How to Establish Remote Desktop Connection on Ubuntu
Accessing a remote desktop from a local computer has become a new normal. Employees need remote access to control their home computers from work, while IT support teams need remote control to troubleshoot issues. Although it is straightforward to do in Windows, what about Ubuntu?
Since Ubuntu is the most widely used Linux distribution, many users want to establish a remote desktop connection on Ubuntu. This guide explains in detail all the steps to set up a remote desktop on Ubuntu.

Part 1. Can Ubuntu Connect to Remote Desktop?
Yes, Ubuntu can connect to a remote desktop and also allows other devices to access it remotely.
Basically, Ubuntu supports Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Virtual Network Computing (VNC) protocols. These protocols empower users to create remote desktop connections. You first have to enable remote desktop access on Ubuntu and then create a remote connection.
The important thing to note is that RDP is considered a more secure protocol than VNC. Therefore, the next parts will guide you through enabling and setting up a remote desktop connection on Ubuntu.
Part 2. Setting Up Remote Desktop on Ubuntu
You can set up a remote desktop on Ubuntu only after enabling "Remote Desktop" access. So, follow the below steps to learn how to enable remote desktop access on Ubuntu:
- Step 1.From the GNOME top bar, click the
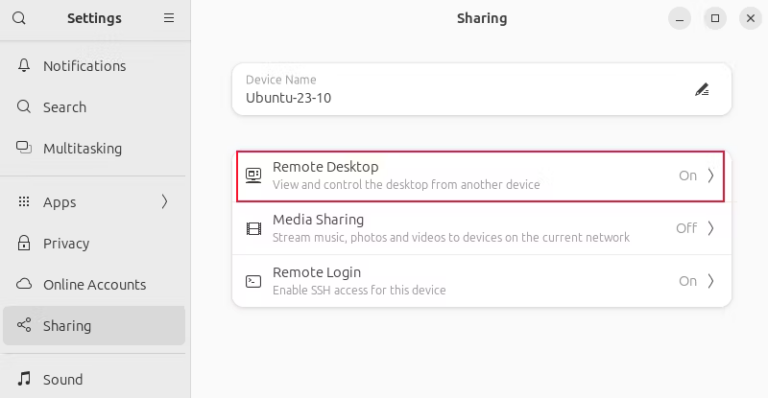
System icons and then click the Settings icon. - Step 2.Under Settings, click Sharing > Remote Desktop.
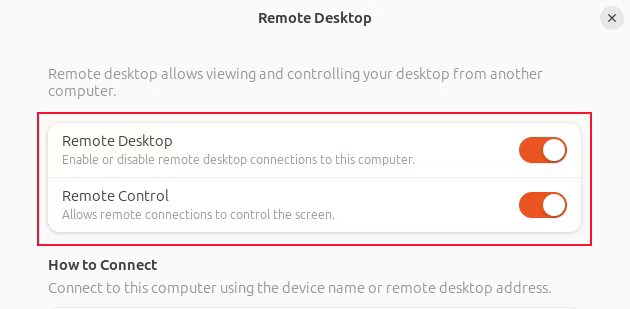
- Step 3.Toggle on Remote Desktop and Remote Control.
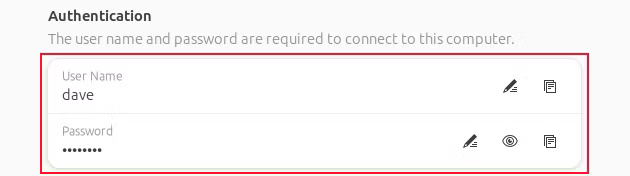
- Step 4.Under the Authentication section, enter the User Name and Password.
- Step 5.Close the Settings app.
Once done, you have enabled remote desktop connection on Ubuntu. It is now all set to be remote-controlled by other devices.
Part 3. Connecting to Ubuntu from a Remote Desktop Client
Connecting to Ubuntu from different operating systems is easier than most think. Below are the steps to connect to Ubuntu from Linux, Windows, and macOS operating systems using different remote desktop clients:
For Linux
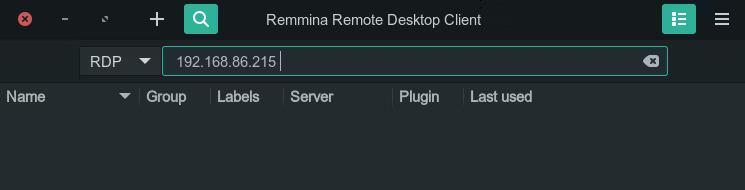
- Step 1.Install and launch Remmina. Select RDP from the drop-down menu and type the IP address of the remote Ubuntu device. Afterward, hit Enter.
