking malicious links that either steal your login information or install malware to capture it later.
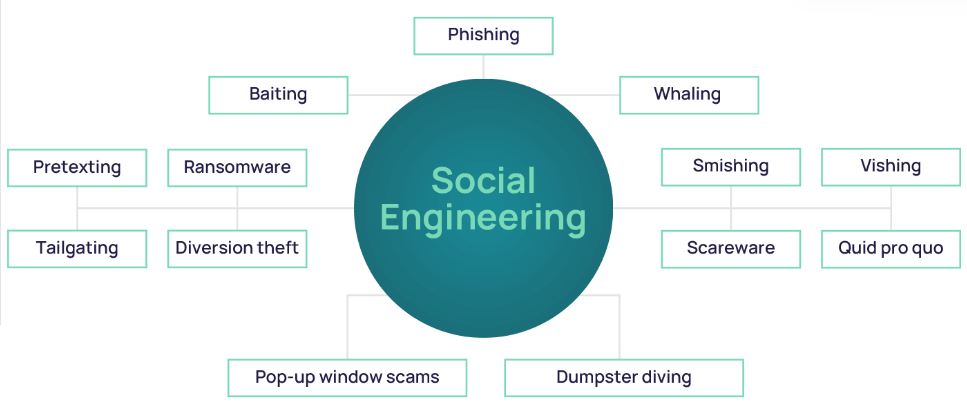
6Malware, Viruses, and Phishing Attacks
Malware: Viruses or other forms of malware can infect your device and either steal your Gmail credentials or allow an attacker to gain access to your email. For example, some types of malware include built-in keylogging or screen-capture functionalities.
Phishing: This involves sending you emails that mimic legitimate services and trick you into revealing your Gmail password by redirecting you to a fake login page. Once you enter your details, the attacker gains access to your account.

Browser Exploits: Certain malware can exploit vulnerabilities in your browser, hijacking your Gmail session or extracting your saved login credentials.
How to Tell If Someone Is Logging into or Accessed Your Gmail
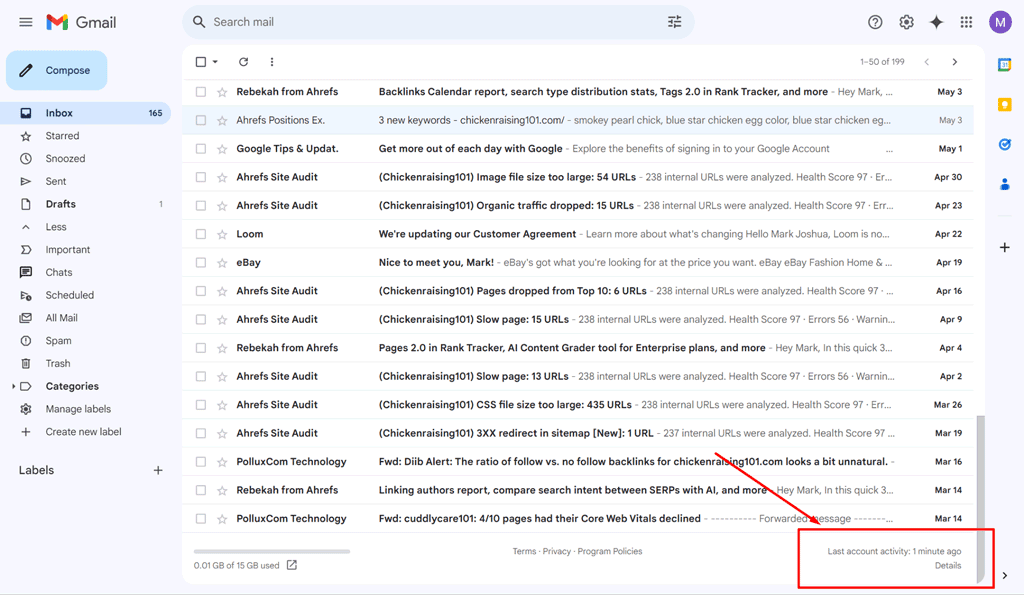
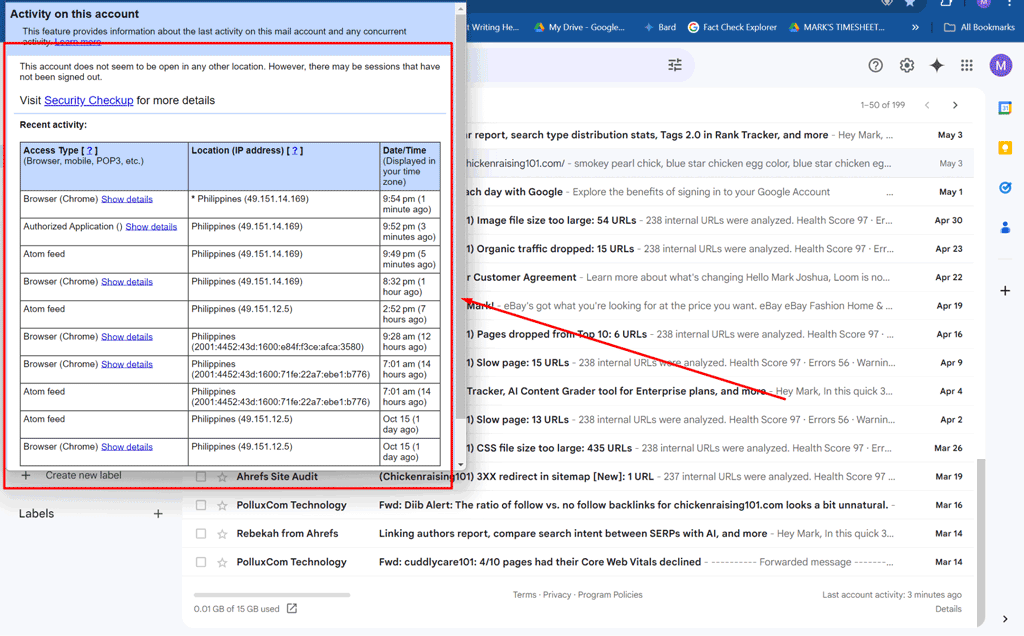
Check Recent Gmail Access Activity
Google provides a way to review recent access to your Gmail account, allowing you to detect suspicious logins. Here are the steps:
- Open Gmail and log in to your account.
- At the bottom right corner of your Gmail interface, you will see text that says, "Last account activity," along with the time of the last access.

