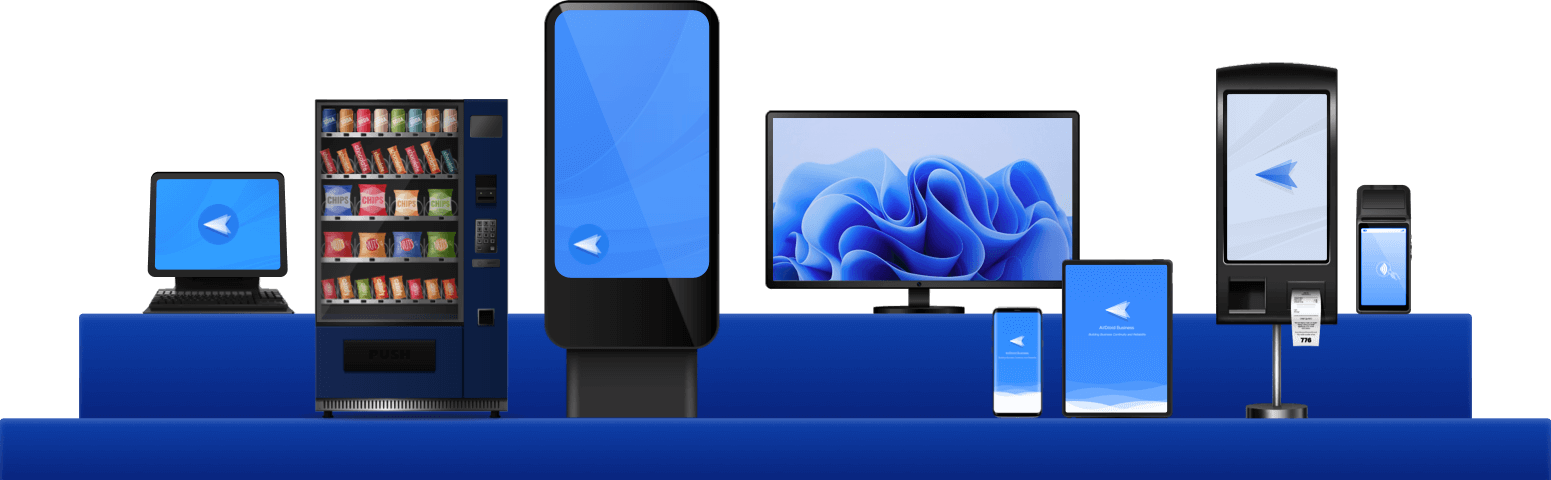
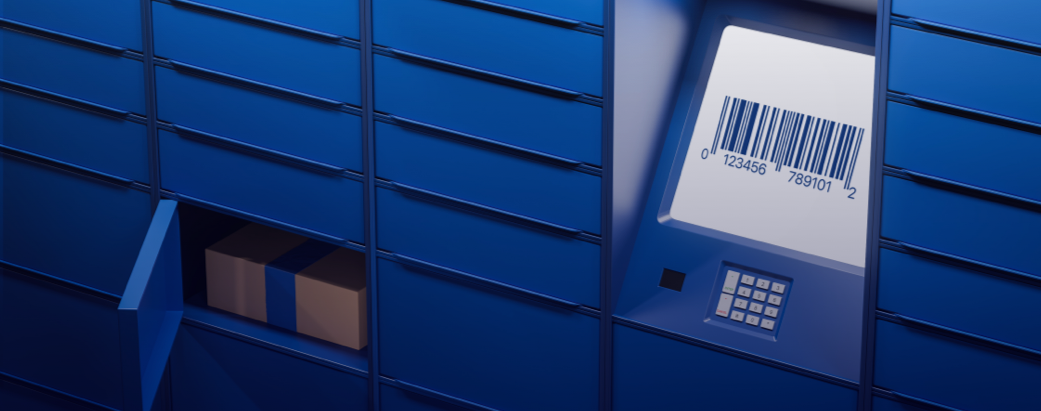
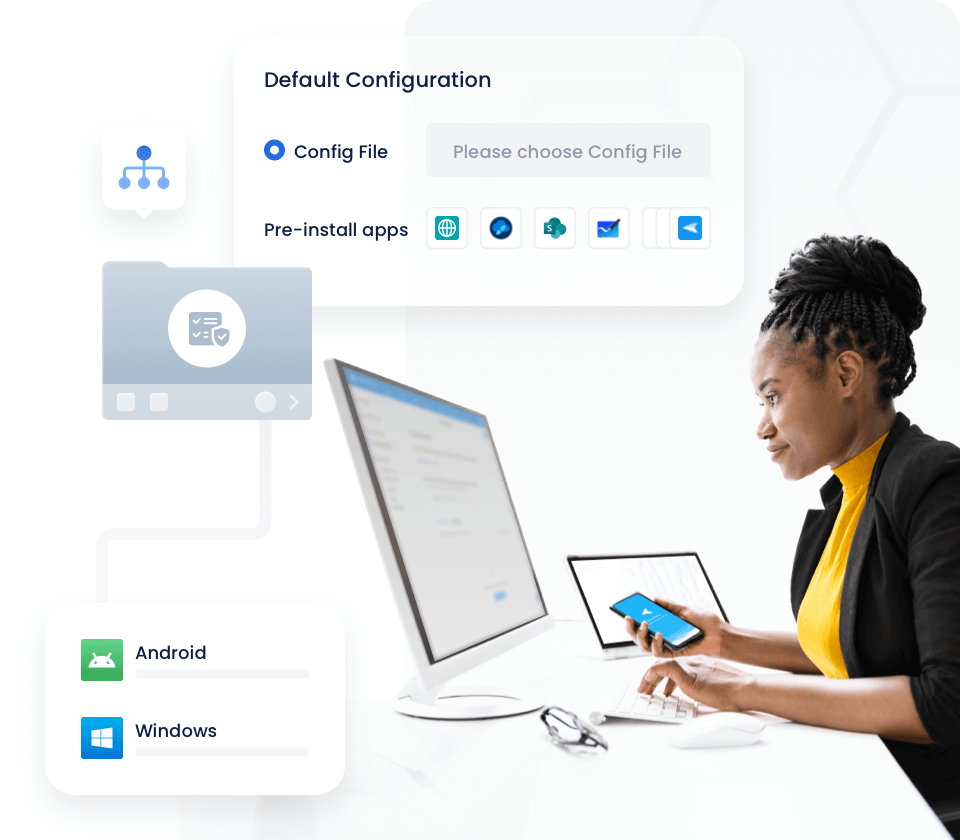
Comprehensive device management solution
Streamline deployment with automated enrollment & configuration
Automated enrollment and configuration tools designed to enhance productivity and ensure compliance throughout your enterprise.
-
Device Enrollment
Simplify enrollment with a variety of flexible, easy-to-implement options.
-
Pre-set Configurations
Pre-set configurations on devices quickly with customizable templates.
-
Standardize Settings
Automate and standardize security settings across your entire device network.
Enhance IT operations with advanced remote access solution
Maximize efficiency, minimize downtime, and ensure top-tier performance across all devices in your enterprise.
-
Black Screen Mode
Black screen mode for secure unattended remote access.
-
Remote Support
Robust remote troubleshooting with extensive support features.
-
API Integration
Enhanced IT and CRM integration with remote control API.
-
Real-time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of device status with immediate alerts for potential issues.

Integrated 360° device management for peak performance
Boost operational productivity, streamline daily tasks, and maintain seamless control over your enterprise devices.
-
Application Management
Simplified bulk app management: install, update, and remove with ease.
-
Kiosk Mode
Kiosk mode to ensure secure device usage in public settings.
-
Policy
Implement and enforce policies for security and efficiency.
-
