A Beginner’s Guide to Windows Registry Regedit: What You Need to Know?
The Windows Registry plays a crucial role in how your computer operates, storing important registry settings that control everything from system performance to software configurations. The tool used to access these settings is called the Registry Editor.

It allows you to view and make changes to the registry files that manage everything from system performance to installed programs. In this guide, you will learn the basics about how to use the Registry Editor. You will learn how to navigate through the registry and make changes safely.
- Part 1 :What is the Windows Registry Editor?
- Part 2 :How to Open the Windows Registry Editor?
- Part 3 :Why is the Windows Registry Editor Important?
- Part 4 :Troubleshooting Common Issues in Accessing the Registry Editor
- Part 5 :Advanced Techniques in Windows Registry Editor
- Part 6 :Risks and Precautions When Using regedit
What is the Windows Registry Editor?
The Windows Registry Editor, or regedit, is a native tool to manage the Windows Registry. A registry is a database where most of the crucial system settings are stored. These settings, called registry keys, control how your computer and programs work.
With regedit, you can view and change these registry keys. It gives you control over many hidden aspects of your system. You can customize how programs run, adjust hardware settings, or fix errors.
But, always be careful. Changing the wrong settings can cause problems. Always make sure you know what you’re doing before making changes.
- All-around Remote Access & Remote Support Solution for Enterprises
- Real-Time Fast Support
- Always-On Unattended Remote Access
- Lightweight Remote Management
How to Open the Windows Registry Editor?
Accessing the Windows Registry Editor is simple. Follow these steps to open regedit on your system:
- Step 1.It's really easy just go to your start menu and type "registry editor".
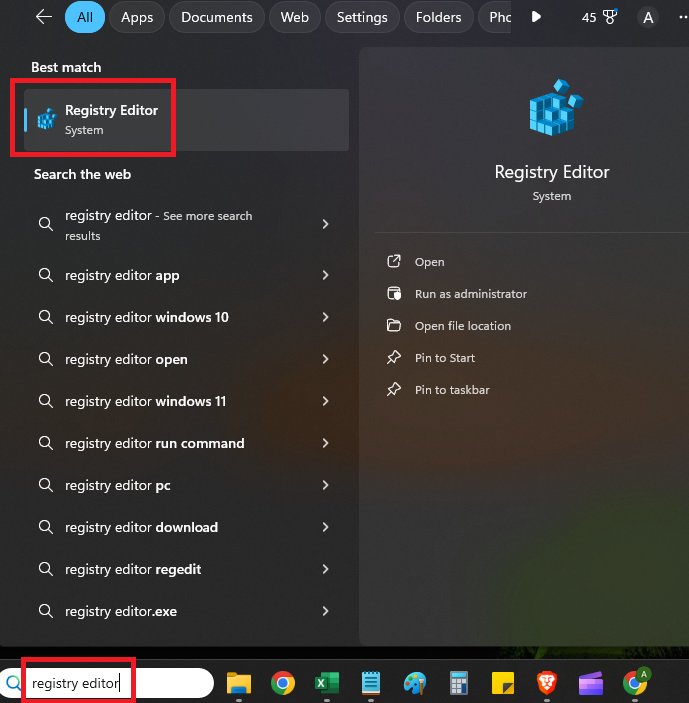
- Step 2.Or you can even access via the command prompt. Open Command Prompt by typing "cmd" in the Start menu.Once open, type regedit and press Enter.
- Step 3.Once you open it, this is how the interface will look like.
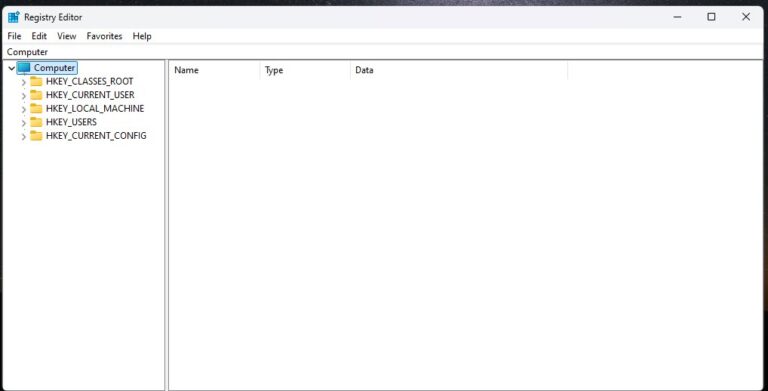
On the left side of the window you'll see what is called a tree of folders similar to the ones you see in windows explorer.
- Step 4.You can open these folders and you can see there's a lot of subfolders.
- Step 5.And if you go deeper and deeper at the bottom level there are these files that are called "registry entries".