- Next to the "Last account activity" information, click on "Details." It will open a new window with more detailed information about recent activity.
- A pop-up window will appear that shows a list of recent activity, including:
- Access Type: Shows whether the access was through a browser, mobile device, or POP3/IMAP (email client).
- Location: Shows the IP address and the associated location of the login attempt.
- Time: Displays the time and date of each login.

Review the information carefully to check if there are any login attempts from unfamiliar devices, locations, or times.
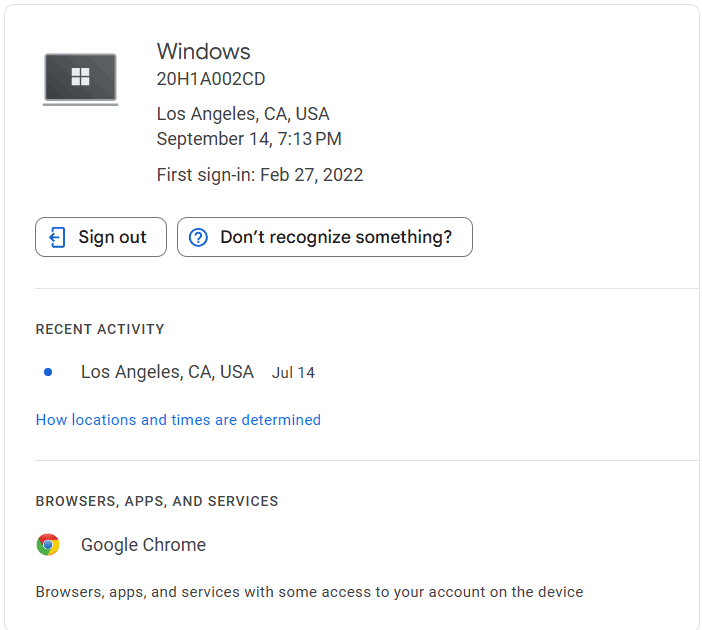
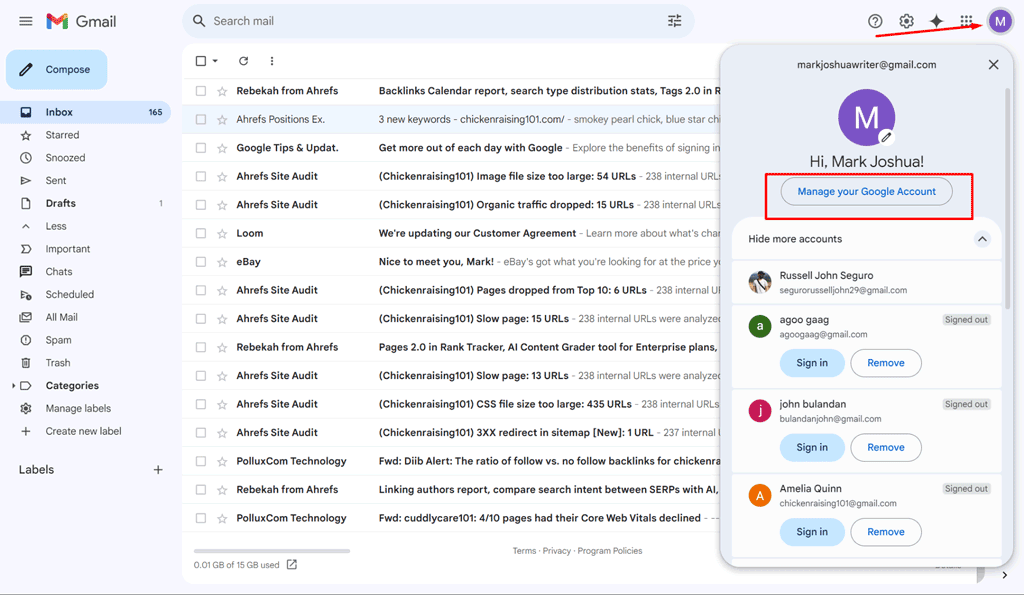
- If you notice any suspicious activity, you can click your profile photo > "Manage your Google Account," > "Security," > "Manage all devices" Under "Your devices." Then, Choose the device and click "Sign out."

Check Recent Google Account Access Activity
You can also check the recent activity across your entire Google Account (not just Gmail). Here's how:
- Visit your Google Account Security Settings at myaccount.google.com and sign in if prompted. Tap your profile photo and then "Manage your Google Account."

