How to Use Password Policy for Windows to Enhance Security?
With the increasing inclination towards digital transformation in present times than ever before, ensuring cybersecurity is super significant. Keeping the requirements of cybersecurity in consideration, one major element is ensuring strong and safe passwords.
Having strong passwords makes it harder for cybercriminals to crack them and get access to sensitive information. This can be ensured by having password policies in place, which define the rules to set a strong password.
It's important to have standard password policies across all systems. With a 68.32% market share held by Windows devices (in February 2024), it is crucial to have password policies defined for these devices.
This article explores password policies in detail with the steps to set standard policies and outlines the important considerations concerning it.
- Part 1 :How to Configure Password Policy for Windows 10?
- Part 2 :Password Policy Standards - NIST Password Guidelines
- Part 3 :What is the Standard Password Policy for Windows?
- Part 4 :How to Enforce Password Length Greater than 14 Characters?
- Part 5 :How to Remove Password Complexity Requirements in Windows 10?
1How to Configure Password Policy for Windows 10?
This section covers the methods and steps to configure the Windows password policy. There are two main methods to do so, including the configuration of password policy via Active Directory and Mobile Device Management (MDM) system.
Method 1: Configure Password Policy Through Active Directory
Active Directory has all the IAM (Identity and Access Management) capabilities to help manage domains, devices, and users on the network from a centralized dashboard. The active directory has a default password policy enabled for all the objects registered on a particular domain.
There are two methods to configure Windows password policy through Active Directory: Using Group Policy Object (GPO) and Using PowerShell script.
Using GPO
GPO allows the centralized configuration settings for all the objects registered on a domain. To update password policy via GPO, follow the steps mentioned below:
- Navigate to the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
- Under the domains folder, click on the required domain.
- Click on Group Policy Objects.
- Under the files, right-click on the Default Domain Policy file and select Edit from the dropdown.
- Access the Password Policy editor by expanding the Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Account Policies.
- Edit the settings per your requirements.
- Lastly, click on Apply to save all the updates.
Using PowerShell Script
Instead of going through all the folders, you can also view the default Windows password policy by using a single PowerShell script. The script is as follows:
Get-ADDefaultDomainPasswordPolicy
Method 2: Use the MDM Solution - AirDroid Business
MDM solution allows you to manage and control all the devices from a centralized dashboard, making it easier to set and apply password policies across all nodes. Using an MDM solution, you can set up a password policy for the devices running on the Windows operating system.
For example, with AirDroid Business you can define the password complexity requirements of a password, which will be enforced on all the user accounts.
2Password Policy Standards - NIST Password Guidelines
With the increase in cybercrimes, it's important to abide by some standards when it comes to password policies, which helps avoid all unpredictable and unwanted security breaches. When it comes to password policy, NIST Password Guidelines is the standard to abide by. NIST is responsible for setting the information security standards and policies.

According to the NIST Password Guidelines, the following are some of the key conclusions:
Dos
- User-generated and machine-generated passwords should have at least 8 and 6 characters respectively.
- Users should be allowed to set passwords up to 64 characters, with the liberty of using any ASCII/Unicode characters.
- Users should be given up to 10 tries for failed login attempts before locking him/her out of his/her accounts.
- The requirements of having a special character or numbers may be skipped as it causes frustration for the user and stands more vulnerable to potential attacks.
- For enhanced security, always check the entered password in the database having the record of vulnerable passwords and if matched, don’t allow the user to set that particular password.
Donts
- Aim to not use sequential or repeated characters as they are easy to crack.
- On the organizational end, the password must not be stored after truncation, instead hashing and salting should be employed.
- Don’t allow the user to set the hints for the password.
- Any sort of knowledge-based authentication must be avoided.
- The usage of context-specific words, for example, username must be avoided.
- Do not get into the hassle of password expiration dates.
- Lastly, when enabling the security mechanism of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), do not opt for the SMS code as the second layer of authentication.
3What is the Standard Password Policy for Windows?
This section covers the standard password policy for all 365 account holders of Windows. The key standards are defined below along with their details and best practices:
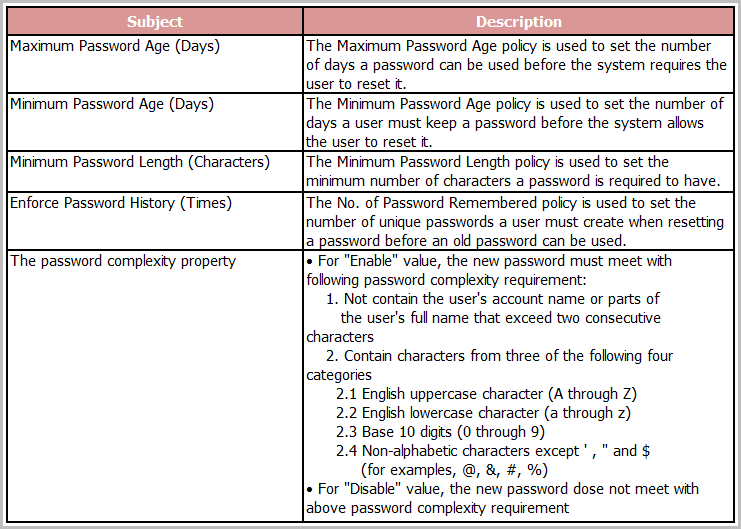
Enforce Password History
Reusing the same password for an account for a longer span of time is preferred by users because of its convenience to remember and manage. However, it can pose security concerns as the longer the password remains the same, the easier it is for the hackers to crack it.
