Lastest Comparison: Device Encryption vs. Bitlocker
Device encryption and BitLocker are considered the same as they serve a single purpose, i.e., security. However, after carefully analyzing compatibilities, functions, and working, they protect different communities.
So, whether you are an individual or a business owner, read it carefully to understand device encryption vs BitLocker, including their steps, unique features, and some technical information. It will help analyze steps and prerequisites, check availability, and determine how to resolve PC support issues.
1 Device Encryption vs BitLocker: Definition, Features and Usages
Device Encryption
Using a robust algorithm, device encryption is a feature-limited security measure for the entire device, including the OS, files, and other data. It is primarily responsible for ensuring essential protection by preventing data from unauthorized access when a device is stolen or lost.
It directly integrates with a user account, so access to data after decryption is seamless. Windows 11 allows automated device decryption, enhancing security even for unfamiliar individuals.
Features
- Simplified Encryption Process: Signing in with a Microsoft account is suitable for non-technical users who want to automatically encrypt all the data on their devices.(The recovery key is linked to the Microsoft account, making it easier to recover)
- TPM (Trusted Platform Module): TPM is used to store encryption keys securely. It is the strongest medium to ensure high security. TPM is a physical chip attached to the motherboard and is known to be an essential component in providing data encryption. Its latest version, TPM 2.0, is primarily authenticated for encryption.
Usage Scenarios
It offers less customization and limited management support, so it is suitable for personal users to keep personal data like pictures, videos, and other files confidential, even if the device is stolen or lost.
Similarly, small businesses without extensive IT needs can also use device encryption to ensure basic security.
BitLocker
Unlike device encryption, BitLocker is a feature-rich and advanced technology for securing data. It offers customization to choose specific drives in a computer to store confidential data and add additional security.
BitLocker is not available on all Windows versions, so it requires confirmation that your OS supports this feature; otherwise, you need to update to a required version.
Features
- Flexibility in Choosing the Authentication Process: It supports TPM only, TPM + PIN, and password-only options to improve security.
- Network Unlocking: It allows network-based decryption for the corporate sector and storing recovery keys on a non-encrypted drive.
- Granular Control: Due to an efficient management panel, IT teams are capable of managing various encryption policies and have firm control over data security.
- Microsoft Encrypted Hard Drive: In the latest Windows OS, Windows 8 and later, Microsoft has added the Encrypted Hard Drive specification in BilLocker. This allows cryptographic operations to be offloaded to the device’s hardware
- Windows To Go: BitLocker can now easily be managed using Windows PowerShell. Windows To Go is available in the Enterprise edition, enabling encryption for removable drives like USBs.
Using Scenario
Due to its advanced security mechanism, it is perfect for large organizations with complicated IT systems. Features like centralized key management and compliance with data protection standards are valuable to them
Various educational institutes, government organizations, and healthcare clinics and hospitals can use BitLocker to ensure data security on devices used by multiple users while keeping specific content encrypted and accessible by designated authorities.
2 Differences Between Device Encryption and BitLocker
Quick View
| Compatibility | Configuration Levels | Encryption Range | Hardware Requirements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device Encryption | All Windows Editions from Windows Server 2016 with strict hardware requirements | Basic | The data stored on the drive | Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0, UEFI Firmware, Modern Standby, and Secure Boot. |
| Bitlocker | All Windows Editions including Edu, Enterprise, and Pro except Windows Home Edition | Advanced encryption option | Full/specific disk encryption | Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 1.2 or 2.0, BIOS or UEFI Firmware, secure boot (optional), Active Directory, and USB startup key or non-TPM integration |
Details
Compatibility
Device encryption is available for all Windows editions, however, it requires some strict hardware requirements; otherwise, it does not work. You can enable it from the device’s Settings tab in the Privacy and Security option.
Contrary to device configuration, BitLocker is not supported by all Windows versions. It is compatible with Windows Server 2016, Windows 10, and Windows 11. Windows 10 and 11 only support Pro, Edu, and Enterprise versions. The home version is not compatible with running it. If your device has a Home version, update it to the supported versions.
Configuration Levels
Device encryption only offers basic security measures, such as encrypting only used disk space or the entire drive. Used disk space is preferably selected for new users, and it is the quickest way to secure the data.
Contrarily, BitLocker offers granular control over the encryption process. It extends encryption for removable drives like USB. It also allows the configuration of policies for system drives like C drive and other fixed drives. Some advanced encryption options include network unlock, BitLocker To Go, automatic device encryption, pre-boot configuration, Active Directory integration for recovery key backup, forced software encryption, and group policy settings for policy management and compliance.
Encryption Range
Device encryption allows one-time encryption of all the system or used drives only. It uses the 128-bit XTS-AES algorithm to develop a balance between security and performance. Another 256-bit XTS-AES algorithm is used to ensure high security. You cannot exclude any drive during device encryption.
BitLocker allows encryption of a complete or single drive with access to a management panel, allowing customization to ensure high-end security.