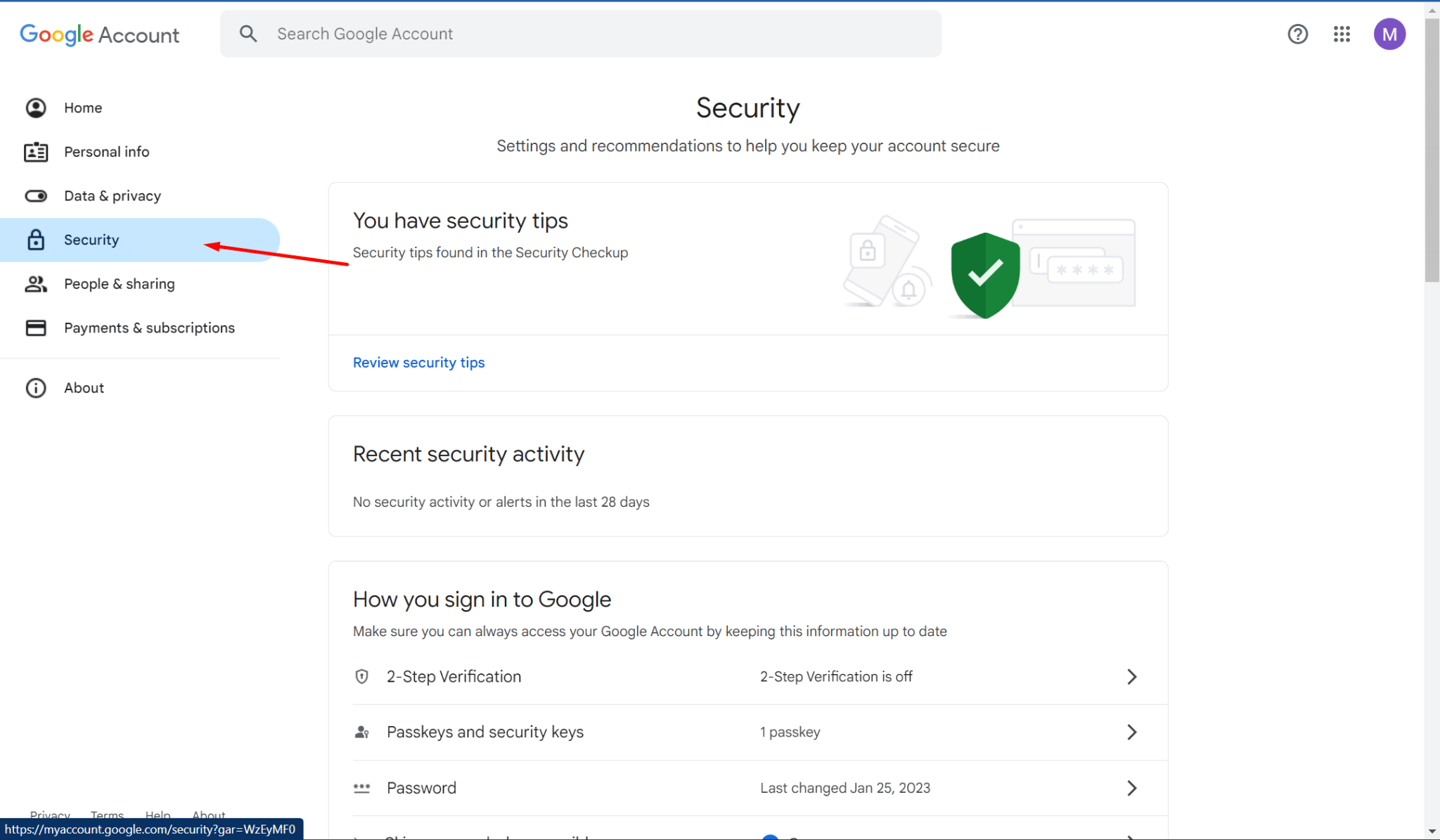
- In the left-hand menu, click on "Security" to access the security settings for your Google Account.

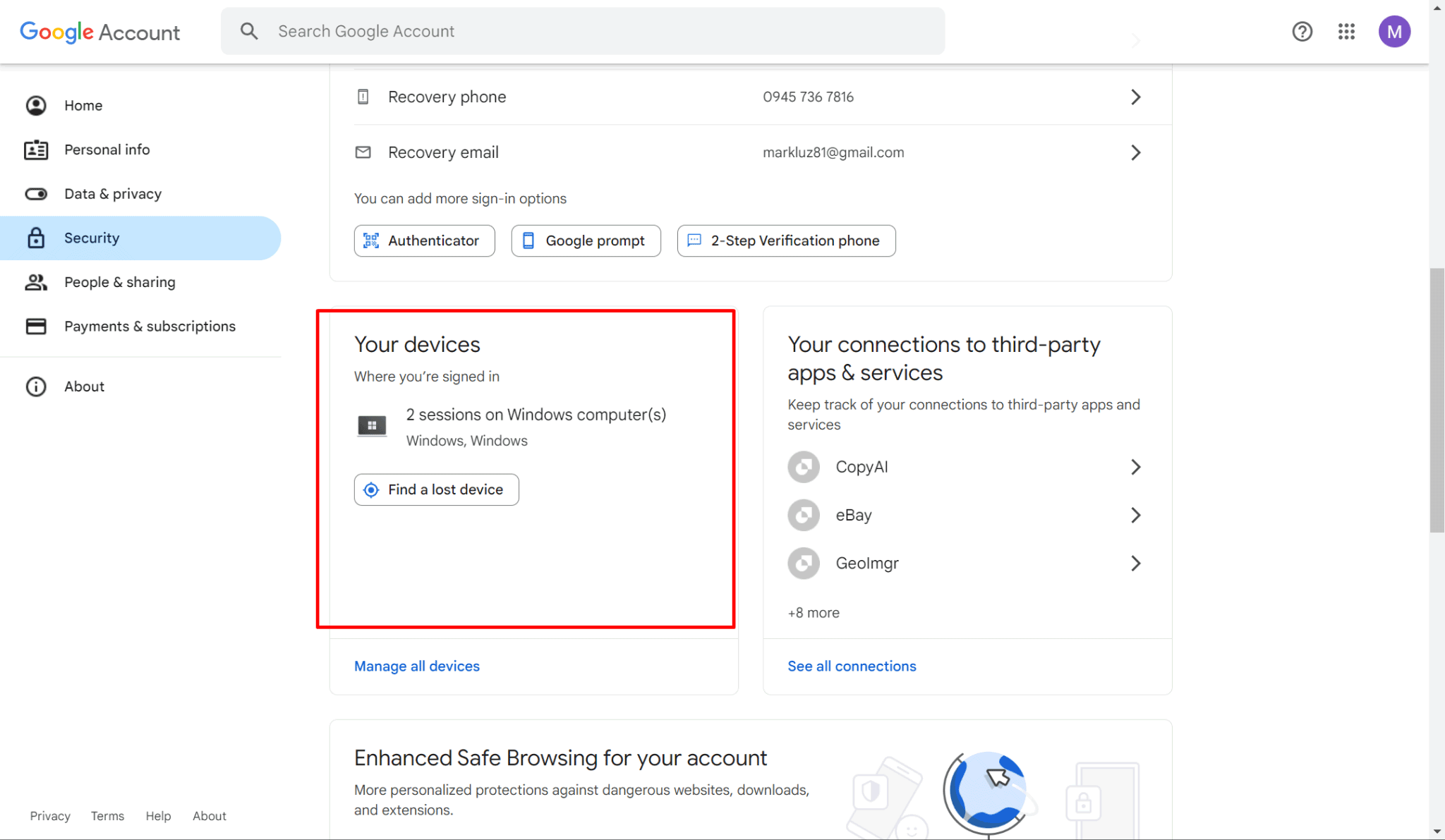
- Under the "Security" section, scroll down to find "Your devices." It will show you a list of all devices currently signed into your Google account.