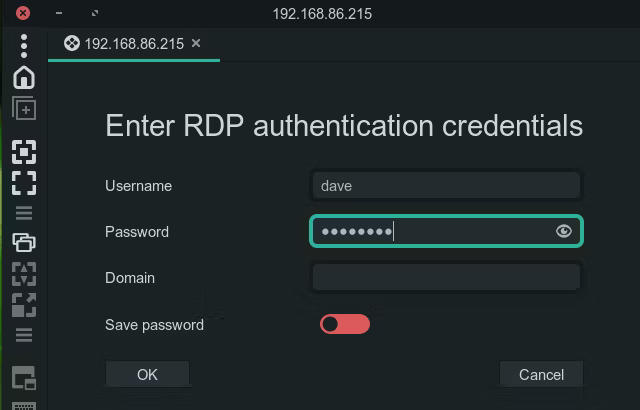
- Step 2.Next, you will be asked to enter the username and password. Afterward, click OK.
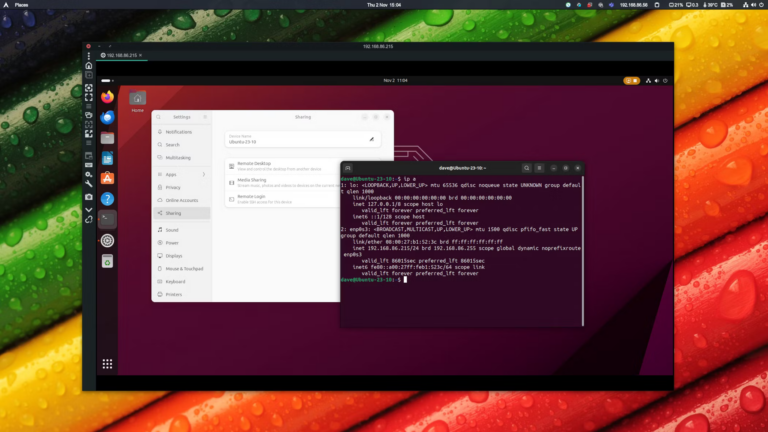
Once the connection is made, you will be able to view and control the Ubuntu computer remotely.
For Windows
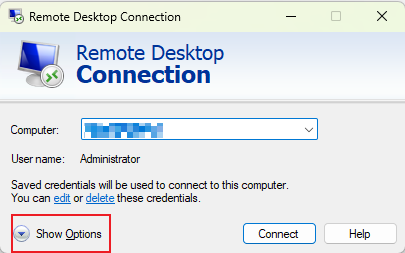
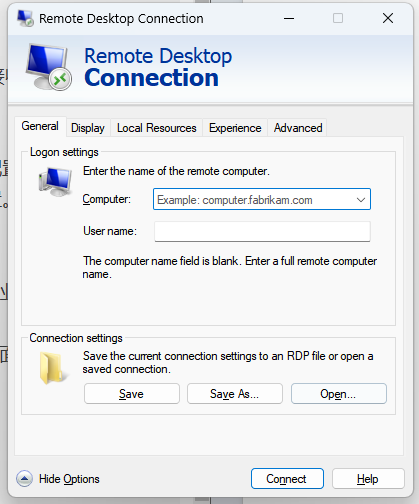
- Step 1.Launch Remote Desktop Connection. Enter the IP address of the remote Ubuntu device and then click Show Options.
- Step 2.Enter the Username and click Connect.
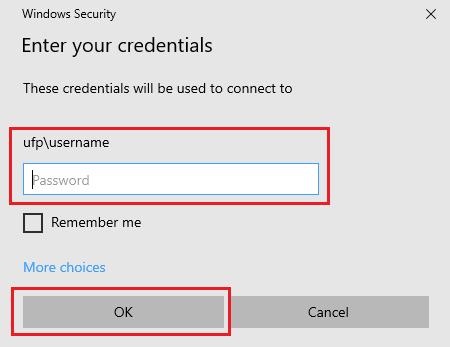
- Step 3.Enter the Password and click OK.