Files Management & Sharing
Securely manage files centrally, distribute efficiently to devices, and remotely control endpoint storage files.
-
Suite of management solutions
Complete MDM suite: Track location, manage patches,enforce security, and much more.
Supported Platforms
| Android | Windows | |
|---|---|---|
| Deivce Policy Restriction | ||
| App Management | ||
| Kiosk Setting | ||
| Alerts & Workflows | ||
| Patch Management |

Security & Compliance
Uncompromising security for corporate devices
Efficient and flexible deployment for any enterprise
-
Cloud Deployment
-
On-Premises Deployment
-
Cloud-based software and data deployment
Utilize AirDroid Business device management and remote control solutions in the Cloud for secure, rapid deployment and adaptable growth.
- Avoid upfront costs of hardware and server installations.
- Flexibly expand plans according to your budget and usage demands.
- Quickly and easily access your data from anywhere.
-
In-house software and data storage
With high standards for data security and ample local infrastructure, on-premises deployment is the best option for AirDroid Business projects, ensuring total control and privacy.
- Run your projects on-premises for full control over data security and privacy.
- Achieve greater control over servers and hardware, managed by your team.
- Lower network bandwidth costs by avoiding shared customer resources.
Real-world success stories
Read more our customer storiesTrusted globally by SMBs and enterprises
AirDroid Business across industries
Get started with device management for business