- Click on "Manage devices" under "Your devices" to see a detailed list of all devices that have accessed your Google account, along with the last activity time and location of each device. If you see any unfamiliar devices, it could be a sign that someone else has accessed your account.
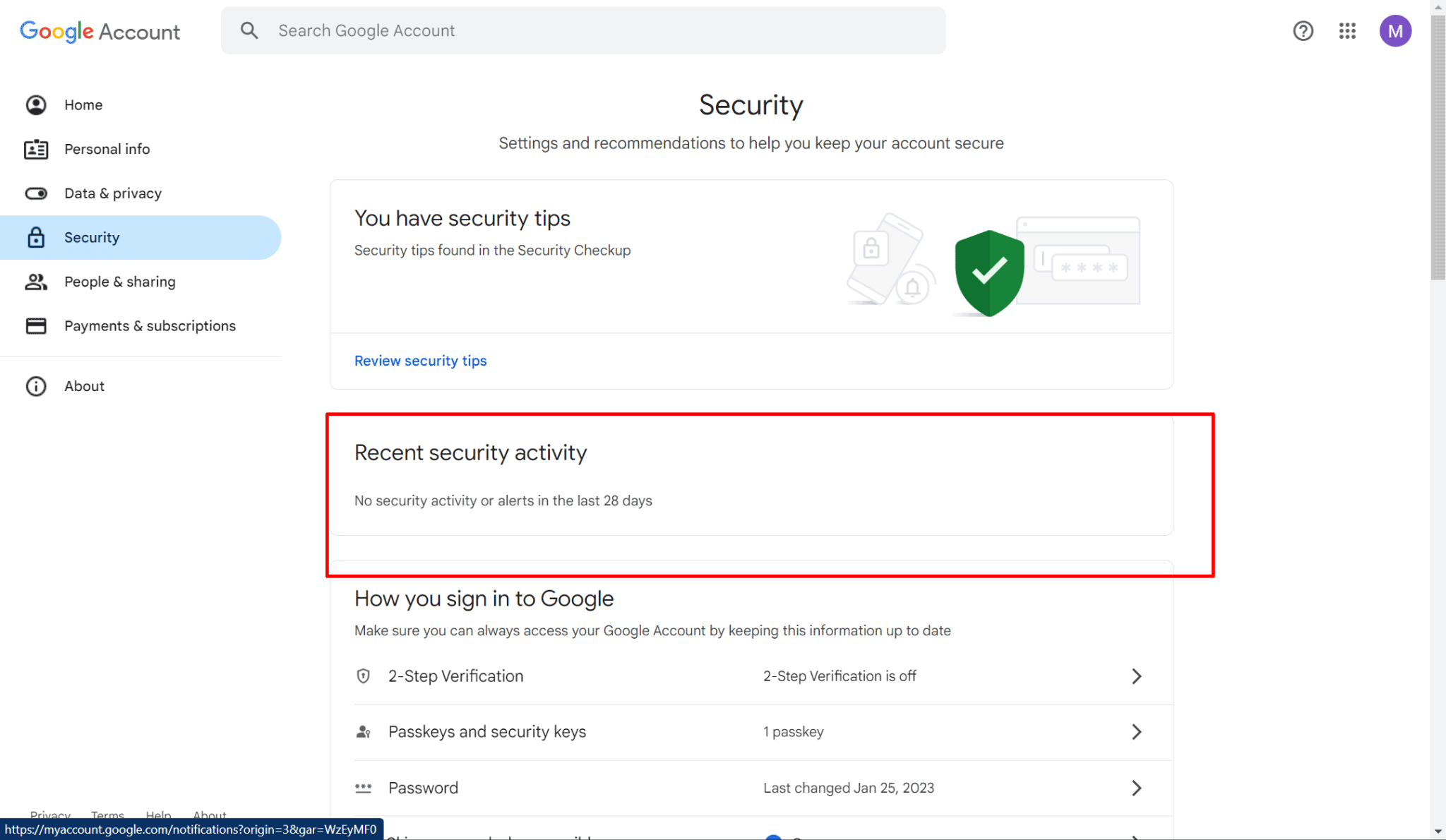
- In the same "Security" section, scroll down to the "Recent security activity" section.

