[Answered] Where Can I Find RDP Logs
In today‘s business environment, where hybrid and remote work has become so common, secure remote connections are vital. In such companies, system administrators, IT professionals, or team managers can utilize the RDP logs to review user activity and spot any potential security breaches. So, where can you find the RDP log and which metrics should you check?
In this article, we are going to guide you on how to find your RDP access logs and go through the most crucial elements of your company’s security.
Part 1. Can You Track RDP?
First of all, you might be wondering if it‘s even possible to track the RDP activity on your organization’s machines. The answer to this is that yes, you can track remote connections with the RDP logs. These are detailed records of events related to remote desktop connections. When you analyze them, you will find critical information that helps you evaluate which users used RDP and for how long, among other things. This way, you will be able to troubleshoot any connectivity issues and even identify potential security threats.
What Is Included in RDP Logs?
An RDP log is such an invaluable record because it holds many information. Indicatively, it typically includes the following:
- Connection events: These are timestamped details of when the remote connections were initiated and when they were terminated.
- User activity: This includes relevant information to user logins, such as usernames and session durations.
- Source IP address: These are the IP addresses of the client that attempted the RDP session.
- Session errors: These include all issues encountered during the remote session. For instance, it will include failed login attempts and unexpected terminations among others.
Why Are RDP Logs Important?
As you can see, this log includes a variety of data that allow you to monitor your organization‘s RDP activity. Nevertheless, there are more reasons why you need to start checking on them. To make you better understand that, RDP logs are important for these reasons:
- Security Monitoring: RDP is a common target for cyberattacks, and for this reason, you need to take every possible measure to prevent them. By analyzing your logs, you can spot unauthorized access attempts and take preventive measures.
- Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues: Your logs will also provide insights into connection failures, which will help you identify network or configuration problems.
- Auditing User Activity: In an organization with a large number of remote employees, monitoring RDP logs ensures compliance with the company’s policies and tracks employee activities.
Part 2. Where Can I Find RDP Logs?
Now that you fully understand their significance, we can go on to explain where to find your RDP logs. In essence, these records are stored in the Event Viewer of your Windows system. In this section, we are going to show you different methods to locate them.
Method 1: Using Event Viewer
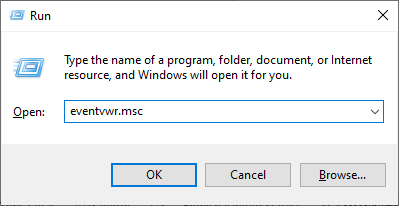
- Step 1.Press Win + R, type "eventvwr.msc", and press Enter to open the Event Viewer.
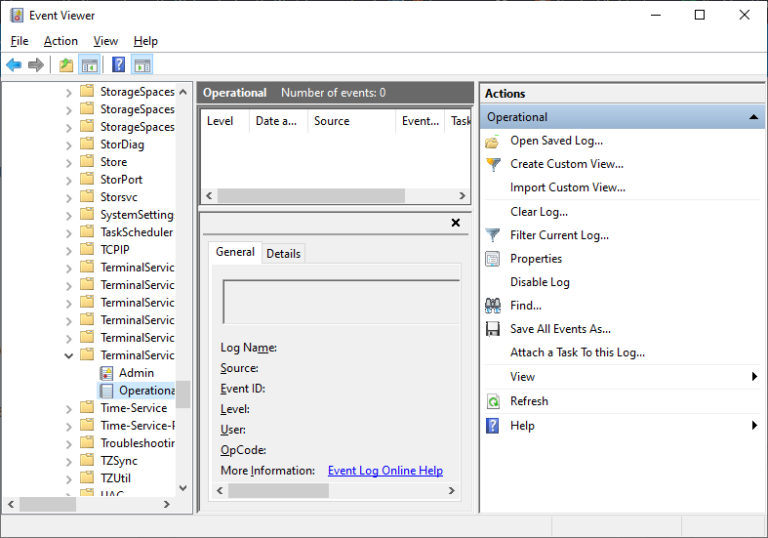
- Step 2.Go to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager > Operational.