Hardware Requirements
Device Encryption
Device Encryption also works without TPM, but having a TPM (2.0 recommended) with PCR 7 support will enhance the security as it secures the keys. For non-TPM support, you have to manage specific policies in the group policy manager.
- Device encryption requires an advanced sleep state (Modern Standby) for instant-on functionality. It is mostly available in the latest modern and lightweight laptops.
- It requires a UEFI firmware with enabled secure boot. This helps ensure that only trusted software and firmware are allowed to load during startup.
BitLocker
TPM 2.0 is required for advanced configurations on Windows 11 devices. However, some Windows 10 devices also support 1.2 TPM. A USB startup key is required to use BitLocker without TPM. Additionally, the non-PTM process requires BIOS or UEFI for USB detection.
- For network unlocking, BitLocker requires Windows Server 2012 to have a WPS role and a DHCP Server on the same network.
- UEFI firmware with secure boot is required on Windows 11, which allows only trusted code to load during startup and improves efficiency.
- Active Directory integration is necessary to store recovery keys, helping IT admins of large companies quickly recover data.
3 How to Enable Device Encryption on Windows Devices?
Enable Device Encryption in Windows 10/11 Home Edition
Although Windows 11 provides automated device encryption when signed in with a Microsoft account, you also enable it manually. First, check the system information to ensure the device meets all the requirements for utilizing device encryption by opening the start menu and typing system information. Scroll down and check the status of the ‘Device Encryption Support’ tab. There are three possibilities:
Meets Prerequisites: It means you are good to go for the next steps.
Elevation required to view: You are not running the system as an administrator. So first, ensure you are running the device as an administrator to process and successfully enable device encryption on your PC.
Any other codes: It means the system critical settings are disabled or the PC does not meet specific requirements.
- Step 1.Open Device Settings
- Click on ‘Start’ menu and type Settings in the search bar to open settings of your Windows device. You can also press the ‘Win + I’ shortcut key to open Settings.
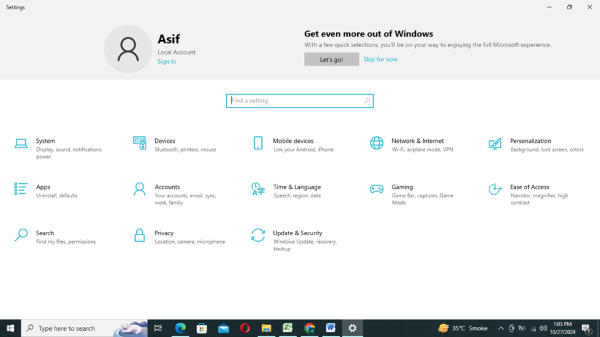
- Step 2.Choose Security tab
- On Windows 10 find the 'Update & Security’ tab while on Windows 11 find the 'Privacy & Security’ tab and tap on it.
- Step 3.Enable Device Encryption
- Toggle the Device Encryption tab to enable it.
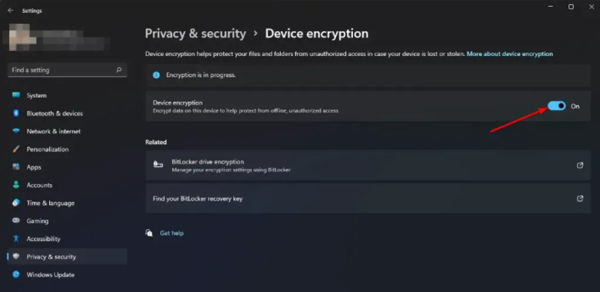
4 Part 4. How to Enable & Configure BitLocker on Windows Devices?
Enable BitLocker on Windows 10 / 11
- Step 1. Open Control Panel
- Open the Start menu, type ‘Control Panel’ and press the ‘Enter’ key.
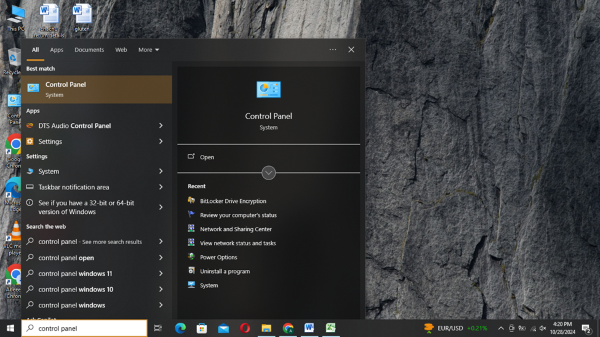
- Step 2.System and Security
- Navigate to the ‘System and Security’ tab and then choose BitLocker Drive Encryption (Manage BitLocker).