- Click on "Review security activity" to see a history of recent changes made to your account, such as:
- Sign-in attempts from new devices or browsers
- Password changes
- 2-Step Verification settings modifications
- If you did not perform any of these actions, it could indicate unauthorized access. If you notice any suspicious activity, you can:
- Change your password immediately to prevent further access.
- Secure your account by following the prompts if Google detects suspicious activity and provides security recommendations.
- Sign out of all devices by selecting the option at the bottom of the device management page.
Other Suspicious Activities to Look For
Unusual Emails: If you start receiving password reset emails that you didn't request or security notifications from Google regarding login attempts, these are clear signs of suspicious activity.
Unfamiliar Sent Emails: Check your "Sent" folder for any emails you didn't send, which could indicate someone is using your account.
Missing or Deleted Emails: If important emails are missing or emails have been deleted that you did not remove, it could be an indication of unauthorized access.
How to Reset Gmail Password with an Alternate Email Address or Phone Number
If you suspect that someone may have accessed your Gmail account or you've forgotten your password, it's crucial to take immediate action to protect your account from further unauthorized access. Google allows you to reset your Gmail password using either your alternate email address or your phone number. Let's take the steps of email as an example:
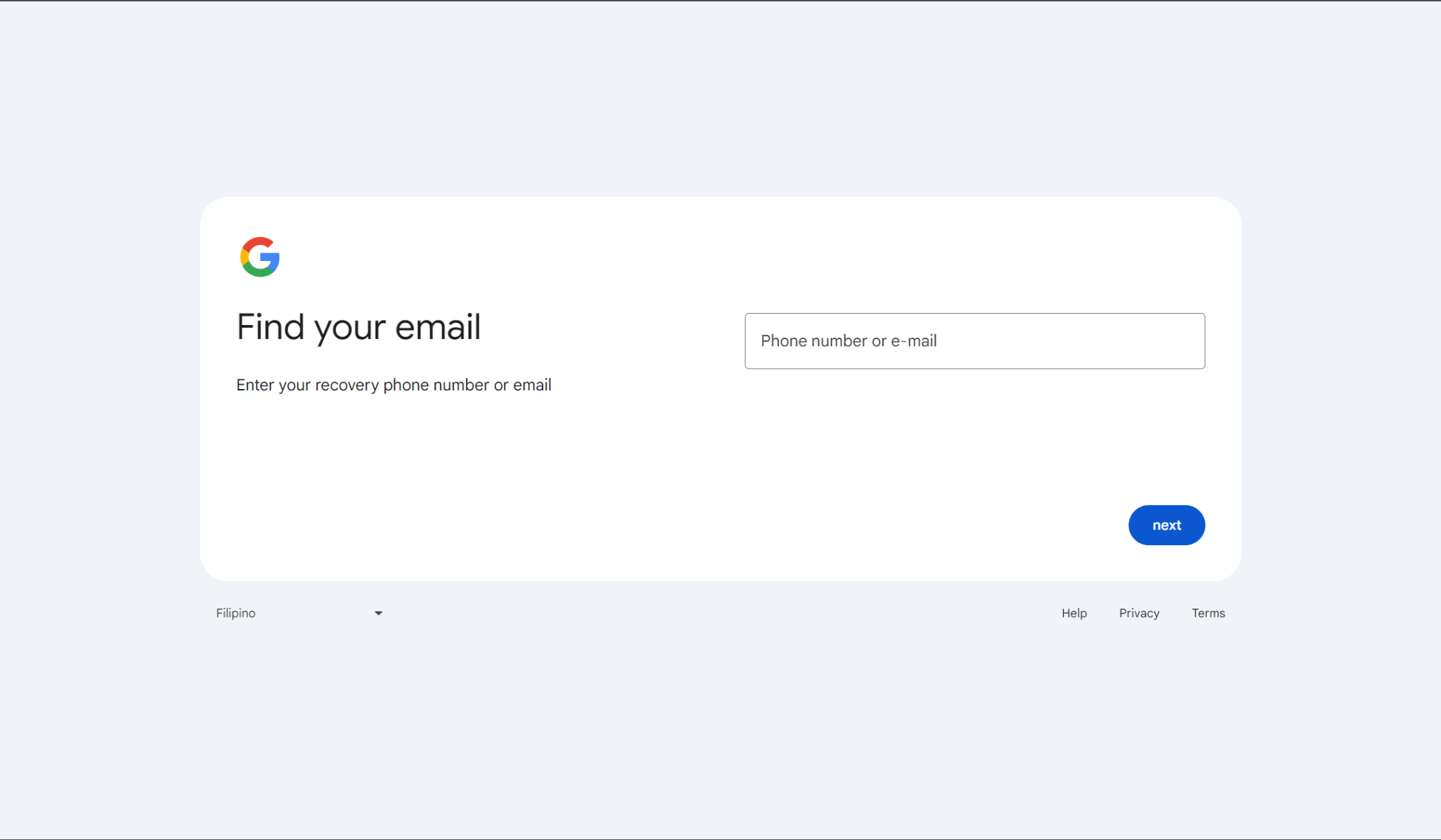
- Visit the Gmail sign-in page, enter the email address for the account you need to reset, and click "Next."

- Click on Forgot password under the password field.