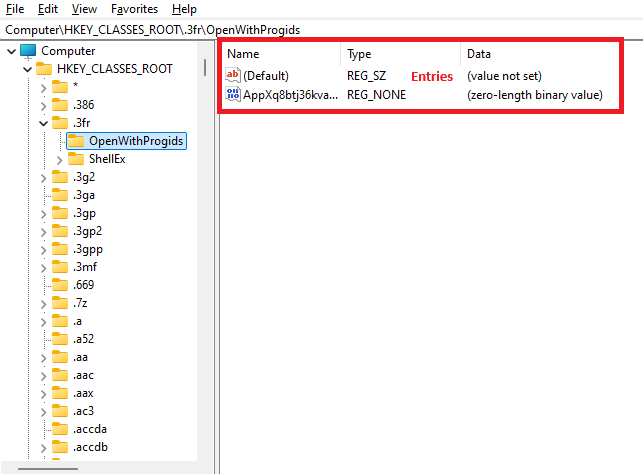
In in reg edits a folders os called "registry key" and the files are called " registry values".
- Step 6.If you would like to add a new key or a new value, you can simple do so by right clicking on the interface.
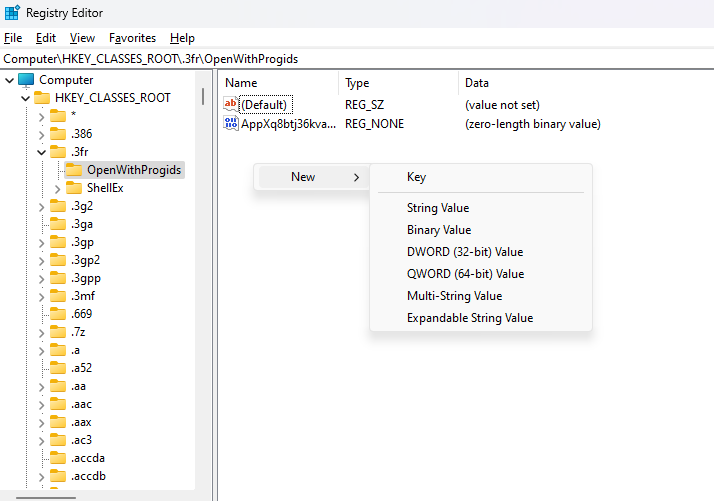
There are different kinds of values like -
- Key
- String Value
- Binary Value
- DWORD (32-bit) Value
- QWORD (64-bit) Value
- Multi-String Value
- Expandable String Value
Navigating the Windows Registry Editor Interface
Once you're familiar with the basic layout, let's dive a bit deeper into how to navigate the interface.
On the left side, the tree of registry keys is your map. Now, if you select any key, the right side of the window will display the registry values related to that key.
These are the actual settings that control different aspects of your system and installed software. Every value has three parts: Name, Type, and Data. The name tells you what the setting is for, the type explains what kind of data it holds, and the data itself shows the actual value.
You can edit any of these values by double-clicking on them. This opens a box where you can change the registry data.
For example, changing a String Value might update a path or change a system setting.
Locating a Registry Key Path
If you're looking for a specific key, you don’t need to scroll through everything.
The Find feature can help.
- Step 1.Click on Edit in the top menu, then select Find.
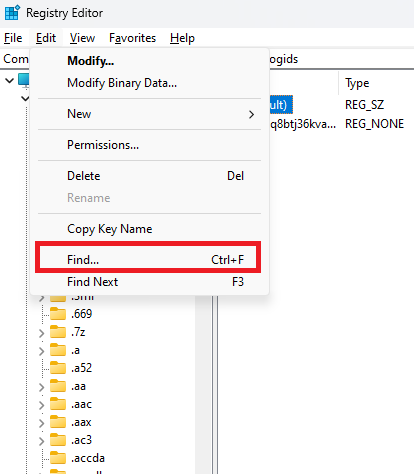
- Step 2.You can type in the name of the key or value you’re looking for, and regedit will locate it for you.This is especially useful when you’re dealing with a large registry.
- Step 3.You also have a few useful options in the top menu, like File, where you can import or export registry files.Exporting is helpful for creating a backup before you make any changes, so you can restore it if something goes wrong.
- Step 4.If you ever need to remove a key or value, right-click on it and select Delete.Be absolutely sure you want to delete it because there’s no undo button. Once it's gone, it's gone.
- Step 5.Again, this is why having a backup is so important.
With these tools, you can effectively navigate, edit, and manage the Windows Registry.
Why is the Windows Registry Editor Important?
1. Enhances System Performance
The Windows Registry Editor is one of the most essential parts that affect the performance of your computer.
Regedit is what permits you to modify registry keys, which in turn can change how your system functions (as mentioned above).
Optimizing these settings can help to reduce boot times, smoother program launches, and better overall performance.
2. Allows Advanced Customization
Regedit is essential for users who want to customize their system beyond what’s available through regular settings.
This provides access to more advanced configuration settings where you can control how your OS behaves like.