Enforce password history is the mechanism to determine what number of unique passwords must be set by the user before he/she opts for an older password. This reduces the number of times a password is reused.
Microsoft recommends setting the Enforce password history to the value of 24.
Maximum Password Age
An organization needs to specify the maximum number of days for which a user can use the same password. After that, the password should be set to expiration and the system should prompt the user for a password change. This maximum duration is known as the maximum password age.
Microsoft recommends setting the Maximum password age between 30 to 90 days.
Minimum Password Age
It's important that an organization set a minimum number of days for which the user must use the existing password before opting for a change. It helps reduce the high number of password changes. An important consideration here is that the Minimum password age must be less than the Maximum password age.
Microsoft recommends setting the Minimum password age to 1 day.
Minimum Password Length
To have passwords that are hard to crack, it's significant that they have a certain number of characters. This minimum length of password is termed as Minimum password length.
Microsoft recommends setting the Minimum password length to 8 characters.
Password Must Meet Complexity Requirements
To make passwords difficult to crack, certain requirements are to be defined. These strength requirements that a password must meet for it to qualify as a strong password are known as complexity requirements.
Microsoft recommends the following complexity requirements to be fulfilled for the passwords:
- Passwords must not contain the user’s account name or the full name.
- Passwords must contain characters from any three of these categories:
- Uppercase letters (A-Z)
- Lowercase letters (a-z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special characters (non-alphanumeric except for the currency symbols)
Unicode character (which is from a category of alphabetic characters, but not uppercase or lowercase).
Microsoft recommends to always set the Passwords must meet complexity requirements option as Enabled.
Store Passwords Using Reversible Encryption
The option of having reversible encryption is useful to support applications that require a password for authentication and use protocols to decrypt them. However, it also makes the password open for all cyber criminals who know decryption. Therefore, it's recommended to not store passwords using reversible encryption.
Microsoft recommends setting the Store passwords using reversible encryption as Disabled. However, in the case of using Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol through Internet Authentication Services or remote access, you need to set this option to Enabled. It is allowed for the latter use case as the application requirements outweigh the security concerns.
Passwords Examples that Meet the NIST Password Guidelines
Lastly, it’s a best practice to set passwords that meet the NIST Password Guidelines as it’s the standard when it comes to password policies for ensuring information security. Following are the three example passwords that abide by the NIST Password Guidelines:
- Winter2023!
- CoffeeMug!22
- Travel@Sunset
As seen in all the above-mentioned guidelines and standards, the importance of password policies and standards is clearly highlighted. Ensuring that standards are in place reduces the chances of potential risks and security concerns.