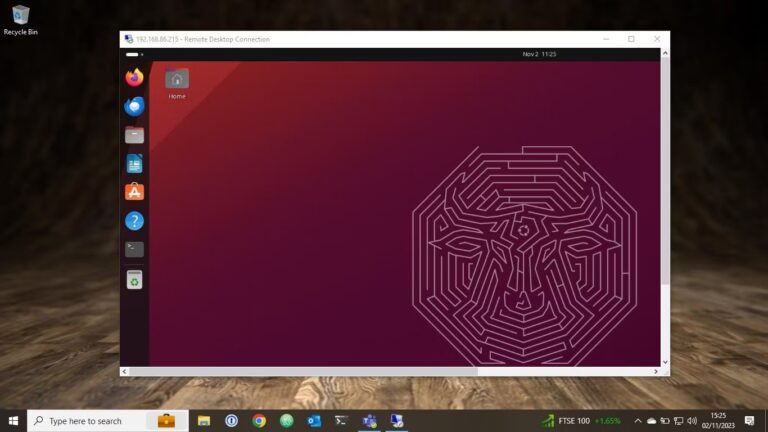
Once done, you will be able to control the Ubuntu device remotely from Windows.
For macOS
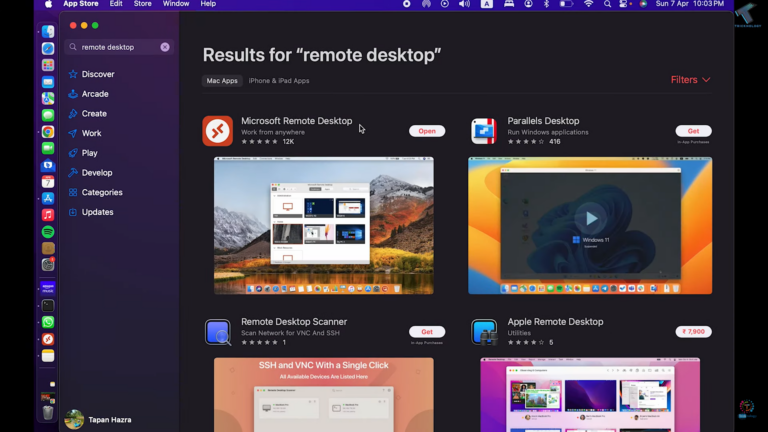
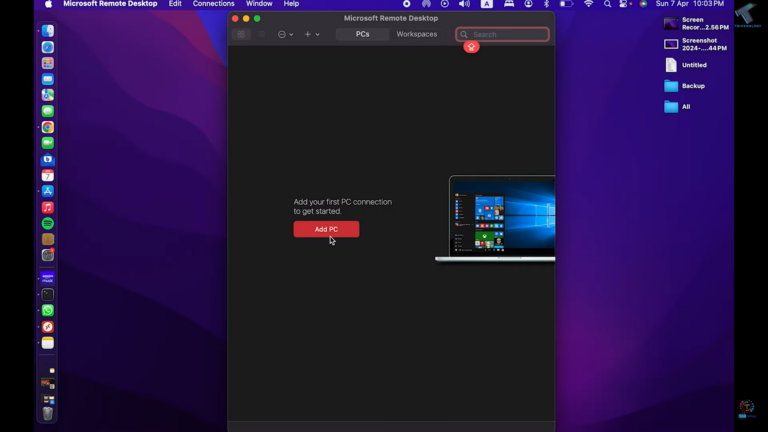
- Step 1.Install and launch Microsoft Remote Desktop from the App Store.
- Step 2.Click Add PC from the home screen.
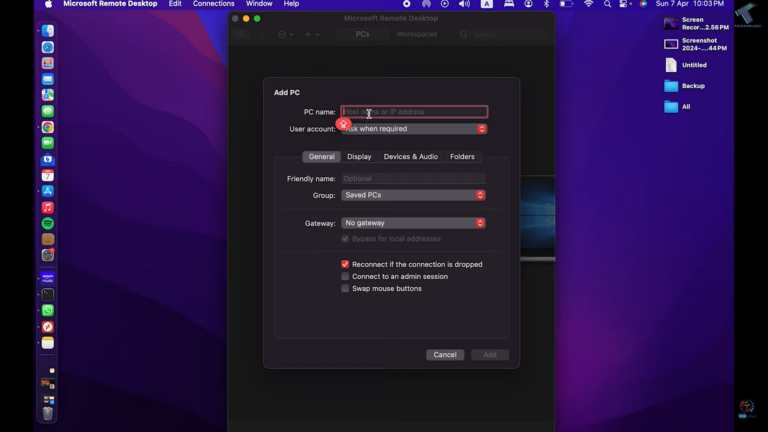
- Step 3.Enter the IP address under the PC name section.