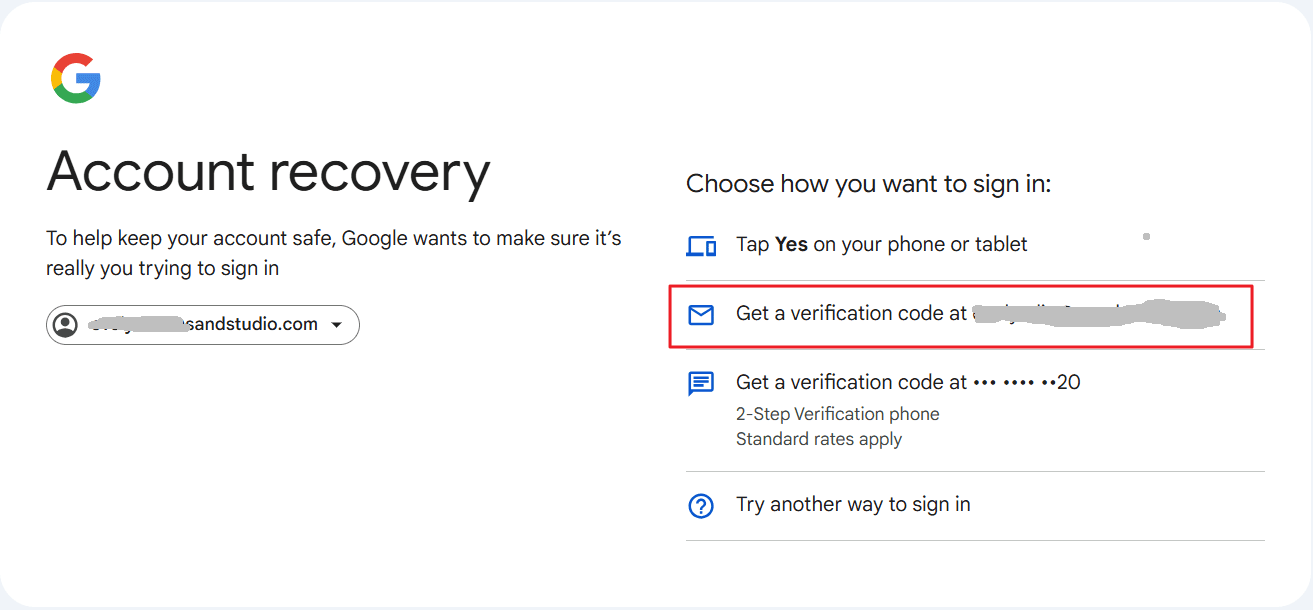
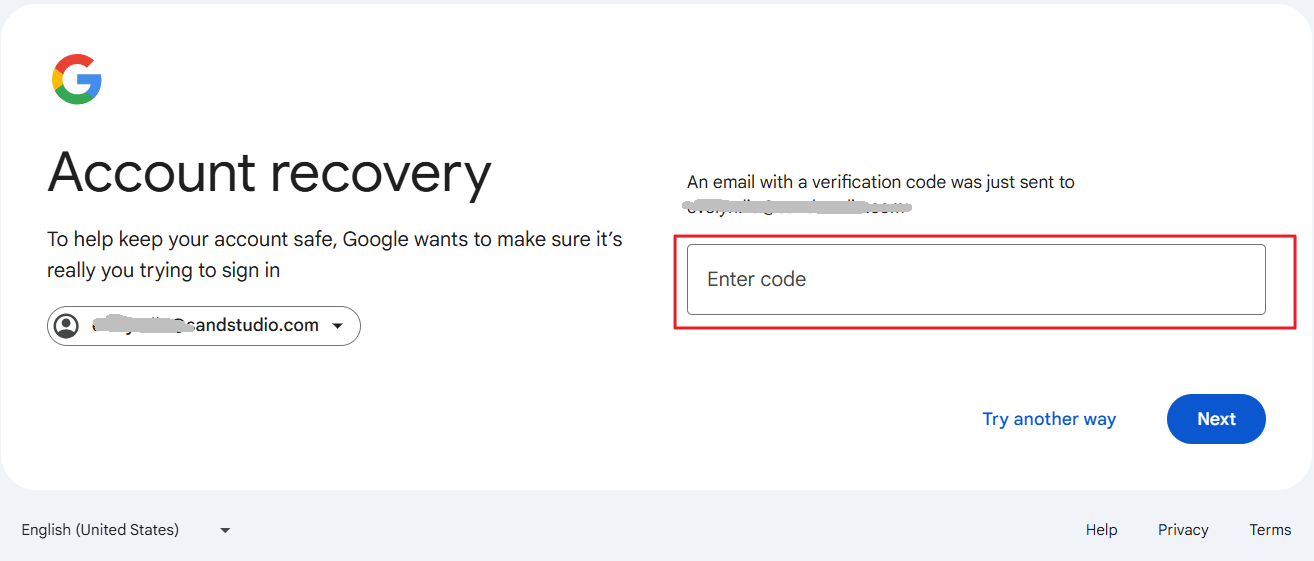
- Google will ask you to confirm your identity. Select your alternate email address to get the verification code.

- Enter the verification code sent to your email and click "Next."

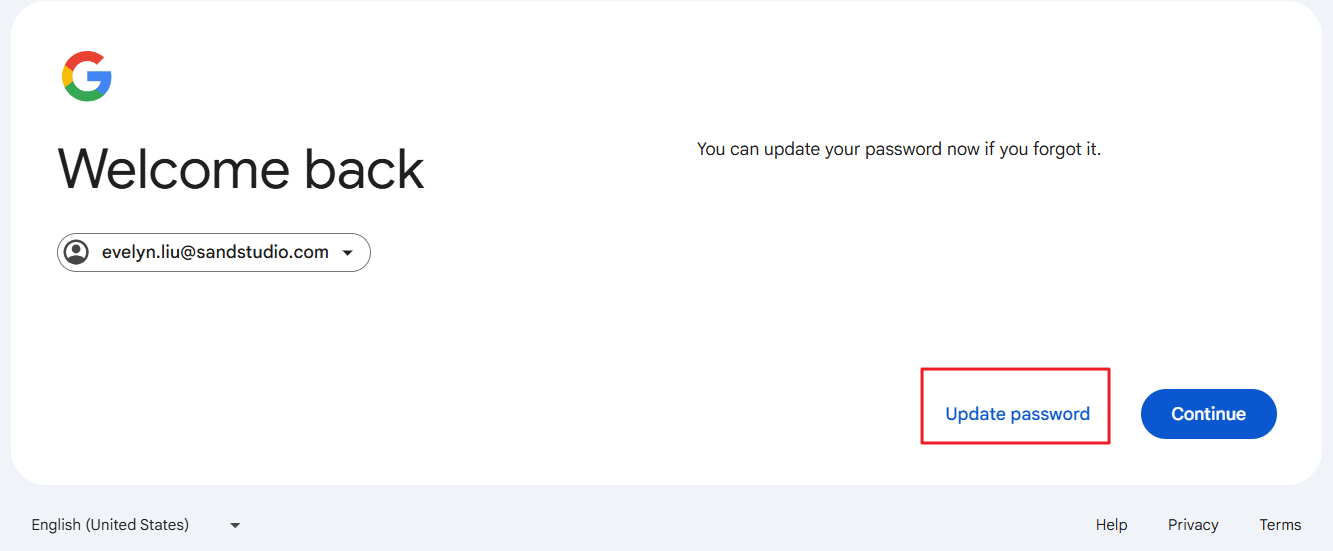
- Once you've successfully verified your identity using either your phone number or alternate email, you'll be prompted to create a new password. Tap "Update password."