4How to Enforce Password Length Greater than 14 Characters?
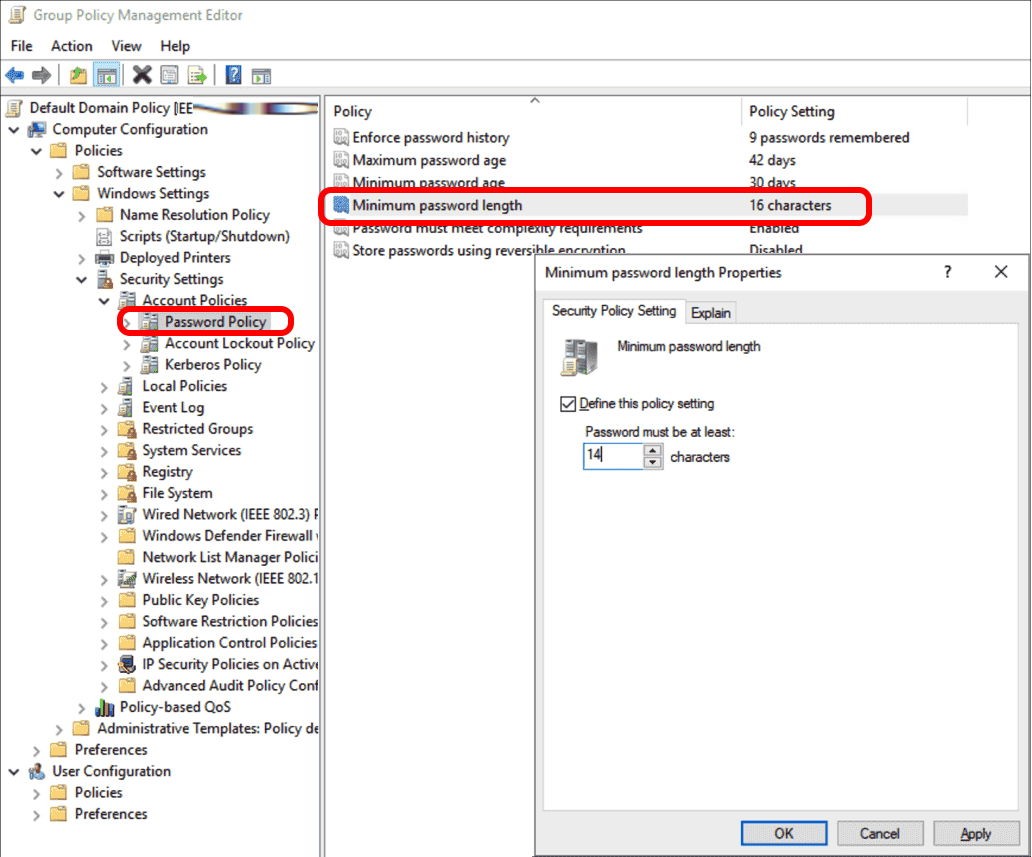
The longer passwords are more immune to cyberattacks because they are hard to crack via guesswork. To enforce password length greater than 14 characters for Windows 2022 server, follow the steps below:
- Navigate to the GPMC.
- Under the domains folder, click on the required domain.
- Click on Group Policy Objects.
- Under the files, right-click on the Default Domain Policy file and select Edit from the dropdown.
- Access the Password Policy editor by expanding the Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Account Policies.
- Set the Relax minimum password length limits field as Enabled.
- Set the value of the Minimum password length audit equal to the number of characters you want your password to be at least.
- Lastly, set the Minimum password length to the minimum number of characters for a password length in a similar fashion.
- After completing all the changes, click on the Apply button to save all the updates.
Although this method can allow you to set a minimum password length of more than 14 characters, it is officially not recommended or supported by Microsoft. It favours the password length of 8 characters as it provides the required security, while still making it easier for the users to remember.
5How to Remove Password Complexity Requirements in Windows 10?
It is recommended to enable the complexity requirements to help set strong passwords, which are immune to potential cyberattacks. However, if certain reasons require you to disable the password complexity requirements, there are two methods to do so:
Method 01: Using the Policy Editor
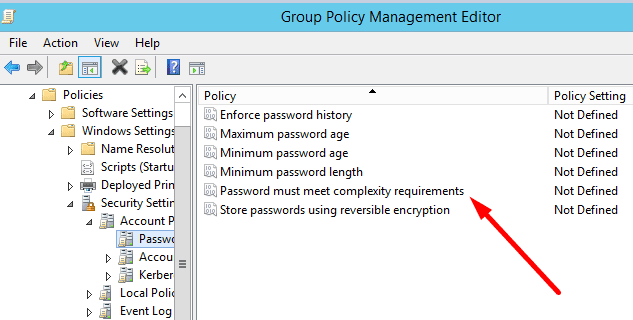
To remove password complexity requirements using the policy editor, follow the steps below:
- Open the new Run window by pressing the Windows + R keys.
- In the prompt box, type gpedit.msc or secpol.msc and press the Enter key to open the Group Policy Editor window.
- From the left sidebar, open the Password Policy editor by expanding Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Account Policies.
- Disable the Password must meet complexity requirements, which completes the process.
Method 02: Editing the Password File
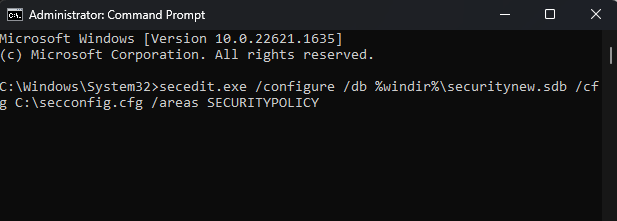
To remove password complexity requirements by editing the password file, follow the steps below:
- Open the new Run window by pressing the Windows + R keys.
- In the prompt box, type secpol.msc and press the Enter key to open the Local Security Policy Editor.
- Click on the Action menu and select the Export policy.
- Once the file is downloaded, open it using Notepad and find the System Access.
- Under that, set the PasswordComplexity to zero.
- After saving the changes, open the command prompt as admin.
- Enter this command: secedit.exe /configure /db %windir%\securitynew.sdb /cfg C:\secconfig.cfg /areas SECURITYPOLICY.
- Lastly, verify that the password complexity setting has been disabled via the Local Security Policy Console.
Bringing it all together, setting password policies stands significant as it helps enforce stronger passwords, ultimately enhancing the security of the information architecture. Therefore, it’s always a recommended practice to set standard password policies.









Leave a Reply.