All About Port 5900 You Need to Know
As remote work and remote access to computers have become the norm, the importance of knowing the relevant tools and protocols is also growing. Port 5900 is one of the crucial ports in Virtual Network Computing (VNC), which lets the user control remote desktops securely and efficiently. In this guide, we will uncover all about port 5900, including its basics, working, troubleshooting issues, and best practices.
Part 1. What is Port 5900?
Port 5900 is the default port for VNC (Virtual Network Computing), which is a desktop-sharing graphical system. VNC utilizes the Remote Framebuffer protocol (RFB) to remotely access/control another computer, troubleshoot issues, and transfer files. However, it is port 5900 that enables this communication by acting as a gateway for all VNC traffic passes.
Simply put, port 5900 allows the VNC server to receive connection requests from the VNC client, transmit graphics and mouse/keyboard commands, and facilitate all the activities during the remote session. In short, port 5900 plays a key role in controlling another computer remotely.
Part 2. How Port 5900 Works?
To understand the working of port 5900, we have to understand how VNC uses port 5900 to transmit display information from the remote desktop.
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) operates on the client-server architecture, where the VNC server and VNC client (the host computer) connect through port 5900.
The server from the remote computer sends the graphics information to the client computer via port 5900 using the Remote Framebuffer (RFB) protocol. The server transmits the small rectangles of the frame buffer to the client over the network via port 5900. This provides real-time updates about the remote screen. This way, port 5900 acts as a route that the server and client use to interact during the entire remote session.
Different operating systems use port 5900 in their unique ways, as follows:
- Windows: VNC servers in Windows, like UltraVNC, RealVNC, and TightVNC use port 5900 to listen for incoming connections and assist the remote control of the desktop.
- macOS: macOS has a built-in VNC server called Screen Sharing. It also uses port 5900 to create VNC connections and then control the remote Mac computer.
- Linux: Linux offers multiple VNC server implementations, like TightVNC, TigerVNC, and x11vnc. You can enable a VNC server in Linux using commands. Afterward, the server will listen to port 5900 to create connections.
Part 3. Methods to Secure Port 5900
Exploiting the vulnerabilities in port 5900 is one of the favorite targets of cybercriminals. They can perform brute force attacks or try to exploit unencrypted connections. Therefore, it is important to secure port 5900.
In this perspective, below are five methods to secure port 5900:
1Changing the Default Port
You can change the default port 5900 to another port to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Here's how to change the default port:
- Windows: Open the VNC server settings, look for the listening port, and change it.
- macOS: In the Terminal, type "sudo nano /etc/services", change the VNC port, and restart the VNC server.
Once the port is changed, attackers cannot exploit port 5900 anymore.
2Using Strong Authentication
Using strong authentication, like strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, can reduce the chances of unauthorized access by guessing passwords. So, try to implement both strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
3Encrypting VNC Connections
You should encrypt VNC connections to avoid interception of data during remote sessions. You can encrypt VNC connections in two ways:
- SSH Tunneling: Create the SSH tunnel by forwarding the VNC port through the SSH connection.
- VPNs: You can encrypt all the network traffic by using the Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection.
4Restricting Access to Port 5900
Another effective security measure for port 5900 is to restrict access so that only authorized users / IP addresses can connect to the VNC server. You can use two techniques to restrict access to port 5900:
- Firewall Rules: You can add a firewall rule that only supports VNC connection through specific IP addresses.
- IP Whitelisting: You can set up IP whitelisting to allow access from specific ID addresses.
5Disabling Port 5900 When Not in Use
You should disable port 5900 when not in use. This minimizes vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit related to port 5900.
Part 4. Troubleshooting Port 5900 Issues
Sometimes port 5900 can encounter issues and may not be able to facilitate remote control requests or data transfer. Below, we have shortlisted a few troubleshooting tips for common port 5900 issues:
1Port 5900 Not Open or Blocked
If you are struggling with port 5900 not open or blocked, you should check if port 5900 is open and accessible. You can do so with various tools as follows:
- Using netstat: Open Command Prompt (as an administrator) and run: netstat -an | find "5900". It will tell if port 5900 is listening. Similarly, you can use Terminal in Mac and run netstat -an | grep 5900.
- Using Nmap: Install Nmap and run nmap -p 5900 <IP address> to check if port 5900 is open on the specified IP address.
- Online Port Checkers: Visit any online port checker and use its click-based interface to check the status of port 5900.