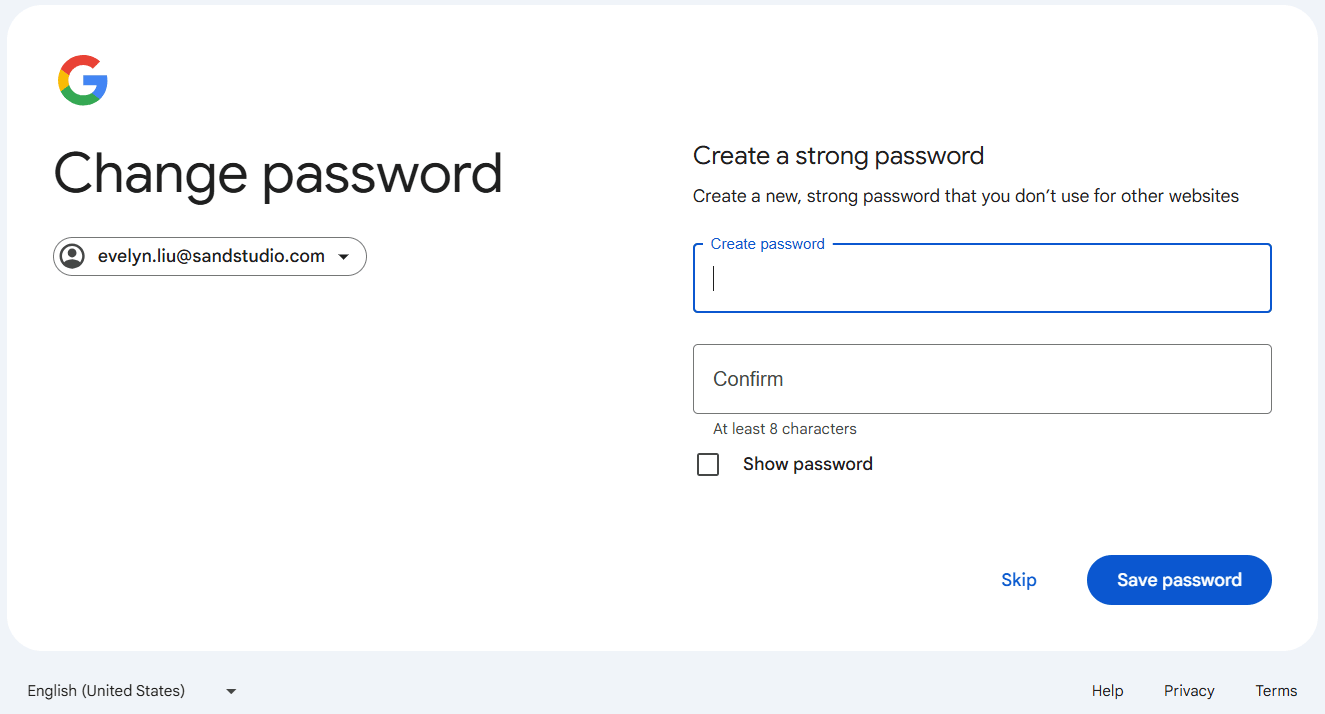
- Choose a strong password that you haven't used before. Ideally, your new password should include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Re-enter the password for confirmation and click "Save password."

- Secure Your Account (Optional but Recommended): After resetting your password, Google will give you options to review your security settings. It's highly recommended to:
- Enable 2-Step Verification (also known as two-factor authentication) to add an extra layer of security to your account.
- Review account activity to ensure there are no unauthorized access or suspicious login attempts.
Tips for Preventing Further Unauthorized Access
Taking swift action will help prevent further unauthorized access to your account. After resetting your password:
- Update your recovery information (phone number, alternate email) to ensure it's accurate.
- Monitor your account activity for any unusual activity, and report it to Google if necessary.
- Consider updating passwords for any other linked accounts (like social media or banking accounts) that use the same email for account recovery.
By following these steps, you'll help secure your Gmail account and reduce the risk of unauthorized access in the future.
Security Measures for Your Gmail Account Safety
Create a Strong Password
To safeguard your Gmail account, one of the most important steps is to create a strong password. A strong password should be long, typically at least 12 characters, and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols.