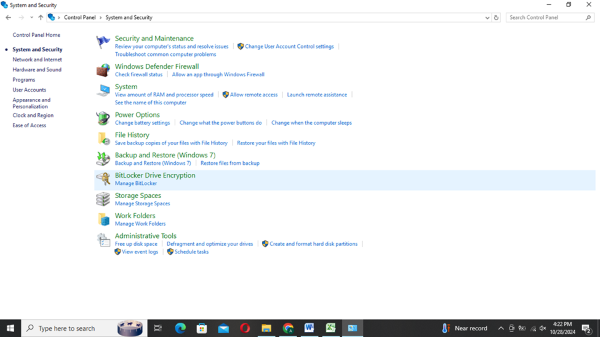
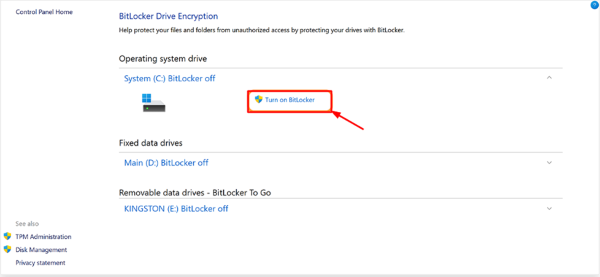
- Step 3. Choose the Drive
- Select any drive you want to encrypt and click ‘Turn on BitLocker’ button.
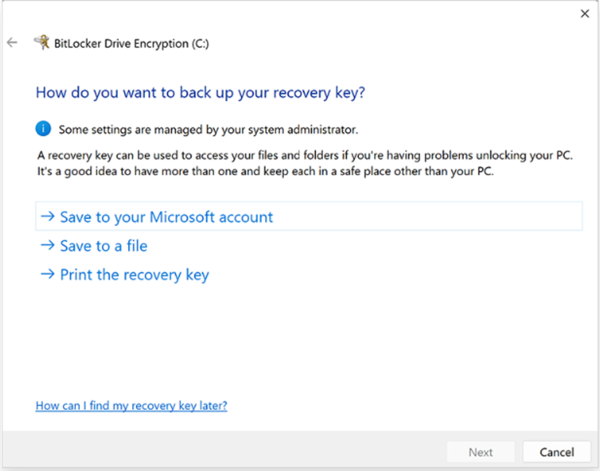
- Step 4.Store Recovery Key
- Now choose the place to store the recovery key. BitLocker allows local storage, in Microsoft accounts, and also prints it. To save it in a file, browse and select the path. After selecting one option, you will be able to press the ‘Next’ button.
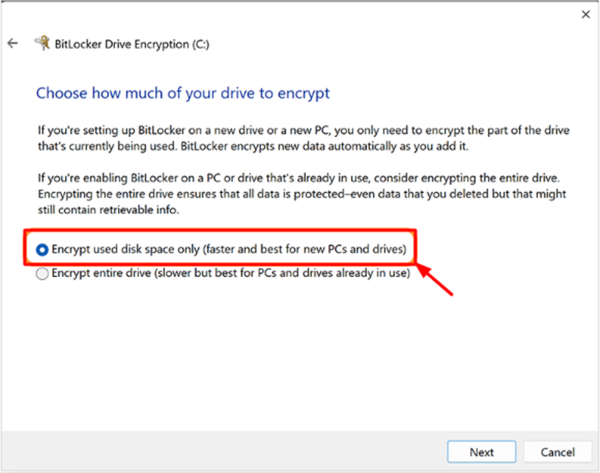
- Step 5.Choose the Disk space
- Choose the specific disk space that you want to encrypt. If you are a new user, prefer the first option as it is the fastest one.
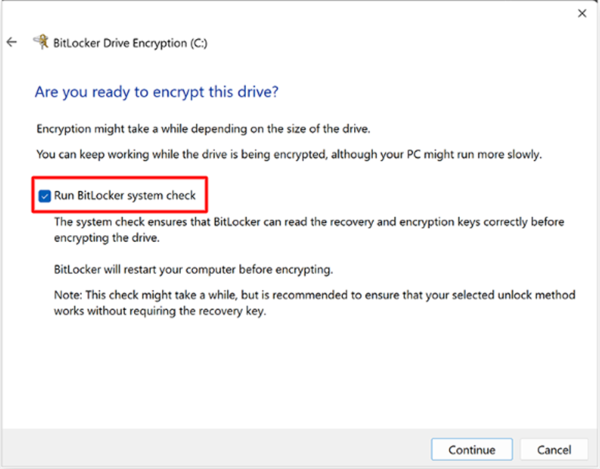
- Step 6.Run BitLocker System Check
- Select the ‘Run BitLocker System Check’ to ensure that BitLocker will check the keys and other details before initiating. Then press the ‘Continue’ button.
- Step 7.Restart PC
- The time taken will depend on the volume of data. So, if you have a large volume of data, be patient and wait until it completes.
5 Which is Better?
Both of them have equal importance, depending on the purpose for which it is required. For example, if you want to secure your personal computer, you can simply use the device configuration option, as it offers basic encryption for the whole device and can easily decrypt just by signing in to the user account.
Contrarily, if you have a large business and the Windows devices are used by multiple employees, then you should try BitLocker. So, multiple users can store relevant data in different drives and encrypt specific drives to ensure they are accessible only when entering the decryption key. BitLocker is suitable for advanced-level security required at large workstations as it offers a management panel to secure and customize policies.









Leave a Reply.