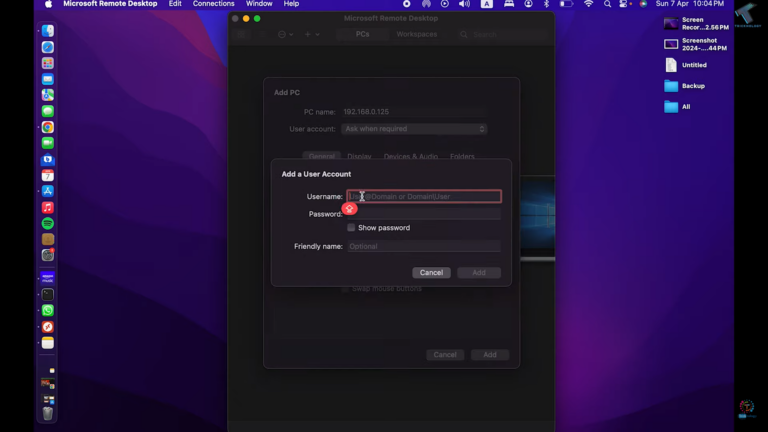
- Step 4.Under the User account section, click Add User Account and enter the username and password. Once done, click Add.
- Step 5.Now that the remote Ubuntu computer is linked, click 3 dots and tap Connect to create the remote connection.
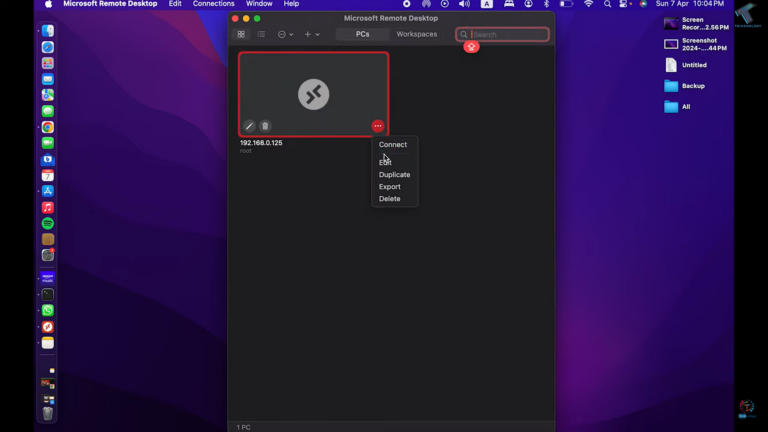
Once connected, you can control the Ubuntu device remotely from macOS.
That's it! This way, you can have a remote desktop connection on Ubuntu using remote desktop clients from Linux, Windows, and macOS.
Part 4. Best Practices for Security
Now that you have learned how to build a remote desktop connection on Ubuntu, the next thing to learn is how to keep the connections secure. In this perspective, below are some best practices for security:
Use Strong Passwords
A strong password makes it impossible for anyone to gain unauthorized access to Ubuntu. Therefore, make sure to set strong passwords that include a combination of upper- and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Enable Encryption
Other than unauthorized access, another threat is eavesdropping on your remote session. To avoid that, enable encryption for your remote desktop connections. This will ensure that your transmitted data remains encrypted and not intercepted by hackers.
Limit Access
Don't openly share the username and password for remote Ubuntu devices. Access should be limited to trusted IP addresses only. Secondly, disable remote access when not required.
Keep Software Updated
Make sure your remote Ubuntu and local devices are up-to-date. Many updates are related to serious security patches. Regular updates of OS and remote desktop software can lower the chances of cyber attacks.
Conclusion
Establishing remote desktop connection on Ubuntu is similar to how we do it in Windows. All we need to do is enable a remote desktop and then use any reliable remote desktop client to make the connection. However, if you want to taste a more powerful and secure remote access experience, then try out AirDroid Remote Support. It provides a more robust remote access toolkit that also supports text/voice communication during remote sessions and encrypts/logs all remote sessions.












Leave a Reply.