This extends to anything from refining how quickly menus pop up, to what you see on your desktop or even control how a few apps operate.
3. Common Uses
A lot of users use the Registry Editor to handle startup programs. When the computer starts, you can decide which software is executed.
This will help with faster boot times and reduce the unnecessary load on your system.
Another frequent use is changing system settings. For example, you can enable or disable features, adjust hardware configurations, or fix issues related to registry files.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Accessing the Registry Editor
1“regedit Not Found” Error
One of the most common error while accessing the regedit is “regedit Not Found” Error
If you encounter the “regedit not found” error, it’s usually due to a restriction or a corrupted system file.
Start by checking if the Registry Editor has been disabled.
To re-enable it:
- Step 1.Press Windows + R and type gpedit.msc to open Group Policy.
- Step 2.Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System.
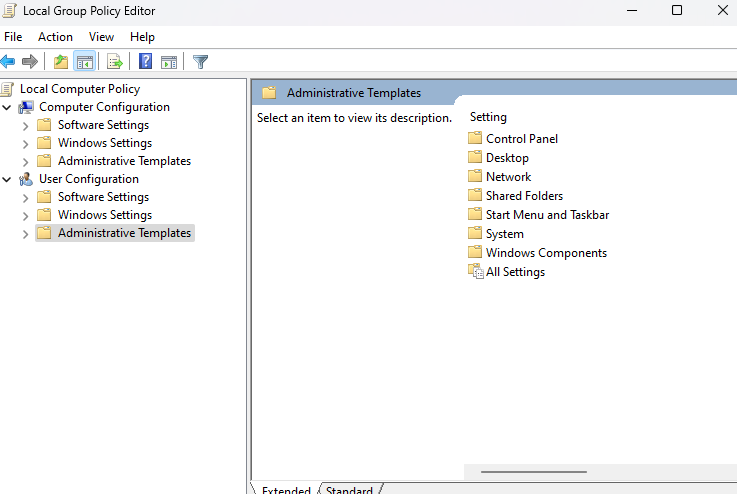
Prevent access to Registry editing tools and set it to Disabled.
If the editor is still not found, run System File Checker:
- Step 1.Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Step 2.Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
Prevent access to Registry editing tools and set it to Disabled.
This will repair any missing or corrupted system files.
2Ensuring User Permissions
Sometimes, the issue isn’t the tool itself, but the permissions.
If you can’t open regedit, you might not have the correct user rights.
To check your permissions:
- Step 1.Right-click on the Registry Editor and select Run as Administrator.
- Step 2.If you’re prompted for an administrator password, enter it.
- Step 3.If you don't have administrator access, ask an administrator to elevate your user permissions.
Only administrators can access all registry keys and make critical changes.
3Handling Access Denial Issues
You may encounter “Access Denied” errors when trying to modify certain registry keys. This happens because some keys are protected by the system. To handle this:
- Step 1.Right-click the key you want to modify.
- Step 2.Select Permissions.
- Step 3.In the window that appears, click Advanced.
- Step 4.Change the Owner to your user account and apply the changes.
- Step 5.After adjusting the ownership, you should have full control of the key.
Advanced Techniques in Windows Registry Editor
After gaining the basic knowledge on regedit, you can always go a bit further by learning some advanced techniques.
These methods will give you more control and make editing the registry faster. Here are a few things that can help out.
1Using .reg Files to Automate Changes
With .reg files, you can automate changes to the registry. So instead of editing one by one, simply create a .reg file with the required settings.
All you have to do is just double-click that file, and it will make implement those changes immediately.
2Command-Line Options for Registry Editing
You can also modify the Windows Registry through the command line.
By using the reg.exe command, you can manage (add/delete/modify registry keys) without even starting the editor.
This method is especially helpful when you need to script changes or automate tasks.
3Remote Registry Editing on Networked Systems
For network administrators, remote registry editing is a powerful feature.
You can access the registry of any computer on your network, provided you have the right permissions.
In regedit, click File, then select Connect Network Registry to begin editing a remote machine.
Risks and Precautions When Using regedit
Editing the Windows Registry can be risky if done without care. Small mistakes can cause big problems. If you change or delete the wrong registry key, it could cause programs to cause errors and even prevent your computer from functioning properly.
It’s important to know what you’re editing. Random changes can cause system failures or crashes.
When in doubt, avoid making adjustments that aren’t clear to you. Always research the keys and values before you edit them.
Always Backup Registry files Before making any changes to the System. Select File from the menu in regedit and choose Export. This will back up the current registry. In case of any mishap, you can restore it from the backup using import option. This simple step can prevent major system damage.
Wrapping it Up
Exploring regedit opens up new possibilities for customizing and improving your system. With the right knowledge, you can make changes that boost performance and fix issues.
Dive in, experiment carefully, and take control of your computer’s settings like never before.






Leave a Reply.