Avoid using easily guessable information, such as your name, birthdate, or common phrases like "password123." Unique passwords that aren't reused across multiple sites offer greater protection against hacking attempts.
For added convenience and security, using a safe password manager can help you generate and store complex passwords.
Enable Two-Step Verification
Two-step verification (2SV) adds an extra layer of security to your Gmail account. Even if someone obtains your password, they will not be able to log in without the second step.
To enable two-step verification:
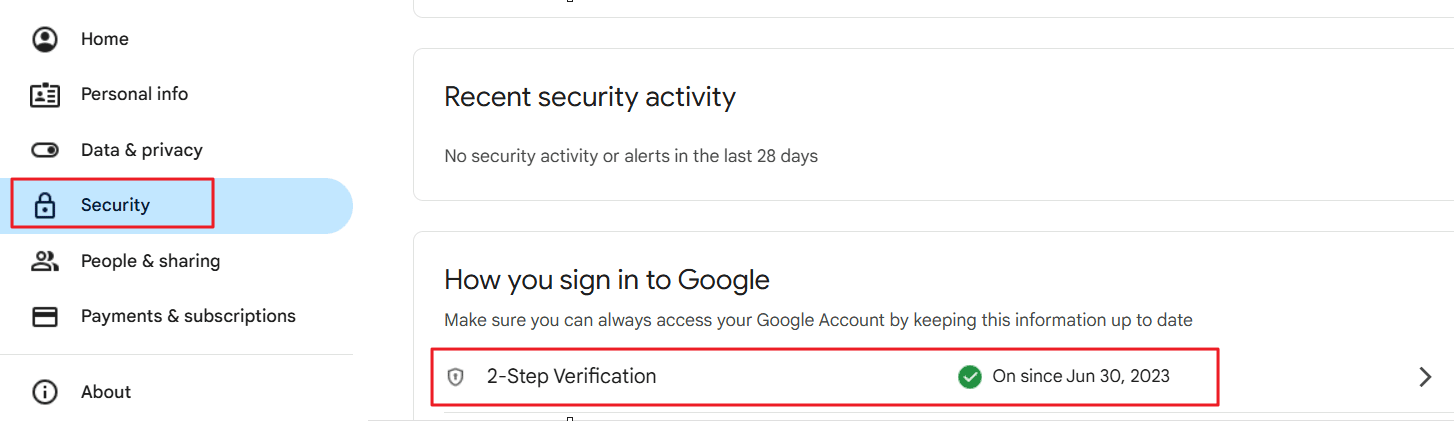
- Go to Google Account Security.
- Under the "How you sign in to Google" section, click on "2-Step Verification."

- If the status is off, follow the steps to set up 2-step verification using your phone number or authentication app (e.g., Google Authenticator).
You can also add backup options like backup codes or a second phone number to ensure you can always access your account.
Regularly Change Your Password
It's also important to regularly change your password to minimize the risk of long-term exposure. Even if you have a strong password, periodic updates—ideally every 3 to 6 months—reduce the risk of it being compromised over time.
If you suspect any unusual activity in your account or have been exposed to a phishing attempt, it's critical to change your password immediately. Each new password should be as strong and unique as the last, avoiding any close variations of the previous one.
Avoid Logging In on Public Devices
Lastly, you should avoid logging in on public devices whenever possible. Public or shared devices, such as computers at libraries or cafes, may not be secure, increasing the risk of your account being accessed by unauthorized individuals.
If you must use a public device, make sure to log in using a private browsing mode and log out completely after your session. Clear any browsing history or cookies to ensure no personal information is left behind. When accessing your account in public spaces, avoid unprotected Wi-Fi networks and consider using a VPN for added security.
Monitoring Someone's Gmail Account without Logging In
If you want to confirm whether your children have received inappropriate content in their Gmail, try AirDroid Parental Control. It can help monitor your children's Gmail accounts directly without logging in. It also allows parents to monitor their children's device activities, including Gmail-related notifications, live screen monitoring and activity reports, securely and responsibly.
- No need to log into Gmail directly: You can monitor Gmail-related activities without violating privacy policies or requiring login credentials.
- Real-time monitoring: With Screen Mirroring, you can observe real-time actions on the device.
- Comprehensive activity reporting: Easily track the usage patterns of Gmail and other apps to ensure safe behavior.
Steps to Using AirDroid Parental Control to Monitor Your Child's Gmail Account
Step 1. Install AirDroid Parental Control
- Download and install AirDroid Parental Control on your mobile from the app store. You can also visit the web version at webparent.airdroid.com.
- Create a parent account and log in.
Step 2. Connect to the Target Device
- Install AirDroid Kids on your child's device. This app will need to be installed on the mobile or tablet you wish to monitor.
- Open the app on the child's device and follow the setup instructions. You'll need to input the pairing code generated from the parent app to link both devices.
- Grant necessary permissions on the child's device to allow access to notifications, screen activities, and app usage.
Step 3. Monitor Your Child Gmail in AirDroid Parental Control
- Access the "Activity Report" feature to view your child's device usage, including time spent in specific apps like Gmail.
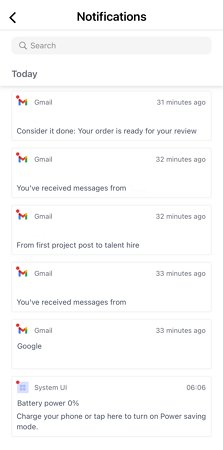
- Select "Notifications" to view the Gmail-related notifications that your child receives, such as emails or alerts from Google. You can know who is sending emails, subject lines, and notification content for any suspicious activity.

- Enable "Screen Mirroring" when necessary to view your child's device screen in real time.
- You can also set "App Limits" to ensure your child isn't spending too much time on Gmail or other apps.
Stay Proactive, Stay Secure: Protect Your Gmail
Keeping your Gmail account secure might seem overwhelming, especially when there are so many ways someone could potentially access it without your password. But now that you're aware of these risks, you can take the right steps to protect yourself.
Whether it's creating stronger passwords, enabling two-step verification, or being cautious of suspicious activity, small actions can make a big difference in keeping your email safe. Stay proactive, stay secure, and don't let anyone slip into your Gmail unnoticed.







Leave a Reply.