2Connection Timeout or Refusal
When the VNC server requests for the connection, there can be a connection timeout or refusal. To resolve it:
Check VNC Server is Running
You can deal with connection timeout or refusal when the VNC server is not running. There are different ways to check the VNC server operational status for different OS:
- Windows: Head to the Services app and check the VNC server service status.
- macOS: Ensure Screen Sharing is enabled in System Preferences.
- Linux: Verify the VNC server process is running using ps aux | grep vnc.
Check Firewall Settings
Maybe your firewall is blocking the traffic from port 5900. To check firewall settings:
- Windows: Open Windows Defender Firewall and ensure an inbound rule allows traffic on port 5900.
- macOS: Go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy > Firewall and ensure Screen Sharing is allowed.
- Linux: Use IPTables command to check and allow traffic on port 5900.
3Conflicts with Other Services
Sometimes another service may be using port 5900 and cause conflicts. To identify that, run the "netstat -anb" command in Windows Command Prompt or the "lsof -i :5900" command in macOS/Linux.
If you identify the port conflict with another service, you can either change the VNC server port or stop the conflicting service.
Part 5. Best Practices for Using Port 5900
If you are regularly using port 5900, here are two best practices to consider to have the secure and best experience using the port:
1Regular Monitoring
There is a possibility that your port 5900 may be compromised and you don't know about it. Therefore, it is advised to regularly monitor port 5900 for unusual activities.
To do so, you can use logging tools or intrusion detection systems. For example, you can use "Event Viewer" in Windows to monitor VNC-related logs. Similarly, you can use Suricata or Snort IDS solutions to monitor network traffic on port 5900.
2Regular Updates
Vulnerabilities can exist in your VNC software or the OS. Therefore, you should make a regular practice of updating VNC software and OS and installing related security patches. This will help you remain protected from potential vulnerabilities.
Part 6. Best Remote Desktop Solution
What if we tell you that there is a highly secure and feature-rich remote desktop solution that offers a modernized remote access experience? That tool is known as AirDroid Remote Support.
AirDroid Remote Support is a comprehensive remote support solution for businesses. It provides an instant, smooth, and error-free remote support and control solution. It lets users control desktop and mobile devices from anytime, anywhere just by using the internet.
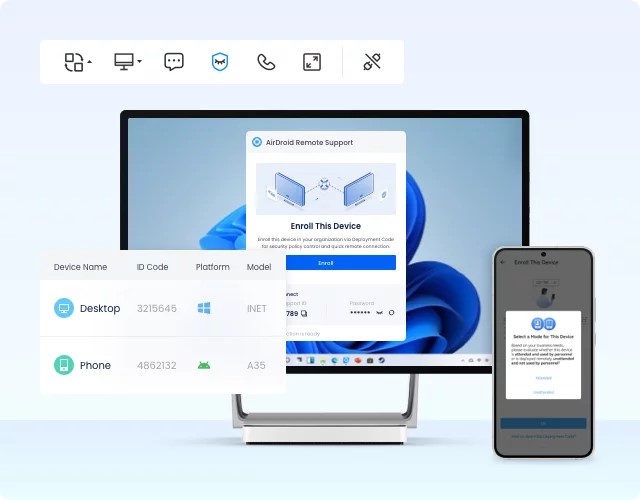
The key features of AirDroid Remote Support include:
- Real-Time Remote Access: Get real-time remote control of Windows, Android, and iOS devices with secured sessions.
- File Transfer: Transfer images, documents, and other file types with a drag-and-drop approach.
- Voice or Text Chatting: Utilize text or voice chat during the remote session.
- Unattended Access: Access the remote device unattended without session approval (best for accessing home/work computer from a remote location).
- Controllable Clipboard and Keyboard: Allow/disallow the control of the clipboard and keyboard of the remote computer.
- Log Record: Keep track of all remote sessions with detailed logs.
All the above features are the reason why AirDroid Remote Support has over 20 million installations and 1 million global customers. So, why think more? Install AirDroid Remote Support and have the best remote desktop solution at your disposal.
Conclusion
Port 5900 is the default VNC port and the key component for remote access to another computer. It provides the gateway to streamline remote control and file transfer. However, it requires robust security measures to protect from vulnerabilities and unauthorized access. In contrast, AirDroid Remote Support emerges as a more secure and reliable remote desktop solution with its feature-rich offerings and industry-grade security. So, why compromise your system with port 5900 vulnerabilities? Try AirDroid Remote Support and have a secure platform to remote control desktops and smartphones.








Leave a Reply.