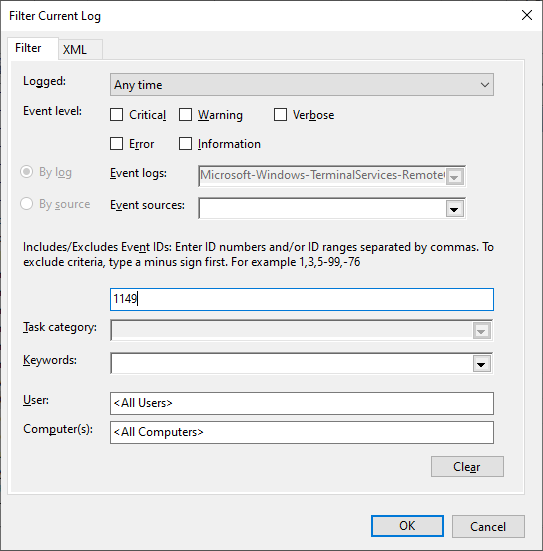
- Step 3.Right-click on Operational and select the Filter Current Log option. Then, type the Event ID to filter through your logs. For example, use these Event IDs:
21: Disconnection events
24: Successful connection events
1149: Remote Desktop Services connection events.
Method 2: Using PowerShell
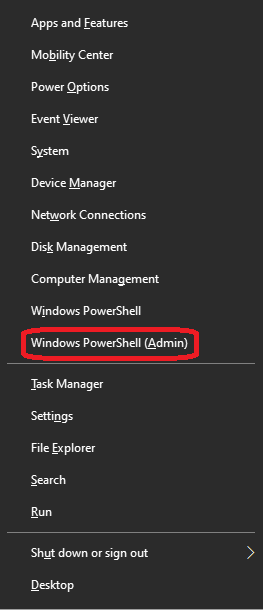
- Step 1.Right-click on the Home button and click the Windows PowerShell (Admin) option to load PowerShell as an administrator.
- Step 2.Run the following script to get a list of all RDP connections of the day:
Get-EventLog -LogName Security -after (Get-date -hour 0 -minute 0 -second 0)| ?{(4624,4778) -contains $_.EventID -and $_.Message -match 'logon type:\s+(10)\s'}| %{
(new-object -Type PSObject -Property @{
TimeGenerated = $_.TimeGenerated
ClientIP = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Source Network
Address:\s+([^\s]+)\s+.*','$1'
UserName = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Account Name:\s+([^\s]+)\s+.*','$1'
UserDomain = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Account Domain:\s+([^\s]+)\s+.*','$1'
LogonType = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Logon Type:\s+([^\s]+)\s+.*','$1'
})
} | sort TimeGenerated -Descending | Select TimeGenerated, ClientIP `
, @{N='Username';E={'{0}\{1}' -f $_.UserDomain,$_.UserName}} `
, @{N='LogType';E={
switch ($_.LogonType) {
2 {'Interactive - local logon'}
3 {'Network connection to shared folder)'}
4 {'Batch'}
5 {'Service'}
7 {'Unlock (after screensaver)'}
8 {'NetworkCleartext'}
9 {'NewCredentials (local impersonation process under existing connection)'}
10 {'RDP'}
11 {'CachedInteractive'}
default {"LogType Not Recognised: $($_.LogonType)"}
}
}}
Method 3: Using Command Prompt
- Step 1.Open the Command Prompt with administrative rights.
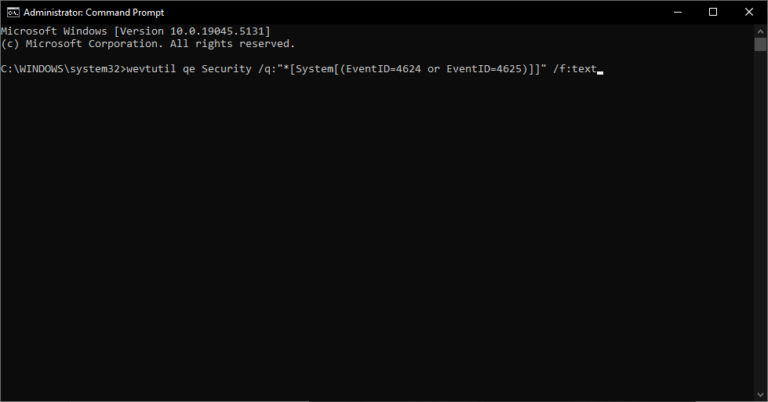
- Step 2.2.Use the following command to query the Security logs:
wevtutil qe Security /q:"*[System[(EventID=4624 or EventID=4625)]]" /f:text
Method 4: Check RDP History in the Registry
- Step 1.Press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
- Step 2.Go to HKEY_CURRENT_USER > SOFTWARE > Microsoft > Terminal Server Client > Default. There, you will find the last 10 RDP connections.
Part 3. How to Analyze RDP Logs
Once you've accessed an RDP log, it is just as important to know how to analyze it. In this section, we are going to explain some key metrics that will help you make the most out of these records.
Key Metrics to Monitor
- Event ID: Events are assigned to specific IDs. Therefore, knowing how to identify and filter for them can help you gain invaluable insights. Some event IDs that you need to know are:
- 4624: Successful login,
- 4625: Failed login attempt,
- 4776: Credential validation failure,
- 4778: A session was reconnected to a Window Station,
- 4779: A session was disconnected from a Window Station.
- 21: Session logon succeeded,
- 23: Session logoff succeeded,
- 24: Session has been disconnected,
- 25: Session reconnection succeeded,
- 39: Session [1] has been disconnected by session [2]
- Source IP Address: This metric shows you the IP addresses that initiated an RDP connection. Keep an eye on it to spot unfamiliar or suspicious IP addresses that might signify a cyberattack.
- Login Time and Duration: With this metric, you can track user session lengths to detect unusual patterns.
- Account Lockouts: Event ID 4740 might also be helpful as it shows you the locked accounts. These might be a sign of malicious activity.
Part 4. Best Way to Manage RDP Logs
Monitoring your RDP logs manually can become cumbersome, especially if you are working in a complex IT environment. That's where tools like AirDroid Remote Support come in.
AirDroid Remote Support is a comprehensive tool designed to streamline remote support and monitoring tasks. Apart from its outstanding remote support capabilities and advanced features, it also simplifies log management. For this reason, it is an invaluable resource for system administrators and IT professionals.
How AirDroid Remote Support Helps with Managing RDP Logs
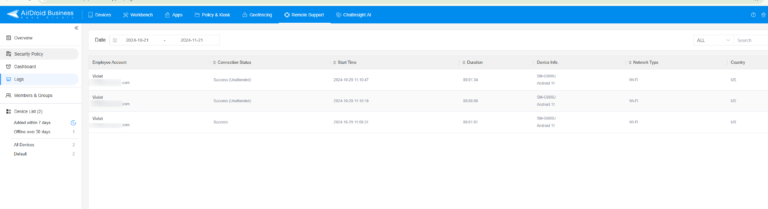
- Centralized Monitoring: View and manage RDP logs across multiple systems from a single dashboard.
- Log Storage: The tool automatically backs up logs to ensure compliance and facilitate audits. You can access these logs by going to your dashboard and clicking “Logs” on the sidebar.
- User-Friendly Interface: The platform has been designed with the user in mind. Therefore, it simplifies log analysis with visual tools that save time and reduce errors.
- Enhanced Security: With end-to-end encryption, AirDroid ensures your remote sessions and log data remain secure at all times.
In Conclusion
Tracking and managing RDP logs is essential for maintaining the security of your system, especially if you are working in a large organization. AirDroid Remote Support makes the process more efficient as it gives you immediate access directly from your dashboard. Try AirDroid Remote Support today and experience the difference in how you manage your RDP logs!








Leave a Reply.